Through the comparison of overmolding and insert molding, this piece delves into their respective strengths and weaknesses as well as sector-specific utilization scenarios.
What is Overmolding?
It is a manufacturing procedure. A single product is made by molding that mixes two or more materials. A substrate, typically found in stiff plastic form, is put inside a mold during processing.
Over the substrate involves molding a second material that is typically soft or more flexible before creating the final product with additional features or improved looks.
- Two-shot overmolding: a type of overmolding. One process requires two separate injections by means of this specially designed injection molding machine. With this methodology, multi-material complex components can be created, like a toothbrush handle with an accommodating grasp versus a plastic handle with soft seals and a stiff center.
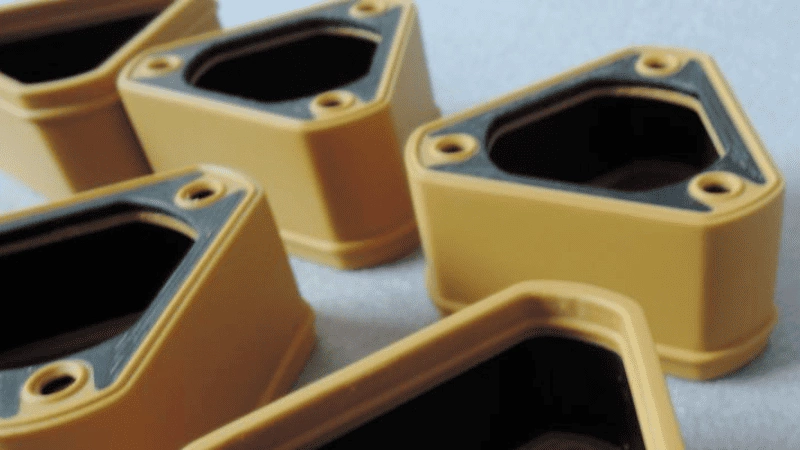

- Pick-and-Place Overmolding: With another approach, the pick-and-place process overmolding is possible. Pre-molded inserts are inserted into a mold cavity through manual or automated means during this process. Integration takes a two-step manufacturing process in place by combining two substances within one finished product.
What is Insert Molding?
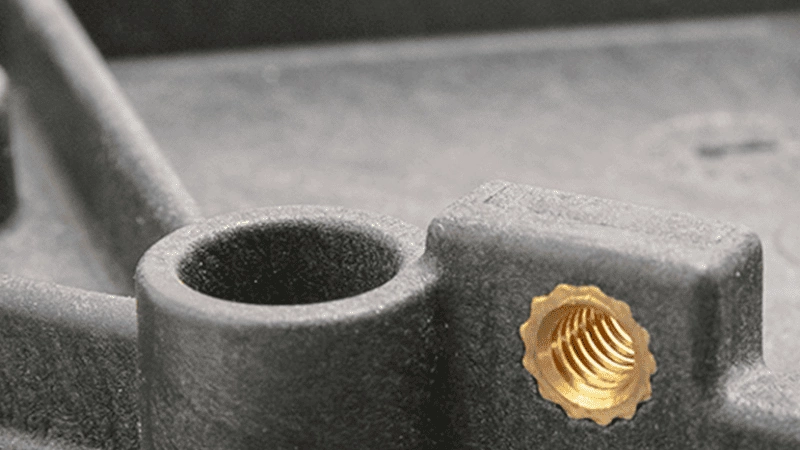
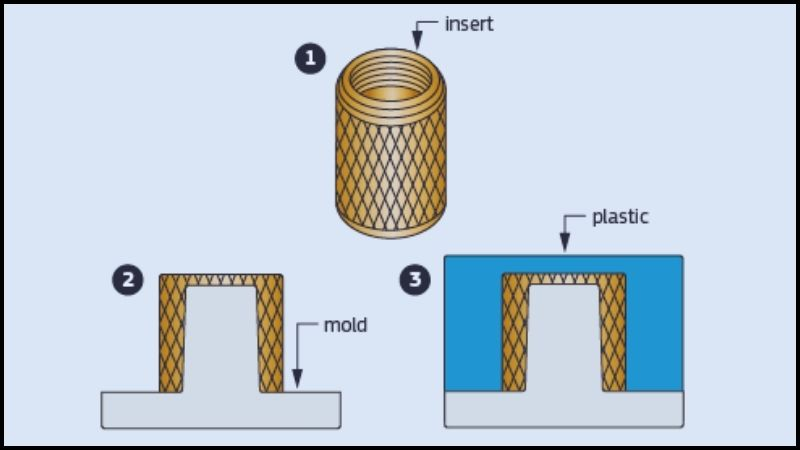
By putting a pre-shaped metal or molten plastic insert inside an insertion molding cavity, and then filling up the space by injecting surrounding plastic.
