Do you want to prevent equipment failures due to incompatible rubber material? Understanding mechanical properties is critical to selecting the right rubber material for high-stress industrial applications. We will explain rubber tensile strength, compressive strength, and elongation in detail. Also, explore essential factors affecting rubber performance.
What is Tensile Strength in Rubber?
Tensile strength in rubber is the maximum stress the material can withstand when experiencing stretch (pulling apart) without being deformed, ruptured, or losing elasticity. It is a crucial performance metric when selecting rubber for different applications. The material’s durability and structural integrity depend on tensile strength.
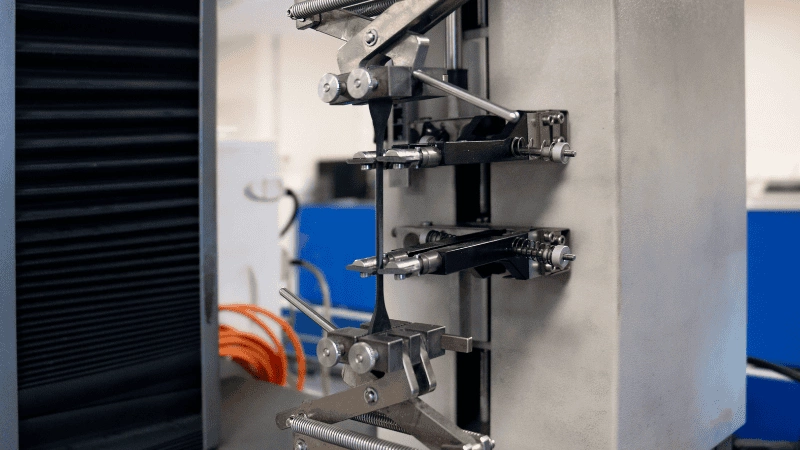

Tensile strength is measured in Megapascals (MPa) or pounds per square inch (P.S.I), a unit for tensile stress. The material is pulled/stretched using a Universal Testing Machine (UTM) to the point it breaks to check the resistance. The maximum stress it tolerated shows the tensile strength. So, when the material is put to use, it tolerates the same amount of stress.
Rubber products like seals, hoses, and gaskets experience tensile stress. You must ensure that the material’s tensile strength is enough to withstand the stress in intended working conditions. Otherwise, you will face issues like premature failure, damage to equipment, and safety hazards.
How Tensile Strength and Elongation Work Together
Elongation refers to the percentage (%) change in length of rubber material when exposed to tensile forces. The change is measured with respect to the original length. For instance, 10% elongation means the material has elongated 10% of its initial length under force.
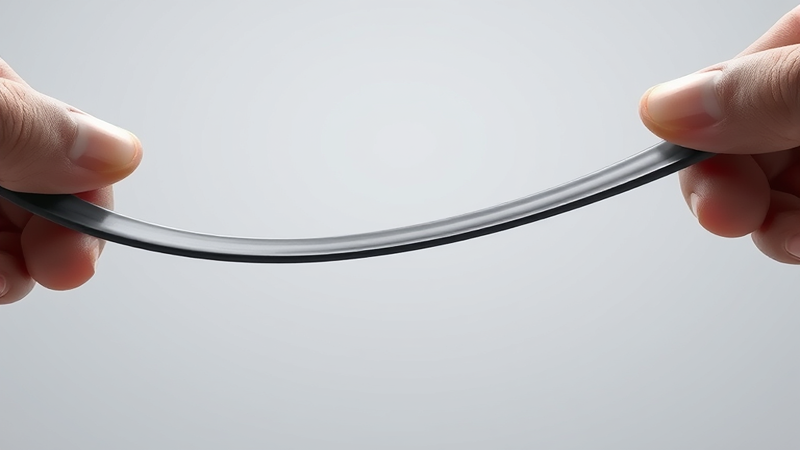

