Need custom molded rubber parts that deliver precision and durability? Explore material options, automotive applications, and advanced manufacturing processes.
Learn how to optimize design, ensure strict quality control, and select the right partner for high-performance rubber solutions. Your roadmap to reliability starts here.
Market & Industry Insights
The global seals and gaskets market is maintaining steady growth, reflecting the rising need for high-performance sealing solutions across automotive, industrial, and energy sectors. According to a recent analysis:
The market size is estimated at USD 13.93 billion in 2025 and projected to reach USD 22.17 billion by 2034, at a CAGR of ~ 5.3 %.
Rubber materials lead the segment: the gasket & seal materials market was valued at USD 61.35 billion in 2024, with rubber accounting for ~40% of that share.
In the automotive sub-sector, the seals & gaskets market is expected to hit USD 15.67 billion in 2025 and grow to USD 25.81 billion by 2033, at ~6.44% CAGR — largely driven by EVs, lightweight design, and stricter emission standards.
Why Custom Molded Rubber Parts?

Custom-molded rubber parts cost more than standard, off-the-shelf parts. However, this cost difference is easy to justify.
1. Design Flexibility
When you can only use standard parts, you will eventually have to make sacrifices in the form or function of your parts. This can lead to unsatisfactory results for you or the end users.
Custom parts remove these limits, allowing you to push the boundaries of your designs. This works well for new parts with greater complexities or intentionally unusual forms.
2. Better Performance
A standard rubber part may not fit as well as a custom one. The result will be poor performance which could translate to excessive noise, fluid leaks, and other problems.

Custom components are likely to perform well because of the focused approach to their design.
3. Better Aesthetics
Similar to performance, custom parts are likely to produce better aesthetics. Design and manufacturing decisions can be made to achieve a custom product that’s visually in tune with the rest of the design.
4. Part Development is Cheaper and Faster
Advancements in computer-aided design, 3D printing, and other forms of manufacturing have made part development less expensive and time-consuming.

Modern CAD software makes it easy to come up with structurally sound designs. Quick prototypes can be made using 3D printing for early testing.
These and other developments have reduced the manufacturing costs of custom rubber products.
5. Lower Long-Term Costs
A poorly fitting rubber part in a car can be expensive for both car owners and manufacturers. It’s not uncommon for manufacturers to issue expensive recalls because of a poorly fitting part that endangers lives. Such events can also lead to expensive breakdowns.
Custom-molded parts that are made to fit can help avoid such situations.

Types of Rubber Materials Used
Manufacturers can make custom rubber parts from a wide range of rubber materials. Some common options are explained below.
Natural rubber
Natural rubber is extracted from plants, mainly the Para rubber tree. This was the earliest form of rubber and is still in use today.
It can be used for shock absorption, vibration reduction, and tubing. It can also be used for belts for power transmission, rubber seals, and flexible couplings.
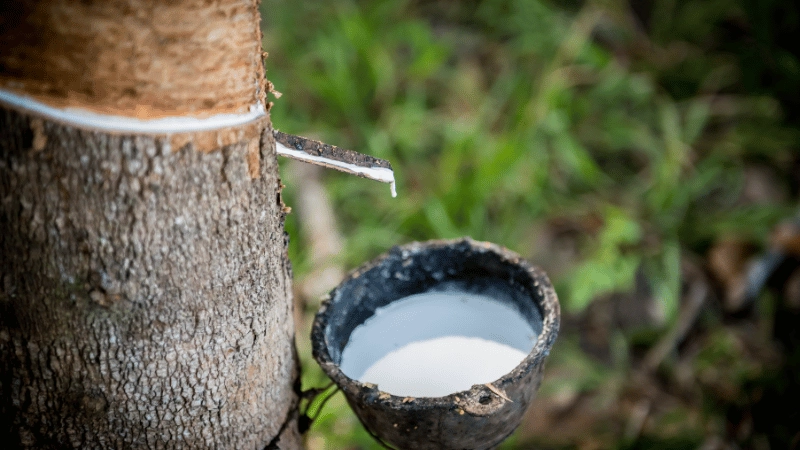