With the insert, the already molten plastic and material form a robust bond, providing security. Through a metal or molten plastic insert, the strength or function of a component can be improved.

Overmolding vs. Insert Molding: What’s the Difference?
Injection molding is classified into three types: insert molding, overmolding, and molding with extra material added. Whereas inserts go inside double-injection molding before plaster material introduction, overmolding adds excess materials outside double-shot molding of the base component.
How this difference impacts the strength, design flexibility, and functionality of injection molded metal parts used in the final output varies.
It is possible to make soft or flexible grips using insert molding and overmolding, as well as improved ergonomics and improved aesthetics.
Additionally, injection molding is unable to match the level of shock absorption and vibration dampening offered by machining. To improve part performance through metal-inserted design, insert molding and overmolding are the way to go.
Connectors, sensors, and terminals are examples of components. It is used in both the electronics and automobile industries.
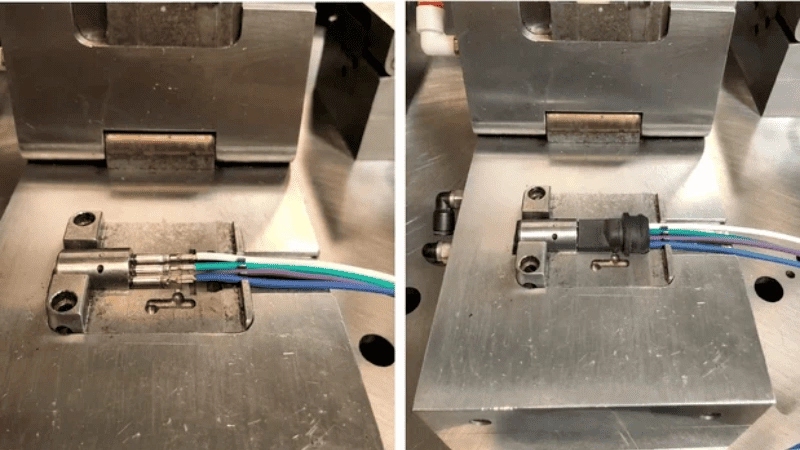
Overmolding & Insert Molding Industry Applications
Due to overmolding and insert molding, each method has a specific use in a variety of sectors. Possibilities exist for designers and engineers to improve product functionality, appearance, and longevity through these methods.
Industrial
Both overmolding of plastic pellets and metal insert molding play key roles in tool, handle, grip, and component manufacturing for the industry.
Comfort and ergonomics advantages stem from overmolding; through insert molding, strength and conductivity are boosted via a seamless combination of plastic and metal elements.
Medical & Healthcare
These moldings are required for medical equipment. Softness or improved hold can result from overmolding devices. By combining metal components or sensors during the multiple layers of materials in the manufacturing process, insert injection molding adds strength and durability to medical equipment.

Electronics
Both insert molding and overmolding together, insert molding and overmolding have advantages that benefit the electronics industry. To improve case durability and aesthetics, overmolding is essential; meanwhile, insert molding guarantees dependable links via added components.
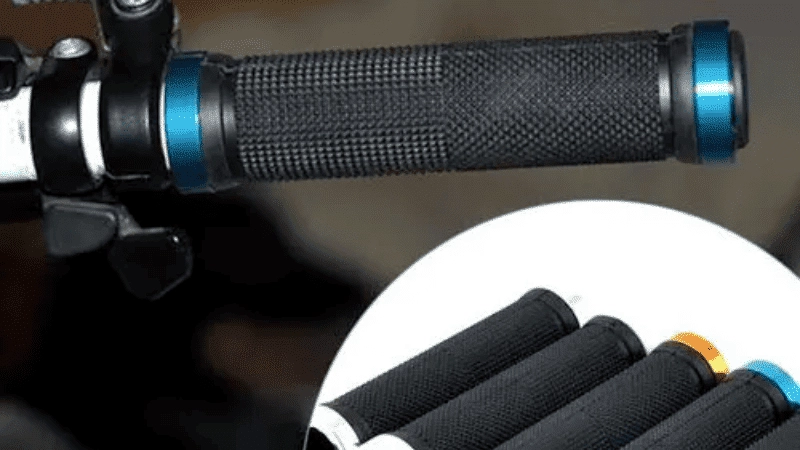
Consumer & Recreational
When producing handles, grips, and distinctive goods, insert molding rather than overmolding is frequently utilized in the consumer and entertainment industries.
Instead, choose insert molding that is used to improve durability and performance in a variety of products, like power tools, athletic gear, and playthings.
Automotive
Strategies for overmolding include direct overmolding, insert molded part molding variation, and overmolding with inserts. Interior and exterior component design benefits from overmolding in terms of ergonomics and aesthetics.
