In this article, we’ll be examining what injection molding is, the steps involved in the process, the different types of injection molding, and the materials commonly used. We’ll also explore the significant challenge of designing parts for this molding process. If you’ve been curious about injection molding, we’ll be answering many of your questions below.
What is Injection Molding?
Injection molding is a process for manufacturing parts using a mold into which molten material is injected at a very high pressure. The melted plastic assumes the shapes or forms cut into the mold and retains the shape after cooling or curing. Injection molding works with many materials including thermoplastics, thermosets, and elastomers.
Injection molding machines work with closed molds. This means that the mold is already closed during the injection process. The result is that injection molding can produce more complex and precise parts. The process also wastes less material.

A single plastic injection mold can produce thousands or millions of parts using this manufacturing process. However, the complex tooling needed to accomplish this scale of production makes the upfront manufacturing costs of injection molding significantly higher than that of other manufacturing processes.
The Injection Molding Process
There are different variations to the injection molding process. However, all these processes typically follow similar steps that are guided by the design of injection molding machines.
Injection molding machines have three key sections. These are:
- The injection unit
- The mold
- The clamping unit
As the name suggests, the injection unit is what forces the molten material into the mold. However, it also consists of parts that feed and melt the material which are usually plastic pellets.
The mold consists of two or more parts onto which the form of the manufactured part has been machined. The material is injected into the mold where the part forms and solidifies before being ejected.
The clamping unit opens and closes the mold at regular intervals. The unit is closed to start the injection of the material and formation of the part and opens when the part is ready to be ejected.
The molding process can be summarised in the steps below.
Step 1: Mold Creation
The molds used for injection molding can be relatively simple or very complex depending on the final part. A plastic injection mold could be nothing more than a cavity and a core. It can also be quite complex requiring the use of inserts, side action cams, and other features.

The mold must be designed and machined onto a suitable material before the actual manufacturing starts.
Step 2: Closing the Mold
Injection molding uses a closed mold. This means the mold must be closed before the material is introduced. The clamping unit closes the two halves of the mold forming a tight seal.
Step 3: Material Feeding
Assuming a suitable material has been selected, the material is placed in the injection unit’s hopper. It can be mixed with suitable additives including colorants, fibers, plasticizers, blowing agents, and lubricants.
Apart from the hopper, the injection unit also has a reciprocating screw inside a heated barrel. The materials are mixed and fed forward by the screw. They are melted by the heat and pressure inside the barrel.
The dimensions of the screw and barrel are designed to increase the pressure of the molten material to the required level before injection.
Step 4: Material Injection
From the injection unit, the molten plastic is injected into the mold through a system that consists of a sprue, runners, and gates.
These are a series of channels and openings that take the material into the mold cavity.
Step 5: Cooling or Curing
Once the material has been injected into the mold, it is held in place for a certain amount of time. This allows the material enough time to cool or cure. The plastic solidifies as a result. Cooling lines can be used to increase the speed at which the parts solidify.
Step 6: Opening the Mold
Once the parts are solid, the mold is opened by the clamping unit.
Step 7: Ejecting the Part
During this step, the finished part is removed from the mold. This can be an automatic or manual process. Ejection pins may be required to remove some parts. A good ejection speed is important for keeping cycle times low. This is facilitated by good mold design.
Step 8: Post Processing (Optional)
Some parts will require additional work before they are ready for use. This could be as basic as the removal of excess material or laser etching certain details on the part. Post-processing is a critical step in the production of many injection-molded parts.
Inquire Now for Fast Quotations!
Types of Injection Molding
Thermoplastic injection molding is what comes to most people’s minds when they hear about injection molding. However, it is just one of 7 types of this manufacturing process.
These seven variations of the injection molding process have made it possible to work with more materials and create new types of products.
Thermoplastic Injection Molding
Thermoplastic Injection Molding is the most common form of this manufacturing process. This form of injection molding is used in the manufacture of a wide range of products from cutlery and bottlecaps to keyboard keys and sports equipment.
