Did you know that silicone and rubber are not the same? Despite their similar appearances, these materials have distinct compositions and properties. It’s crucial to grasp the disparities between silicone and rubber to make informed decisions.
This article aims to shed light on these dissimilarities, providing you with a clear understanding. By delving into special properties of their dissimilarities, we can better appreciate the strengths of each material and determine which one suits our needs.
Understanding the Composition and Materials
Silicone and rubber may seem similar, but their composition sets them apart. Let’s dive into the breakdown of these materials to understand the key differences here.
What is Silicone?

What is silicone? Silicone is a synthetic material made up of silicon, oxygen, and other elements like carbon, hydrogen, and fluorine. Silicone gets its name from the word “silicon” which is the key element in this polymer.
Silicone is a form of synthetic rubber. We can synthesize it by modifying silicon. Furthermore, this material consists of a backbone of silicon atoms with alternating oxygen atoms.
It is known for its versatile properties, such as heat resistance, cold resistance, and chemical resistance. It offers a unique combination of chemical and mechanical properties that organic elastomers cannot match.
Silicone is used in a variety of applications including medical devices, food handlers, and construction materials.
What is Rubber?
Rubber was originally a natural product, latex from the rubber tree. The discovery of vulcanization gave an improved version by cross-linking the polymer chains with sulfur.
Rubber, on the other hand, is a natural or synthetic polymer that consists of repeating units of isoprene molecules.

There are several types of rubber, including natural rubber, styrene-butadiene rubber, silicone rubber, nitrile rubber, and hydrogenated rubber, each with unique properties.
However, the most common type of rubber is called natural rubber. This type of rubber is produced from rubber trees found in tropical and subtropical regions worldwide.
The natural rubber is extracted from the rubber tree and then processed into a variety of products such as tires, cables, and medical devices. Rubber is known for its elasticity and durability.
It’s worth mentioning that silicone rubber is a useful if more recent, addition to the rubber family.
Silicone rubbers offer better performance at temperature extremes than natural rubber and can be tailored for a broader range of physical and mechanical properties.
The composition of silicone differs significantly from that of rubber. While silicone contains elements like silicon atoms and oxygen, rubber relies on polymers for its structure.

The biggest difference between silicone rubber and natural rubber is that silicone rubber is made while natural rubber is harvested.
One of the key differences between silicone rubber and natural rubber is that most rubbers contain polymer chains of carbon; however, silicone rubber contains silicon in polymer chains instead of carbon.
The performance divergence originates at the atomic level: the Si-O bond in silicone has a dissociation energy of ~444 kJ/mol , significantly higher than the ~347 kJ/mol of the C-C bond in rubber. This stronger bond is the fundamental reason for silicone’s superior thermal and chemical stability.
So, we can distinguish silicone from rubbers by the atomic structure.
Understanding this material breakdown helps us differentiate between silicone and rubber. By grasping their fundamental compositions, we can appreciate why each material possesses specific characteristics.
Take the First Step:
Requst for an Inquire
Quality Meets Affordability. Inquire Now for High-Quality Products at Low Volumes.
Understanding the Manufacturing Process
Silicones and rubber may seem similar, but their manufacturing processes differ significantly. Let’s dive into how these materials are produced.
Silicones
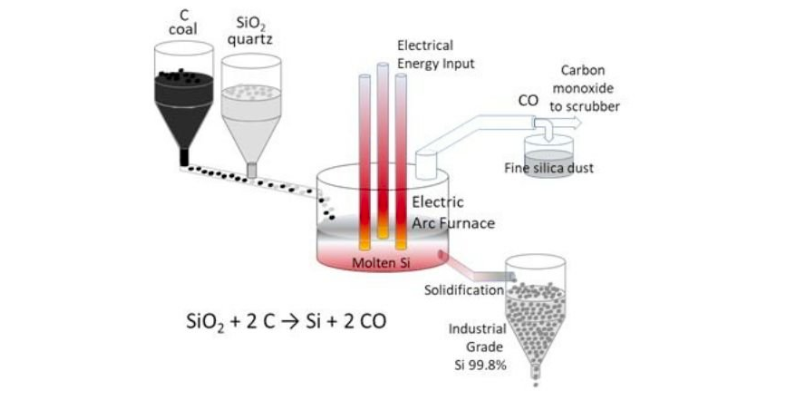
- Silicones undergo a complex chemical process called polymerization.
- This process involves combining silicon with other elements like oxygen, carbon, and hydrogen to create a unique polymer structure.
- The resulting silicone material possesses exceptional heat resistance, flexibility, and durability.
Rubber
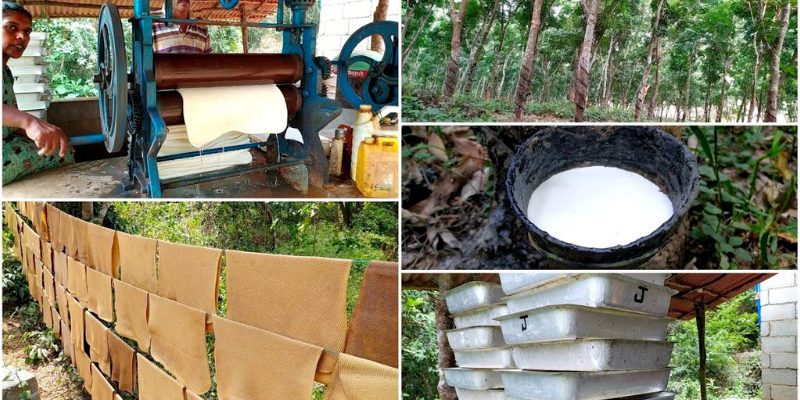