Natural rubber is outperformed by synthetic rubbers in many use cases, e.g., in high or low-temperature applications. But it is also vulnerable to petroleum-based liquids.
Neoprene
Neoprene is also called polychloroprene and was invented by DuPont in 1930. It is more resistant to degradation than natural rubber.
This rubber material is used for gaskets, noise control, padding, and electrical insulation. It’s also used to make automotive fan belts.
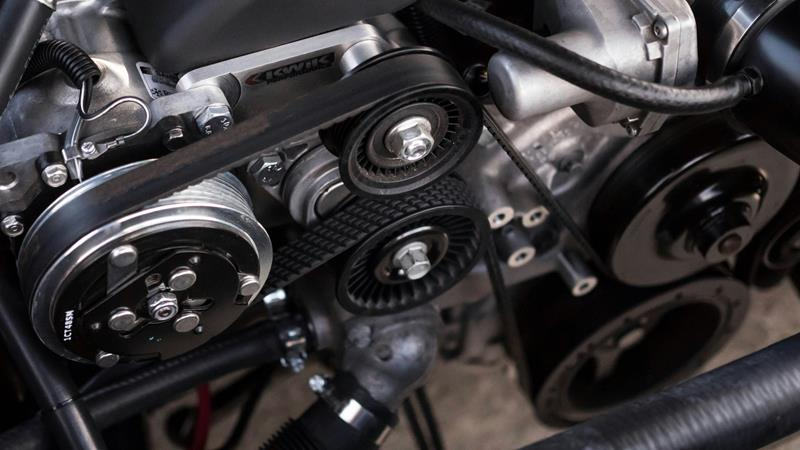

Silicone Rubber
Silicone rubber is made from the silicone polymer. There are different formulations of this elastomer depending on the intended applications. Silicone rubber can be used in temperatures as high as 300°C or as low as -55°C.
Applications of silicone rubber include the manufacture of O-rings and electrical insulation. In the automotive industry, this material is used for radiator seals, grommets, airbags, vibration dampers, and other forms of sealing.
Viton
Viton is another elastomer developed by DuPont. These rubbers are collectively called FKMs and are known for their outstanding heat and chemical resistance which covers oxygenated fuels, lubricants, oils, and many mineral acids.

Viton has been used to make O-rings and rubber seals for fuel injectors, hoses, gaskets, and cable insulation.
EPDM
EPDM rubber was developed in the 60s. It’s made using ethylene, propylene, and diene and is known for its resistance to sunlight.
It also performs well against heat, steam, and ozone and has good chemical resistance against ketones, alkalis, and hydraulic fluids.
EPDM is commonly used to make the seals for car doors and windows. It can also be used for wiper blades, bellows, grommets, wiring harnesses, hoses in the cooling system, etc.

NBR
Nitrile rubber is made from butadiene and acrylonitrile and is more resistant to fuels, oils, and acids than natural rubber. This material was made in 1931 and commercial production began in Germany.
In the automotive industry, this elastomer is considered a good choice for seals, oil hoses, grommets, and fuel systems. It also features in the suspension systems of some race cars.
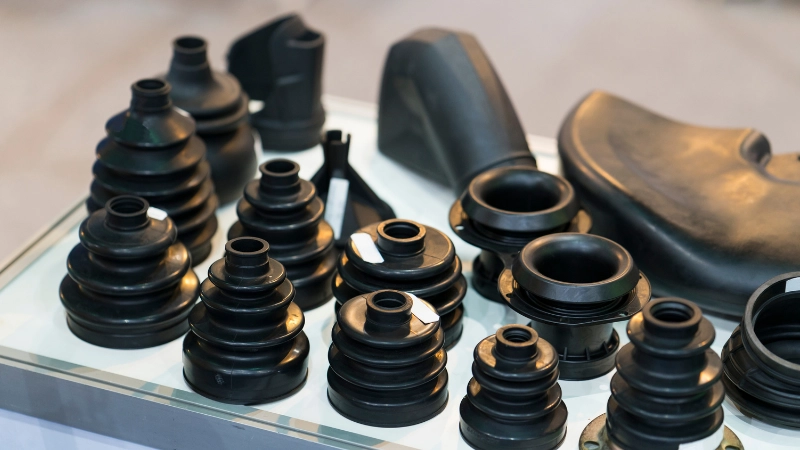
Common Custom Molded Rubber Parts in Automobiles
The types of rubber parts that can be custom-molded are only limited by imagination. In automobiles, these parts often include:
- Seals: Seals are used to keep fluids inside or outside. Seals can be found in radiators, fuel systems, exhaust systems, around instruments, etc. Gaskets and O-rings are examples of seals used in cars.