In this process, the material is a thermoplastic which melts when heated and solidifies when cooled. The thermoplastic is melted in the injection unit, and forced into the mold where it cools, retaining the molded shape.
There are many thermoplastics that can be used for this process including ABS, Nylon, Polycarbonate, Polypropylene, etc.
Thermoset Injection Molding
This injection molding process swaps thermoplastics for thermosetting plastic resins to make products. Thermosets are formed by irreversible chemical reactions and don’t melt when heated. Knobs and cooking pot handles in the kitchen are some of the products made using this process.
The overall process is similar to that of molding thermoplastics but the barrels in the injection units are usually shorter.
Additionally, the materials used to mold the thermoset parts have to be specially formulated for injection molding. The materials need to be stable below specific temperatures to prevent the material from setting inside the barrel.
Liquid Silicone Rubber (LSR) Injection Molding
This is an injection molding process that also involves a thermosetting process. However, unlike the previous process, a base material and a catalyst, stored separately, are first mixed before being injected into the mold. Vulcanization follows and the part cures in the shape of the mold.
This form of injection molding produces medical tubing, syringe stoppers, protective sleeves for electronics, and nose pads for spectacles. Silicone rubber is also very safe and the process is even used to make pacifiers for babies.

Other Injection Molding Processes
In addition to the above three, other injection molding processes you might be interested in are:
- Micro injection molding: Used for injection molding of very small parts. Parts produced can weigh as little as 0.1 grams e.g., watch gears.
- Multi-component injection molding: Used to make multi-material or multi-colored parts. It can combine different colored plastic materials and can be used to add a soft touch surface to a part.
- Two-shot injection molding: This form of injection molding is also used to produce plastic parts that combine colors and materials. This process uses special molds into which two shots of molten plastics are introduced in quick succession.
- Insert molding: The thermoplastic or thermosetting polymer is molded over a part that is inserted before the mold is closed. Metal inserts are commonly used when manufacturing plastic parts with metallic threads.
You can read more about these molding processes in this article.
Inquire Now for Fast Quotations!
Common Materials for Injection Molding
The types of plastics that can be injection molded are over 25,000. These materials have a wide range of properties to suit an ever-expanding list of applications.
Elastomers
Elastomers are polymers that exhibit a significant degree of elasticity. These are materials that can be compressed or pulled to several times their size without being permanently deformed.
Materials that are classified as elastomers are usually also thermosets. As stated earlier, this means that they cannot be melted down and reformed into different shapes by cooling. However, there are some thermoplastic elastomers.
The two commonly used elastomers in injection molding are liquid silicone rubber and natural rubber.
1. Liquid Silicone Rubber
This thermosetting elastomer is formed by combining two components in a reaction that is catalyzed by platinum. This material has many valuable properties and is used for medical-grade parts in addition to many consumer products.
Chemically, the ‘backbones’ of this elastomer are chains of siloxane molecules.
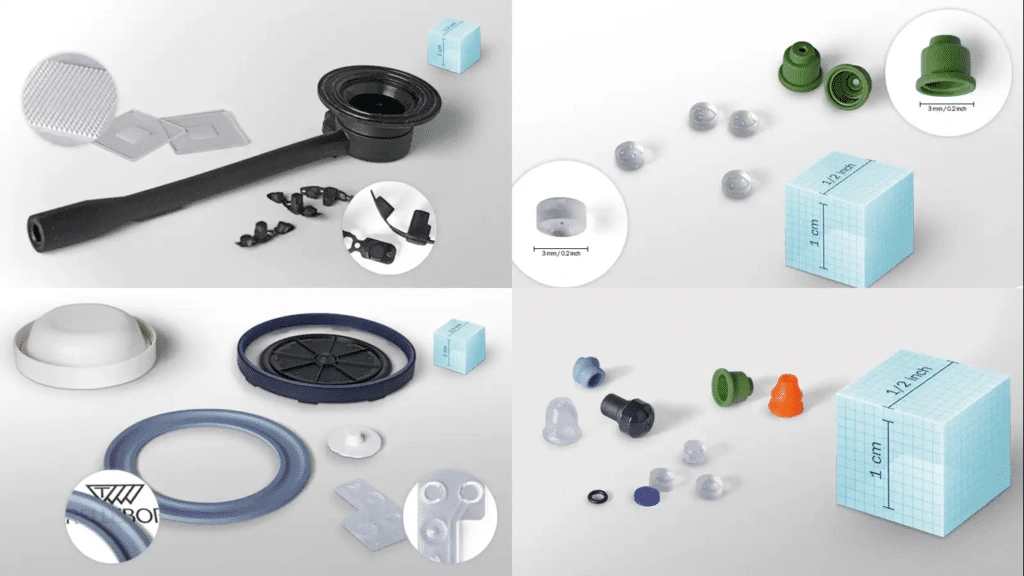

This material is injected through a special process called liquid silicone rubber injection molding. This process is specially designed for the two main components to be mixed along with pigments and any other required additives before being injected into the heated mold.