- Rubber can be manufactured using natural or synthetic methods.
- Natural rubber is obtained through latex extraction from plants like rubber trees.
- Synthetic rubber production involves various techniques such as vulcanization, where sulfur is added to improve its strength and elasticity.
- Both natural and synthetic rubber offer excellent resilience and elasticity.
- Rubbers offer superior abrasion resistance compared to silicones due to their higher hardness levels.
The manufacturing processes for silicone and rubber vary in complexity and techniques employed.
While silicones require intricate chemical reactions to form their distinct properties, rubber can be derived from natural sources of oil or created synthetically using different methods.

Understanding the production process and methods sheds light on how silicone and rubber are made.
By delving into the intricacies of polymerization for silicones and the diverse approaches used in both rubber and silicone manufacturing, we gain insight into these versatile materials’ origins.
Silicone vs. Rubber: Recognizing the Properties’ Differences

All the elastomers are considered rubbers. These materials show a glass transition temperature due to their amorphous structure. Silicone and rubber may seem similar at first glance, with carbon bonds but a closer look reveals distinct differences in their properties.
Understanding these disparities is crucial for distinguishing between the two materials. Let’s explore some key points to help you recognize the dissimilarities:
Water Absorption Resistance
- Silicone possesses low surface tension, granting it resistance to water absorption that some rubbers lack.
- Unlike certain rubbers, silicone remains unaffected by prolonged exposure to moisture.
Abrasion Resistance
- Generally, rubbers offer superior abrasion resistance compared to silicones due to their higher hardness levels.
- In scenarios where durability against wear and tear is vital, rubber outperforms silicone.

Electrical Insulation Properties
- Silicones excel in electrical insulation capabilities when compared to most rubbers.
- Their unique composition allows silicones to provide better protection against electric current flow.
Heat Resistance
- Silicone rubber is known for its exceptional heat resistance. It has a wide temperature range and can withstand extreme temperatures, ranging from very low (around -100°C) to high temperatures (up to 300°C). It can maintain its properties even at high temperatures, making it a reliable choice for various applications.
- Rubber’s heat resistance varies depending on the specific type. While some rubbers can handle moderate temperatures, others are less tolerant of extreme heat compared to silicone.
- Comparing the thermal performance of silicone and rubber highlights their disparities in heat resistance capabilities. Silicone stands out with its ability to withstand higher temperatures.

These differentiating properties highlight the contrasting nature of silicone and rubber materials.
While silicone excels in temperature resistance and chemical resilience, rubber takes the lead with its superior elasticity.
Understanding these distinctions helps determine which material is best suited for specific applications.
Take the First Step:
Requst for an Inquire
Quality Meets Affordability. Inquire Now for High-Quality Products at Low Volumes.
Applications: Versatile Uses in Various Industries
Silicone and rubber are two distinct materials that find versatile applications across various industries. Let’s explore their unique uses and properties:
- Silicone rubber, known for its excellent sealing properties. For example, silicone O-rings are extensively utilized in industries such as automotive, electronics, medical devices, and construction. Its ability to create a tight seal makes it ideal for applications where preventing leakage or contamination is crucial.
- Silicone exhibits a wider chemical resistance than natural rubber, often making it the better choice for chemical sealing applications. Silicone has a wide temperature range, is resistant to UV and ozone, and is non-reactive, making it suitable for medical and kitchen products.