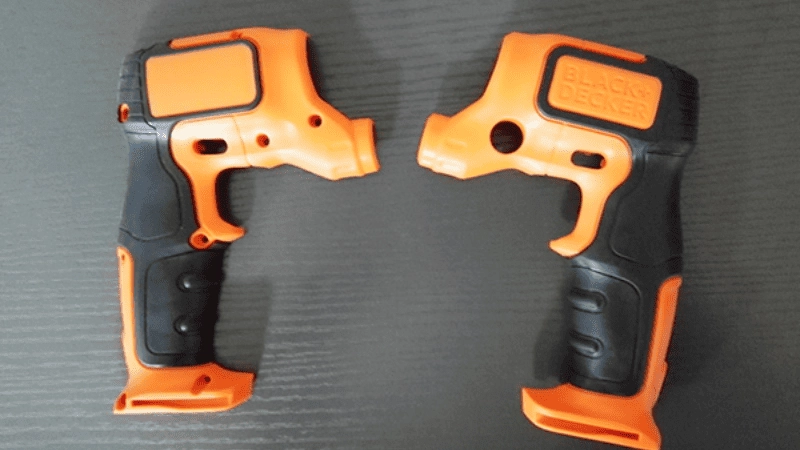

By including metal components like connections, switches, and sensors, the insert molded part molding, on the other hand, provides an alternate method for enhancing component performance and dependability.
Designing for Overmolding and Insert Molding: Tips and Best Practices
With these injection molding methods, multiple components can be integrated into a single part, offering increased aesthetics, functionality, and endurance. Here are some tips on hand tools and best practices to consider when designing two-shot molding:
Early Collaboration with Manufacturers
Early involvement of an injection molding manufacturer leads to more efficient and cost-effective production processes. Identify potential difficulties, their expertise, and reusable connections they can help you with.
Ensuring consistency across various injection molded part manufacturers requires coordination, which also helps you stay within their capabilities and restrictions.
Material Selection
Compatibility with the process should be considered when choosing materials. A solid mechanical linkup needs to exist between the fundamental material and whatever else that will get injected. Find the optimal mix of materials with input from your manufacturing expert.
Component Geometry and Placement
For Overmolding:
- Made to be easily ejected from the overmolding process, the major component (base) should have sufficient draft angles.
- Between the base and overmolded plastic materials, pay close attention to the interface. Process simplicity is hindered by design factors like undercuts.
- To avoid part distortion when cooling, consider material shrinkage rates first.
For Insert Molding:
- Attaching them to the insert injection molded parts requires designing components with undercuts, knurls, or grooves.
- Insert placement must be precise for correct positioning during the insert injection molding itself.
- Spacing between inserts should be just right to avoid disruption during insertion.
Tolerances and Clearances
Components threaded inserts must have well-defined interface areas with tolerance and clearance parameters. Tight fittingness between the malleable material and either the foundation or between molten plastics of an insert guarantees a robust connection without any undesirable motion or space.
Surface Finish and Texture
The surface finish and texture for the base plus the complementary or contrasting color of the overmolded plastic material must be considered together. Clear communication with the manufacturer regarding the desired texture or look is crucial when engaging other manufacturing services in overmolding.
Gate Locations and Flow Analysis
Determine the most effective spots in collaboration with your production partner. Identify potential quality issues like air traps or insufficient material flows by analyzing the flow of materials, these tools allow.
Part Orientation
Consideration must be given to how your role fits into the bigger picture of the entire double injection molding process, so that you may simplify things. Better material flow results when the proper orientation of plastic parts is maintained complex two shot involves molding is up.
Prototyping and Testing
Prototype creation or small-scale testing before full-scale production complex two-shot mold, is key. Identifying and addressing any necessary adjustments enables optimization of the both processes.
Pros and Cons of Overmolding vs. Insert Molding
Two options for injection molding, both with pros and cons. Knowing the pros and cons of the two-step process makes it easier to decide on the ideal method that involves injection molding for your unique project. Let’s compare the above two processes:
Overmolding
Pros:
- Enhanced Aesthetics: With the overmolding process, products gain an appealing visual component and improved ergonomics through mixing various materials, colors, and textures within a single component.
- Improved Sealing: Resistance to moisture, dust, and other substances results from overmolding. Harsh environments provide value to this.