Rather than cooling, it is the chemical reaction called crosslinking that causes this material to solidify.
LSR cures quite quickly and also exhibits excellent resistance to tearing, heat, oil, and water. It’s also quite durable. LSR comes in different grades depending on the desired properties of the final product.
2. Natural Rubber
Natural rubber compounds can also be injection molded. In these situations, the rubber essentially undergoes vulcanization inside the heated mold.
Like other thermosetting compounds, injection molding of natural rubber requires careful control of many process parameters including temperatures and pressures. Certain additives can also increase the cure times.
Silicone rubber is preferred over natural rubber for many applications. However, natural rubber is still widely used in applications such as manufacturing of seals and gaskets.
Plastics
The second group of materials that are injection molded are plastics. These are specifically thermoplastics and thermosets. Plastics are materials that can be easily molded into different shapes and retain their new shapes easily. Unlike elastomers, it is easy to permanently deform a plastic material.
1. Thermosetting Plastics
Thermosets are materials that cannot be softened once they have hardened. The hardening of these polymers is the result of curing rather than cooling. Curing is a chemical process during which polymer chains irreversibly crosslink. When heated to a high temperature, thermosets burn.
Injection molding of thermosetting polymers was a greater engineering challenge compared to that of thermoplastics. Without the right process control, the materials can cure and set inside the barrel rather than in the mold.
This challenge was overcome by changing the designs of the screw and the barrel, as well as improving the stability of the materials at higher temperatures. Thermosets have several advantages over thermoplastics including:
- Better heat resistance
- Greater durability
- Allowing for high-glow finishes
- Better dimensional stability, etc.
On the other hand, thermosets are also brittle and can’t be recycled.
Examples of thermosets that can be used in injection molding include epoxy, phenolic, and polyurethane.

Thermosets are used for manufacturing high-speed bearings, housings for electronics, plastic components in kitchen equipment, and automotive parts and components.
2. Thermoplastics
Injection molding of thermoplastics was well-established long before the technology was used to mold thermosets. As a result, thermoplastics are still the most common materials used in injection molding.
Thermoplastics are polymers that melt when heated and solidify when cooled. The solidification of thermoplastics is reversible. There is no risk the material will permanently set inside the barrel as with thermosetting polymers. This makes them easier to use for this molding process.
Thermoplastics have many good properties including:
- Better corrosion and chemical resistance than thermosets
- Great ductility
- Excellent impact resistance
However, perhaps, the main advantage of thermoplastics is that they are highly recyclable. This means there is potential to significantly reduce the amount of waste generated by these materials. On the other hand, they have poor heat and UV resistance.