- On the other hand, rubber is widely employed in applications requiring flexibility. It can be found in tires, gaskets, seals, and footwear due to its elasticity. Natural rubber exhibits much higher tensile strength, tear strength, and abrasion resistance than silicone.
- Rubber’s ability to withstand bending and stretching without losing its shape makes it perfect for these specific purposes.

Highlighting the versatile elastic properties of both silicone and rubber reveals their distinct roles in different industries.
While silicone excels in automotive applications by providing effective sealing solutions, rubber shines when flexibility is paramount.
The unique properties of each material make them suitable for specific purposes:
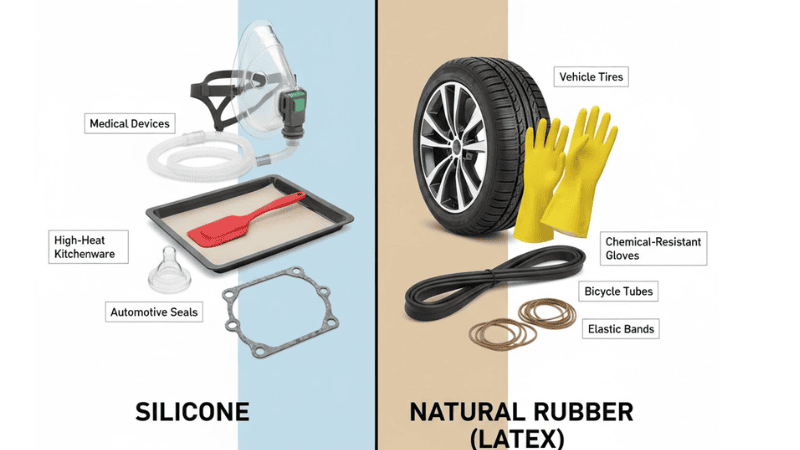

- Silicone:
- Automotive application: Sealing components to prevent water or air leakage.
- Electronics industry: Encapsulating sensitive electronic parts to protect against moisture or dust.
- Medical device: Creating sterile barriers with excellent biocompatibility.
- Construction: Weatherproofing structures by sealing joints and gaps.
- Rubber:
- Tires: Providing traction on various surfaces while absorbing shocks.
- Gaskets and seals: Preventing leaks between two mating surfaces.
- Footwear: Offering comfort, flexibility, and durability.
Take the First Step:
Requst for an Inquire
Quality Meets Affordability. Inquire Now for High-Quality Products at Low Volumes.
Conclusion
Silicone and rubber may share some similarities, but they are not the same. These materials’ composition, properties, manufacturing process, and applications differ significantly.
You should carefully evaluate your requirements before deciding whether to use liquid silicone rubber or rubber. Their unique characteristics will determine which material best suits your particular application.
Buy High-Quality Silicone and Rubber Products from Hongju
Hongju Silicone is your ideal partner. We offer rapid CNC prototyping in 3-5 days to accelerate your validation, support production with flexible low MOQs to reduce your inventory risk, and back every project with over 20 years of craftsmanship to ensure reliable quality.
Visit our website and contact our team to take your product development to the next level.
FAQs
Q1. How does the manufacturing process affect the quality of silicone and rubber materials?
Precision in synthesis and curing determines consistency and performance. Hongju’s advanced processes ensure uniform quality, reducing defects and enhancing durability for demanding applications.
Q2. What’s the Core Chemical Difference ?
Silicone is based on a silicon-oxygen backbone, offering superior heat resistance and stability, while rubber is carbon-based with greater elasticity.
Q3. What is silicone’s source material?
Silicone is a synthetic material derived primarily from silica (abundant in sand). It does not exist in a naturally usable form; instead, it is manufactured through controlled chemical processes that transform silica into versatile silicone polymers.
Q4: What is your typical manufacturing lead time?
Hongju’s standard production lead time ranges from 9 to 15 working days. Specific timelines depend on order volume, product complexity, and seasonal factors, which we clarify and confirm with each project.
We welcome your inquiries — let’s discuss how we can meet your timeline needs.