- Grommets: These are rings placed inside holes to protect cables or anything else that will be run through the hole from abrasion.
- Bushings: These are used to absorb vibrations. They can also be referred to as antivibration mountings.
- Tubing: Tubing and hoses channel liquids and gases between components.

- Suction cups: These can be used to secure parts without fasteners or adhesives.
- Caps: Used to cover openings such as the open tops and the ends of tubes.
- Bellows: Deformable pneumatic devices that resemble accordions. They are filled with and contain air up to certain pressures before releasing it.
Manufacturing Processes for Custom Rubber Parts
Custom rubber molding services come with different process options. The choice of process is determined by the complexity of the features, the size and geometry of a part, and other factors.
Injection Molding

Injection molding is a process where molten rubber or liquid rubber precursors are injected into a sealed mold to form a part.
The liquid or molten rubber material is injected at a high pressure. The pressure and heat cause the part to undergo curing or vulcanization before being ejected.
This process is one of the most expensive rubber molding methods but is the best for mass production of parts especially those with complex geometries.
Compression Molding
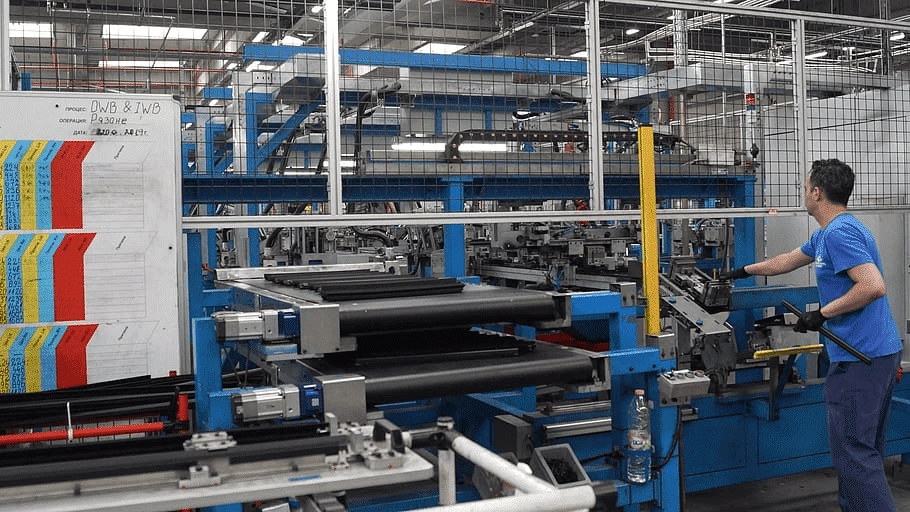

In this manufacturing process, a deformable rubber material is placed inside one half of an open mold before the other half is closed on top of it. The material is held inside the mold under pressure until it cures.
Compression molding is cheaper than injection molding when you need large parts with simple geometries. You can also have multiple cavities in the mold to make several parts in each cycle.
Transfer Molding
Transfer molding has similarities to both injection and compression molding.
A specific quantity of material is prepared and placed inside a chamber on top of a closed mold. A plunger then closes down on the chamber and forces the material into the mold via a channel.
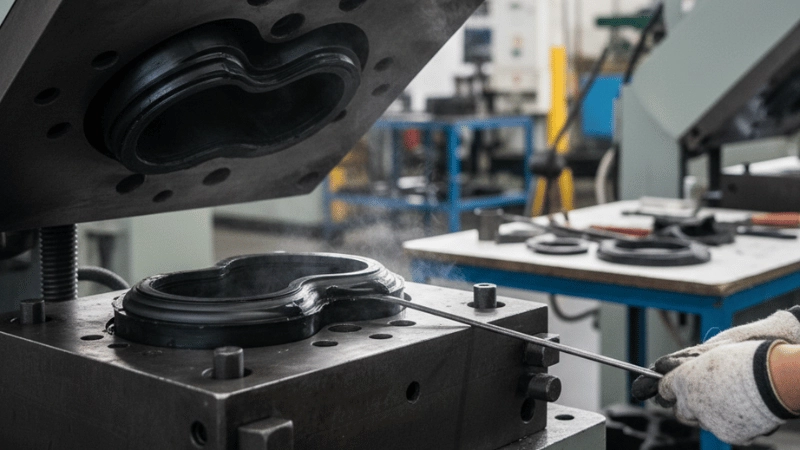