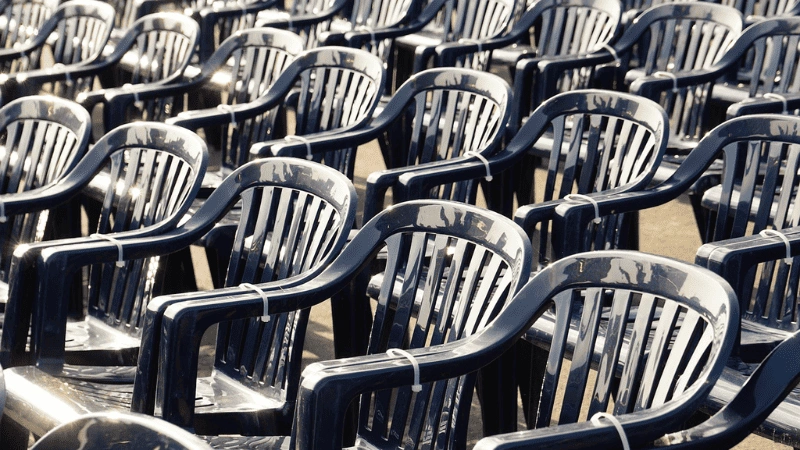

Commonly used thermoplastics include:
- ABS
- Polypropylene (PP)
- Teflon
- Acrylic
- Polystyrene
- Nylon
Thermoplastics are used to manufacture plastic containers, furniture, kitchenware, automotive parts, etc. using injection molding technology.
Prototyping and Design in Injection Molding
Prototyping is an important step in the initial stages of injection molding. Without prototyping, you could spend tens or hundreds of thousands of dollars on a defective product.
Proper design is also important in injection molding. Any product design used should be optimized for the injection molding process.
- Importance of Prototype Production in Injection Molding
Prototypes are early samples of the final product. Prototypes are used to test how the product will look, function, and perform once it’s finally produced. Prototypes are used in many manufacturing processes. They are important in injection molding because:
- Prototypes confirm that the product will function as expected.
- Prototyping allows designers and customers to identify problem areas in the design and make improvements.
- Prototyping helps to identify features that may not be feasible for injection molding.
- Potential users can provide feedback on early prototypes to prevent the manufacturing of unpopular products.
- Prototyping ensures that the customer or client approves the final product before production begins.
- Prototyping eliminates costs that would be incurred if a faulty design was put into production.
There are different ways of prototyping products for injection molding. One option is the use of 3D printing. This can be a very affordable option for prototyping but it has its limitations. Injection molding can also be used for prototyping. Prototyping molds can cost a fraction of what production molds cost. You can find out more about these two prototyping options in this article.
- Mastering Draft Angles in Injection Molding Design
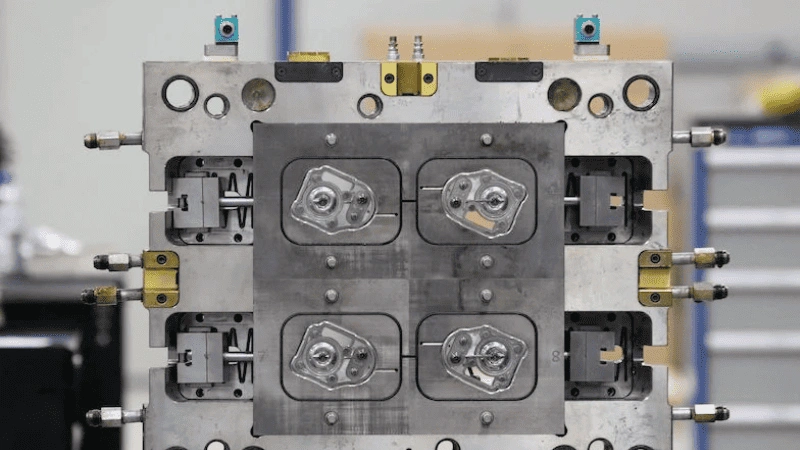
A draft angle is a slight taper of the vertical walls of the molded part that ensures they are not parallel to the walls of the mold. This reduces the friction between the finished part and the walls of the mold during ejection.
Draft angles make it easier to remove finished parts from the mold. As a result, they have additional benefits such as:
- Improved surface finish on molded parts
- Increased lifespan of molds
- Helps to preserve textures on finished parts
- Improves part integrity
- Reduces cycle times due to faster ejection speeds, etc.