Tensile strength and elongation are interdependent. The tensile strength is the amount of force the material can withstand without breaking while elongation is the change in material’s length when experiencing that force. Both measures affect the performance of rubber materials.
Rubber material is opted for applications where flexibility and strength are crucial. For example, rubber gaskets need to be flexible to form a perfect seal and maintain structural integrity under stress. Similarly, vibration dampeners require a high level of elongation and tensile strength.
Factors That Affect Rubber Tensile Strength
Rubber tensile strength is affected by different factors associated with the production process and operational conditions. Let’s understand how these factors influence rubber tensile strength.
Material Composition
Processed rubber is composed of raw rubber (natural or synthetic), compounding agents, and fillers. The composition of these constituents affects the rubber’s tensile strength. Natural rubber exhibits good elasticity but low tensile strength while synthetic rubber shows exceptional strength. Similarly, compounding agents affect cross-linking which gives the rubber its flexibility.
Vulcanization Process

Vulcanization is the process of improving the mechanical properties of rubber with vulcanizing agents like sulfur under high temperatures. The vulcanization agents trigger the formation of cross-linking chains between rubber molecules that give inherent properties like elasticity, tensile strength, and flexibility. Any change in the measure of the vulcanization agent can affect the material’s strength.
Environmental Conditions
Environmental conditions can highly impact rubber tensile strength. Extreme high temperatures can lead to thermal degradation causing the material to lose tensile strength and elasticity. Continuous UV exposure impacts the cross-linking and leads to surface cracking ultimately affecting tensile strength. Harmful chemicals like acids and solvents also affect rubber strength.
Fillers and Additives
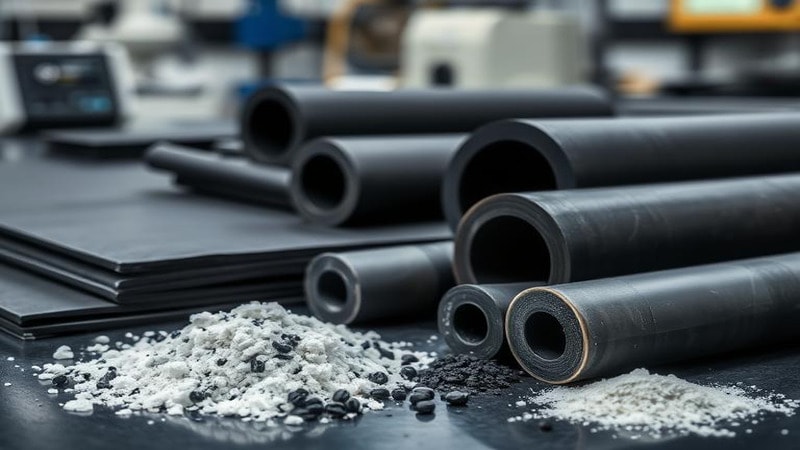

The addition of fillers and additives to rubber’s composition helps improve mechanical properties like tensile strength, flexibility, and durability. Compounds like carbon black are added to rubber formulation to improve UV resistance. Silica is also used to give rubber its water-resistant properties. Other compounds like curing agents also help improve rubber characteristics.
Tensile Strength Ranges for Different Rubber Materials
Let’s explore tensile strength and other key properties of different rubber materials. Compare and contrast to select the one best suited for your applications.
| Rubber Type | Tensile Strength Range (P.S.I) | Elongation (%) | Temperature Range (°C) | Key Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Natural Rubber | 500-3500 P.S.I. | 700% Maximum | -50 to 80°C | Tires, belts, seals |
| Nitrile Rubber | 200-3000 P.S.I. | 600% Maximum | -40 to 100°C | Oil-resistant gaskets, hoses |
| Silicone Rubber | 200-1500 P.S.I. | 700% Maximum | -60 to 230°C | Medical devices, food-grade products |
| EPDM Rubber | 500-2500 P.S.I. | 600% Maximum | -50 to 150°C | Weather seals, automotive components |
| Fluoroelastomers | 1500-2600 P.S.I | 300% Maximum | -20 to 250°C | Chemical-resistant seals, aerospace parts |
*These values are tested under normal conditions following ASTM standard testing guidelines.
Tensile Strength and Ultimate Tensile Strength
How is tensile strength different from ultimate tensile strength? Most people use these terms interchangeably but they’re not the same. Tensile strength is the material’s ability to withstand tensile forces (pulling and stretching) without rupturing or deforming. The ultimate tensile strength is the total force required to break a material by pulling it apart.