The material is kept under pressure inside the mold which only opens after the part has cured. The transfer rubber molding process features simpler tooling than injection molding.
It’s well-suited for small production batches and is commonly used for molding rubber around metal parts.
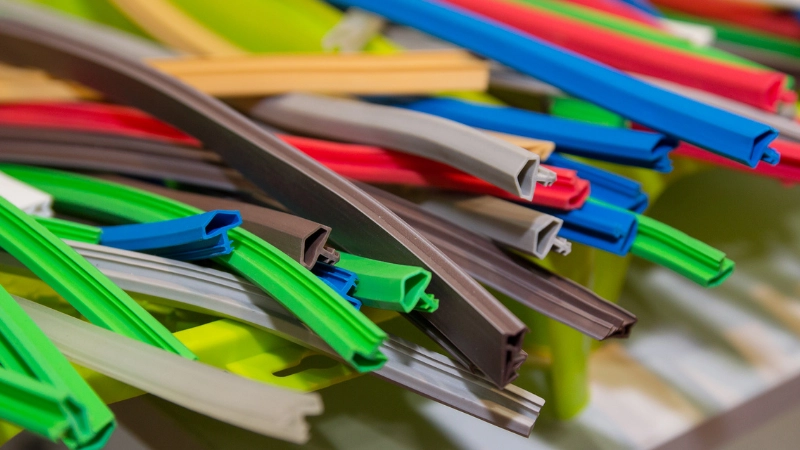
Extrusion
Extrusion involves forcing a material through a die to produce parts with a consistent cross-section. A die is a tool with the cross-section’s profile cut into it. This process produces little waste which leads to lower costs.
Extrusion can produce molded rubber components with simple cross-sections such as tubing or complex cross-sections such as door seals. Extruded parts can be cut into different lengths depending on the application.

Factors to Consider When Creating Custom Molded Rubber Parts
Creating a custom-molded rubber component is a significant investment. To ensure this investment is put to good use, there are key factors you should consider such as:
Part Geometry: Part geometry will affect the design process, material selection, and manufacturing process selection. Some geometries can only be economically achieved using certain processes and materials and can be challenging to design.
Material Selection: Material selection is a critical process because not all rubber materials perform well in certain automotive environments. You will have to consider the temperatures and chemicals present where the part will be installed.

Tolerances: Some rubber parts must be molded with very tight tolerances to achieve the desired form and function.
However, this raises the manufacturing complexity and cost. Therefore, there must be a balance to keep costs within certain limits.
Planned quantity: This determines the best rubber molding method. Injection rubber molding has a high tooling cost but is usually the most cost-effective solution for mass production.
Compression molding and transfer molding are better suited for smaller production volumes.
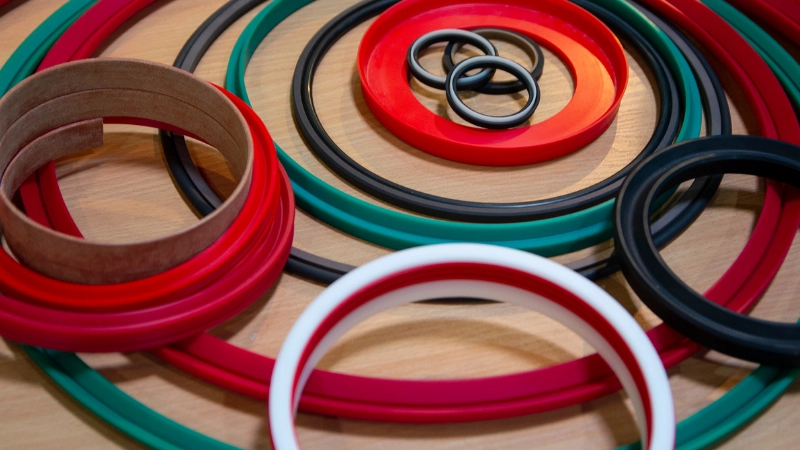