All vertical faces should have at least 0.5 degrees of draft. However, it is often necessary to apply more than this.
For instance, if there is a light texture on the finished part, the draft angle should be around 3 degrees. For heavy texturing, the draft angle should be at least 5 degrees. Other features that need specific draft angle considerations include threads, holes, and ribs.
Draft angles are some of the most important design features to consider and discuss with your manufacturer before production.
Inquire Now for Fast Quotations!
Systems and Tools In Injection Molding
The systems and tooling used in injection molding are anything but simple. Even the simplest, no-frills parts can require the use of fairly complicated systems to ensure the parts are produced at optimal speeds and low costs without sacrificing quality.
- Role of Cooling Systems in Injection Molding
Cooling is an understated part of the injection molding manufacturing process. Despite this, it is one of the most crucial systems in ensuring successful and cost-effective production of parts.
Cooling is necessary in injection molding because this is what ensures the material solidifies and retains the shape of the mold before ejection. To keep production times as short as possible, cooling must be done as quickly as possible.
Injection molded parts can be cooled using air or using water. Air cooling is adequate for parts with minimal cooling requirements, but it still results in longer cycle times and transfers the heat to the surrounding area.
Water cooling is more effective since water is a better thermal conductor. The ‘water’ in this case is actually a mixture of water, glycol, biocide, and other substances that result in better cooling or prevent problems like bacterial growth and corrosion.
When properly implemented cooling systems in injection molding have benefits that include:
- Reduction in cycle times. This results in faster, and therefore, lower cost of production.
- Fewer part defects caused by uneven cooling of the molded part e.g., warping and sink marks
Cooling systems used in injection molding can be very complex. You can find out more about them in this article.
- Optimizing Tolerances in Injection Molding
Tolerances in manufacturing ensure that specific design dimensions will fall within a certain range on the finished product. This ensures that a manufactured part will have the size needed to perform its function. This is also important if the product is part of an assembly.

Without the right expertise, manufacturing parts that have the right tolerances can be quite challenging because:
- Injection molded parts will shrink by some degree when cooling.
- Warping, sinking, and other deformations that may occur on injection molded parts can alter part dimensions.
As a rule, the tighter the tolerances needed, the more expensive the manufacturing process will be. Attaining tighter tolerances requires a greater degree of care when selecting materials and machining the mold. It also requires closer monitoring of process parameters.
Some of the measures that can be taken to achieve tighter tolerances include:
- Choosing materials with highly predictable shrinking rates.
- Choosing a mold material that behaves consistently across production cycles.
- Optimize the cooling for the injection molded part.
- Use sensors to closely measure process parameters such as injection pressure and temperatures throughout the cycle.
- Avoid design features that are likely to result in defects such as thick walls.
- Automate process controls so parameters can be automatically adjusted to keep them within certain limits.
The client must know the tolerances that will be used to manufacture their part. Parts required to perform specific functions must meet specific tolerances to perform their function correctly. If a part is to be included in an assembly, it will have to meet specific tolerances to fit in the assembly.
For the manufacturer, the importance of optimizing for the right tolerances is that it will result in a lower part rejection rate. Any rejected part is waste and a high rejection rate will result in a more expensive process.
Inquire Now for Fast Quotations!
Techniques and Processes in Injection Molding
Having the right tooling is important for achieving good results in injection molding. However, there are other factors that contribute to good results and a successful production cycle. Keeping cycle times low and implementing an effective quality control system are two such factors.
Strategies for Reducing Cycle Time in Injection Molding
Achieving a short cycle time is one of the most important goals in injection molding. A percentage reduction in your cycle times could translate to savings in the range of thousands to tens of thousands of dollars annually per machine.
Some of the approaches used to reduce the cycle times in injection molding are discussed below.
1. Fine Tune Your Machine
Performance issues can result in longer injection times. This is a particular concern in older machines that may not consistently achieve the correct injection speeds and pressures. As a result, the machine may take longer to fill the mold on some occasions.

The slow filling of molds increases the cycle times, but it can also lead to part defects and, therefore, a higher part rejection rate. This means it will take even longer to fill the order.