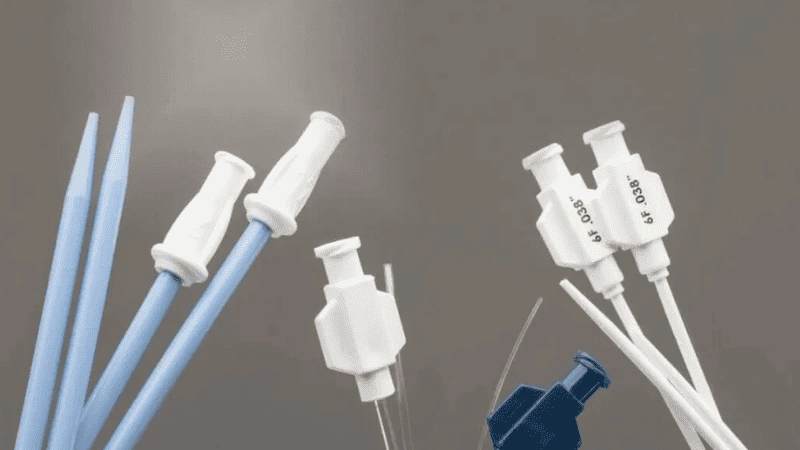
- Reduced Assembly: Reducing the need for additional assembly steps through the overmolding process leads to cost savings and faster production.
- Design Flexibility: Design flexibility allows overmolding to create one-of-a-kind and sophisticated part shapes and details.
- Reduced Material Waste: Efficiency is key when it comes to overmolding, thanks to the injection molding process, which minimizes waste by maximizing materials.
Take the First Step:
Requst for an Inquire
Quality Meets Affordability. Inquire Now for High-Quality Products at Low Volumes.
Cons:
A few cons follow when it comes to overmolding.
- Complex Tooling: Standard injection molding may have higher initial setup costs than tooling that is more complex and costly.
- Longer Cycle Times: With longer cooling times and multi-material processes involved in injection molded parts, the cycle time. efficiency in production could suffer as a result.
- Limited Material Compatibility: Material compatibility is crucial for successful overmolding processes.
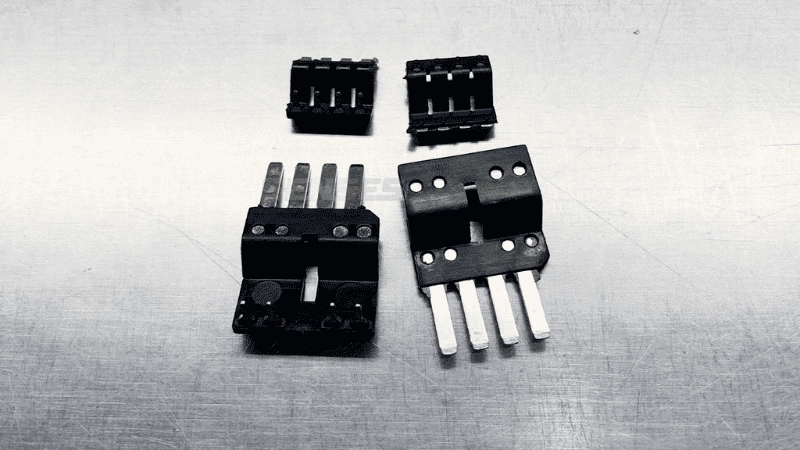
Insert Molding
Pros:
Insert molding has numerous positive and useful properties, including:
- Strength and Durability: Strong bonds between components and the plastic surroundings create parts exhibiting great mechanical qualities.
- Cost Efficiency: By cutting down on waste disposal fees and streamlining manufacturing processes, high production rates become more affordable.
- Design Precision: With precision control over insert positioning, this approach works well for components boasting particular functionality or built-in attributes.
- Versatile Material Compatibility: Plastic, metal, and electronic components are some examples of items used in molding through insertion.

Cons:
Despite offering advantages, the use of insert molding carries unexpected repercussions. It includes:
- Assembly Complexity: Planning and tooling modification must be exact to guarantee correct insert positioning and adhesion through the design process.
- Limited Aesthetic Options: When it comes to colors and textures, overmolding offers more aesthetic flexibility than it does.
- Higher Initial Tooling Costs: Standard injection molding has higher initial tooling costs compared to while being cost-effective for high-volume production.
- Material Compatibility: Compatibility between the insert material and the surrounding plastic is crucial to prevent future bonding issues.
Take the First Step:
Requst for an Inquire
Quality Meets Affordability. Inquire Now for High-Quality Products at Low Volumes.
Conclusion
In conclusion, overmolding and insert molding have significant value because they help in industrial production methods. With multiple manufacturing technologies, each offering distinct pros and uses, companies can fabricate practical and visually appealing plastic and metal parts and components.
Two manufacturing approaches provide cutting-edge solutions—overmolding and insert molding.
Why go to Hongju for your Manufacturing needs?
Feel free to contact Hongju immediately. We look forward to engaging in collaborative discussions about how our state-of-the-art processes and tools can be the catalysts for your business growth and success.
Contact us now and get a free consultation. Rest assured, our dedicated team will be there for you every step of the way, fully committed to turning your visionary ideas into tangible realities.