Expertise: The design and manufacturing expertise of your manufacturer can save you a lot of time and money. Experienced manufacturer like Hongju Silicone will tell you which designs are achievable, what changes should be made, and what processes and materials work best for your situation.
This will save you the trouble of learning from failed attempts.
Quality Control and Testing
Custom-molded parts must be subjected to different tests to ensure they will perform as expected. Materials may behave unpredictably when subjected to certain conditions.
Quality control also ensures that product quality remains the same across different batches.
1. Material Inspection
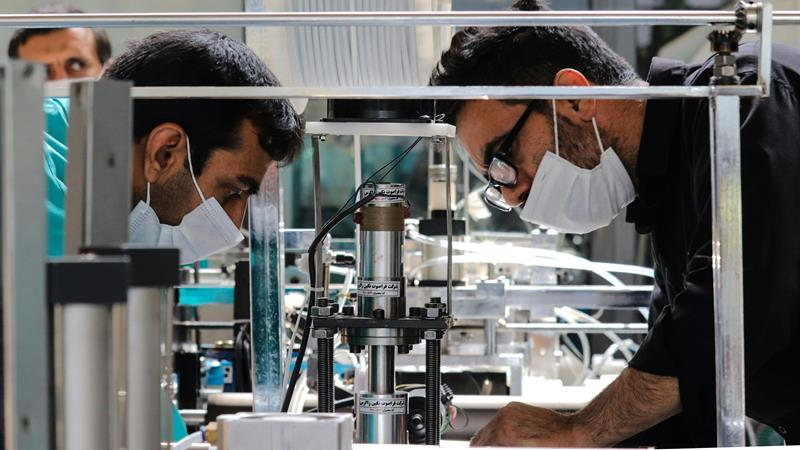

Materials used for custom molding rubber parts should be subjected to certain tests before production. Materials with the same names can have different properties which impact the product quality.
This can be due to adulteration, differences in formulation, environmental exposure, etc.
Material inspection may include different levels of visual analysis, and physical or chemical testing.
2. In-Process Inspections
Small differences in process parameters can cause large differences in product performance. Discovering such issues after production raises production costs.
The manufacturing process should have systems for visually inspecting parts and checking dimensions. Process parameters such as temperature and pressure should also be closely monitored.
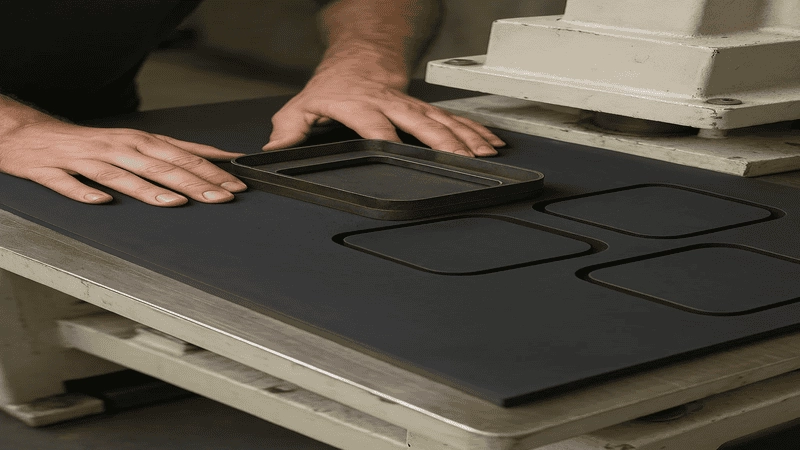

3. Post-Manufacturing Testing
These might be the most comprehensive set of tests because they are performed on finished products.
There should be established standards before the testing is done to ensure the correct tests are performed to predict the performance of the custom-molded rubber part in real life.
Tests conducted on custom rubber products include:
- Compression set: Compression set is to determine how much the material can recover after deformation.

- Hardness: Some applications need hard materials while others don’t.
- Rubber aging tests: These are used to predict how the material behaves over time and how long it can reliably function.
- Tensile strength: Determines how much pulling force is needed to permanently deform the part.
A good manufacturer will have access to the systems needed to perform such tests.
Conclusion
Custom molded rubber parts deliver precision sealing, vibration damping, and durability for automotive and industrial applications. Using materials like silicone, EPDM, and Viton, manufacturers employ injection, compression, and transfer molding to produce complex components.
Key considerations include material compatibility, design precision, and rigorous quality control to ensure performance, safety, and longevity in demanding environments.
Choose Hongju Silicone for Custom Molded Rubber Parts
Hongju Silicone has been delivering on its promise of high-quality rubber products for over 20 years. Accelerate your production with our 3–5 day CNC prototyping, low MOQ flexibility.
Get the quality your business deserve. Rreach out for a competitive quote today!