The best way to avoid this is to keep your machines in excellent operating condition through regular and proper maintenance.
2. Optimize Mold Design for Cooling
Cooling takes the most amount of time in the injection molding cycle. The rate of the cooling system is significantly affected by the design of your mold.
Your mold should be designed to encourage good distribution of the cooling agent. The cooling channels should also be situated to achieve optimal cooling rates. They should also be cleaned regularly and kept in good working condition.
Good cooling also reduces part defects. This means fewer parts will get rejected, resulting in faster product delivery.
3. Use Thinner Walls
Thinner walls result in faster injection and faster cooling. This significantly impacts the cycle time. Choose the thinnest wall that still gives you a viable part.
4. Revisit Material Choice

Some materials flow more easily or can be filled at higher pressures. This means the fill time, which also takes a significant percentage of the overall cycle time can be reduced. You may have had a particular material in mind, but it may be a good idea to see what else is out there.
5. Work With the Right People
The right people will have the right ideas on how you can optimize your mold design, choose the right material, and pick the right approach to injection molding. You also need people with the right expertise to make small adjustments that can impact cycle times during the process. Making these adjustments without increasing cycle times or compromising part quality is a skill that takes time to learn.
In some cases, a specific machine may need adjustments that only work with it. This means you’ll need to work with individuals who have worked with that specific machine many times before.
Quality Control in Injection Molding Process
Quality control is necessary in injection molding because things will not go 100% according to plan. At the very least, a few things will go awry and when they do, it’s important to have systems in place that will catch the errors early so corrective action can be taken.

There are different ways that quality control can be implemented in injection molding including:
- Communication and collaboration between manufacturers, clients, and end users.
- Redesigning products to suit the injection molding process
- Installing in-process inspection and control equipment
- Addressing manufacturing problems as they come up during the production process
Manufacturers also need to invest in continuous improvement to ensure they are working with the best injection molding tools and methods available. They should also be implementing measures that prevent the recurrence of past mistakes.
Inquire Now for Fast Quotations!
Choosing a Silicone Injection Molding Manufacturer
Getting good-quality silicone products starts with selecting the right silicone injection molding manufacturer. Some of the key factors you should consider when choosing a silicone injection molding manufacturer include:
- Experience: A lot of the expertise needed in injection molding takes time to learn. A manufacturer with more years of experience will have a lot of knowledge gained from past successes and failures.
- Team: In addition to experience, having the right team is also crucial. Injection molding requires working with experts in mold design, process control, quality control, customer care, etc. The input of all these experts contributes towards the success of the project.
- Prototyping ability: Rapid prototyping, especially using technologies like CNC machining, can ensure your product progresses quickly through the early design stages. A good manufacturer can have a prototype ready in days rather than weeks.
- Variable capacity: Some manufacturers are only an option when producing large quantities of a product. However, sometimes you need smaller volumes for a niche market. Manufacturers who can satisfy this need can be crucial to a product’s success.
- Turn-around time: A product you can’t get in time is of no use. You should always choose a manufacturer who can commit to a quick delivery schedule.
Hongju Silicone has more than 20 years of experience providing silicone injection molding services. Their delivery speed is unmatched, as is their record of producing high-quality silicone rubber parts. They are an example of a manufacturer that meets the criteria above.
Conclusion
Injection molding is one of the best manufacturing methods for plastics today. It is the reason we can get many products we use daily at affordable prices. Injection molding is an ideal manufacturing option when it comes to high-volume production.
Getting the best out of the injection molding process requires making the right decisions at different stages. This includes designing a good mold, choosing an excellent manufacturer, and having quality control measures in place.
Ask Hongju Silicone About Injection Molding
Wrapping your head around injection molding can be a challenge. Figuring out which form of injection molding is right for you or which of the 25,000+ available materials you should use seems quite daunting. This is where you can rely on the experience and expertise of the team at Hongju Silicone to guide you. Reach out to find out what you need to know about injection molding and how it can be the solution you need today.