A material’s ultimate tensile strength is normally 1.5 to 2.0 times higher than its usual tensile strength. It’s often referred to as buffer strength or highest tensile strength. Tensile strength varies in different types of materials. Rubber is best known for its highest tensile strength and flexibility. To your surprise, human hair and synthetic rubber such as EPDM have a relative tensile strength of 10 MPa.
When selecting a material for any application, you need to consider both tensile strength and ultimate tensile strength. Ensure that the maximum stress the material will experience is below ultimate tensile strength and within the normal tensile strength range. You will easily avoid premature failure and enable efficient operation.
Compressive Strength in Rubber
Compressive strength in rubber is its ability to regain its original shape when exposed to compressive forces (pressing against or inward). It’s a critical property of rubber for applications like gaskets, vibration isolators, and cushioning pads. The rubber experiences constant compressive stress and needs to maintain structural integrity for efficient operation.

Tensile strength and compressive strength in rubber are relatable. Compressive strength is the material’s ability to withstand inward forces whereas tensile strength is the material’s ability to tolerate outward forces like stretching.
Mechanical Properties and Stress-Strain Behavior
Mechanical properties of rubber include compressive strength, compressive force, and tensile curve. These properties are crucial to evaluate rubber performance under different operating conditions. You need to be mindful of these characteristics when choosing rubber material for specific applications. It will help you determine how strong is rubber compound.
Stress-strain behavior of rubber signifies the changes in mechanical properties when encountering different levels of stress or strain. The rubber tends to expand under tensile stress, some types of rubber show high elongation while others show high tensile strength depending on their inherent properties.
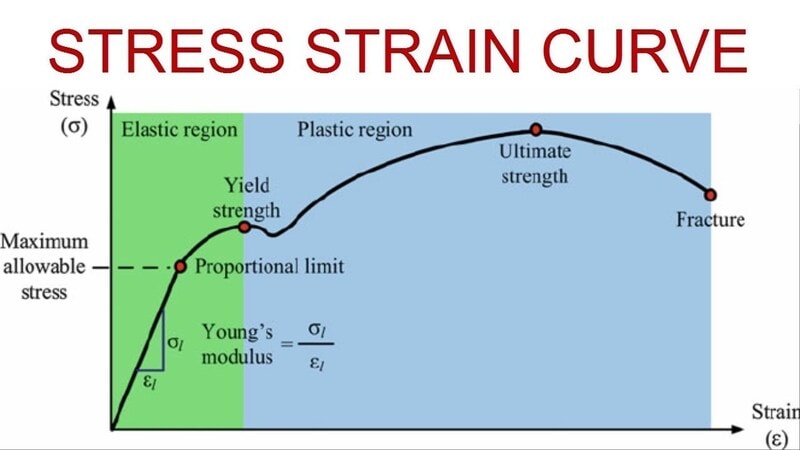
A stress-strain curve is used to examine rubber performance under stress. The changes to the material structure are represented through a graph. It is divided into multiple regions, each region depicts a specific property like tensile strength, flexibility, etc. Understanding the stress-strain curve is critical to choosing the right material as per requirements.
Comparison of Rubber and Plastic Materials
Rubber and plastic materials have distinct properties and are used for unrelated applications. Plastics appear as rigid and hard materials while rubbers are soft materials and flexible. Both materials differ in mechanical properties. Plastic types like polyurethane materials have high tensile strength compared to rubber. But rubbers stand out with their flexibility, especially a low modulus.

Rubber and plastic are extensively used in almost every sector. You can check your requirements to see which material suits your needs. Rubber is ideal for applications involving tensile and compression forces. Plastic is rigid and durable and offers better resistance to harmful chemicals. Both materials have their advantages and disadvantages.
Factors Affecting Rubber Material Performance
Rubber material performance is critical to ensure smooth operations. Here are critical factors that affect rubber performance:
Temperature Changes
Rubber material is not highly temperature resistant. Under extremely low temperatures the material loses elasticity and becomes brittle. When exposed to high temperatures its tensile strength is affected and the material becomes soft.
Working Pressure
Working pressure directly affects the physical properties of rubber like compressive strength. In a high-pressure environment rubber experiences compressive forces that may cause ultimate elongation. Exceeding specified compressive force leads to permanent deformation.
Chemical Exposure

Exposure to harmful chemicals like acids and solvents affects the internal structure of rubber material. It starts to degrade and lose structural integrity. Although synthetic rubbers are made chemical resistant, prolonged chemical exposure leads to degradation.
Additives & Fillerssssre43
Additives and fillers can help improve rubber properties. However, excessive use of additives and fillers can have adverse effects. Commonly used additives like Carbon Black & Silica enhance tensile strength, wear resistance, and overall durability of rubber.
Applications of High-Tensile-Strength Rubber
High-tensile strength rubber is used across various industries. The material is resilient to compression and tensile forces. Let’s explore more:
Automotive

High-tensile-strength rubber is used to manufacture car tires, engine belts, and gaskets. All these products experience constant tensile forces and require a flexible material with high durability. The rubber material is resistant to temperature, weathering, and abrasion.
Aerospace

Rubber has made it to space due to its high tensile strength and elasticity. It is used to produce high-performance seals and hoses used in rocket engines, satellites, etc. The rubber material is also employed for thermal insulation.
Construction

High-tensile-strength rubber has applications in the construction industry. It is used in vibration dampeners, concrete mixers, and other equipment. Rubber has a closed structure and is ideal for waterproofing. It is also used for waterproofing membranes.
Healthcare
Rubber material is chemically inert and biocompatible. It has wide applications in healthcare, especially medical equipment and patient care products. High-tensile-strength rubber is used in medical tubing, diaphragms, prosthetics, etc.
Choosing the Right Rubber for Your Application
Are you considering using rubber material for any specific application? Here are some essential factors to check:
Mechanical Properties
Before selecting any material understand the operating conditions like stress levels, pressure, temperature, load bearing, etc. Choose a compatible rubber material reviewing its mechanical properties; tensile strength, compressive strength, and elasticity.
Environmental Exposure
Rubber material performance is highly affected by environmental exposure. When selecting a rubber material consider its resistance to UV radiations, chemicals, and heat. Rubber can lose its elasticity and tensile strength when exposed to harmful environmental conditions.
Regulatory Compliance

If you’re using rubber material for application in the food industry, medical equipment, or patient care, you must ensure regulatory compliance. The material should be approved by FDA (U.S. Food and Drug Administration) and other regulatory authorities. For instance, RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances – EU) checks rubber material for hazardous substances.
Any Questions?
How is tensile strength tested in rubber?
Tensile strength is tested following ASTM D412 standard testing guidelines. A Universal Testing Machine is used to stretch the rubber material and calculate its tensile strength.
What is the difference between tensile and compressive strength?
Tensile strength is the material’s ability to withstand tensile force (stretching and pulling) whereas compressive strength is the material’s ability to withstand compressive forces (inward pressing).
Which rubber has the highest tensile strength?
Natural rubber has the highest tensile strength due to efficient cross-linking. It can tolerate excess tensile forces without breaking or losing structural integrity.
Conclusion
What’s the most critical safety risk associated with rubber material? Choosing an incompatible rubber material for critical applications. You need to be very careful about rubber tensile strength and other properties to prevent equipment failure, costly downtime, and accidents. Follow our comprehensive blog to understand rubber tensile strength and select the right material.
Are you looking for high-tensile-strength rubber material? Look no further! Hongju provides top-quality rubber material for a variety of applications. It serves customers in diverse industries including medical, consumer goods, and automobiles.
Hongju: Top Manufacturer of High-tensile-strength Rubber
Do you want application-specific rubber material? Hongju is a world-leading manufacturer of top-quality rubber material. It has over two decades of manufacturing excellence and a vertically integrated business model. If you want tailored solutions, there’s no better option than Hongju. Get in touch with our representative for detailed information.