Wondering how rubber components get their precise shapes? The rubber die cutting technique is used to make gaskets, seals, and pads.
It is a fast process that transforms rubber sheets into functional parts for industries like automotive, aerospace, electronics, and medical devices.
Read on to learn how the process works, which machines to use, and how to choose the right materials for your application.
What Is Rubber Die Cutting?
Rubber die cutting is a fabrication process. This process includes using a metal die cutter with specific die-cutting machines. Rubber sheets are cut into shapes by applying pressure with die-cutting machines.
Die cutting rubber works the same way as a cookie cutter, where the cookie dough is placed under a cutter. The tool presses and out comes a clean, uniform cookie.
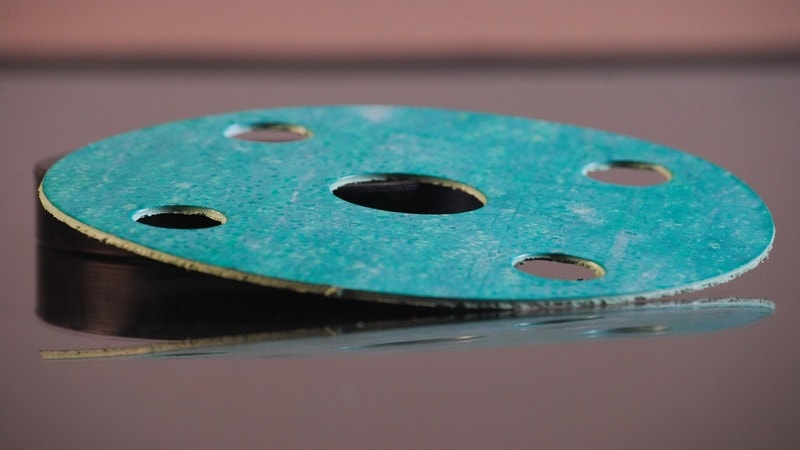
In rubber die cutting, types of rubber like EPDM, silicone, nitrile, and other rubber materials are cut into gaskets, washers, and seals.
This method is most suitable for silicone and rubber components because of speed, precision, and repeatability. It works well for a wide range of thicknesses and hardness levels. That’s why most industries rely on this process to cut rubber and silicone components.
How the Rubber Die Cutting Process Works (Step-by-Step)
If you are sourcing custom parts or designing your next product, this step-by-step guide will help you make an excellent final product:
Step 1: Design & Technical Drawing
First, you need to create a design of a 2D technical drawing using CAD software. The CAD files define the shape, dimensions, material thickness, and tolerances.
Step 2: Material Selection & Feeding
The next step is loading the rubber sheets onto the cutting bed or feeder. Usually, silicone, neoprene, EPDM, or nitrile are selected based on mechanical, thermal, and chemical properties. Place the sheet correctly for accurate cutting.
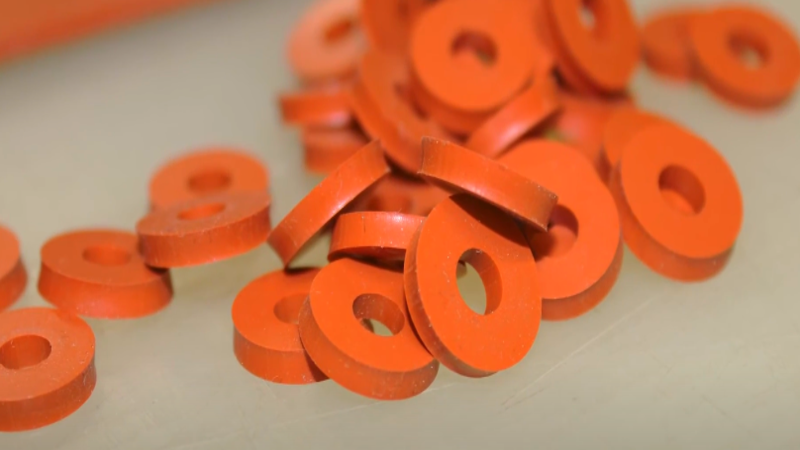

Step 3: Cutting Process (Punching, Perforation, Kiss Cutting)
A die is typically a steel rule that cuts through the material. The cutting tool cuts the material by punching, kiss cut, or perforation. The cutting technique is based on the component requirement.
Step 4: Stripping and Ejection (use of ejection rubber)
Ejection rubber or foam pushes the finished part out of the machine. Excess material is removed by manual or automatic stripping.
Step 5: Finishing & Quality Control
At last, edges are checked for burrs. Dimensional inspection is essential to get high-quality results. Tolerance checking is also critical to ensure the finished product meets specs.
Types of Die-Cutting Machines for Rubber
There are different die-cutting machines available for different applications. Popular die-cutting systems for rubber are:
| Machine Type | Best For | Material Thickness | Speed | Cost Efficiency |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flatbed Die Cutters | Kiss cutting, prototyping | Thin sheets | Moderate | High for small runs |
| CNC Die Cutters | High precision, automation | Thin–medium | High | Excellent for volume |
| Beam Presses | Thick rubber, low runs | Thick sheets | Low | Moderate |
| Digital Slitters | Continuous roll cutting | Thin rolls | High | Efficient |
| Steel Rule Dies | Complex shapes with moderate volume | Medium | Medium | Tooling cost upfront |
| Rotary Die Cutting | High-speed, repetitive patterns | Thin sheets | Very high | Cost-effective for volume |
Rotary die cutting is not always suitable for thicker rubber due to die depth limitations.
Die Cutting Silicone Rubber vs. Other Rubber Types
When choosing a rubber for die-cut silicone rubber excels for its unique properties. It is temperature resistant, flexible, and biocompatible, with weather. It can compress and rebound quickly. Ideal for high-temperature gaskets and medical-grade components.
Every rubber type has distinct abilities suitable for different environments:
- EPDM: It has excellent weather-resistant ability, ideal for weather seals and outdoor use.
- Neoprene: Neoprene rubber resists oil and aging, used in automotive and HVAC.
- Nitrile: Ideal for automotive and oil-resistant applications.
- Natural Rubber: Natural rubber has high elasticity, not suitable for UV exposure.
- Butyl: High gas impermeability, great for sealing.
- Viton: It is a premium rubber that can bear extreme chemical environments.
The selection of rubber depends on the rubber’s abilities and the environmental demands.

When to Choose Silicone Rubber
Silicone rubber is the superior choice if you are designing components to withstand temperatures above 200°C. It remains flexible under compression and does not tear.
Key Factors to Consider When Die Cutting Rubber
Consider these factors when die-cutting rubber:
1. Geometry & complexity
Simple 2D profiles are better to use. For complex drawing patterns, laser or water jet cutting is suitable.
2. Thickness and edge quality
Thinner materials are easy to cut in die cutting. Thicker sheets are not easy to handle and cut cleanly. They can cause tears or deformation if handled wrongly. They also need beam or CNC presses for crisp edges.
3. Required tolerances
Die cutting rubber tolerance is varied based on material elasticity, component size, and tooling. It can affect the dimensional accuracy. Specify RMA tolerance classes where needed.
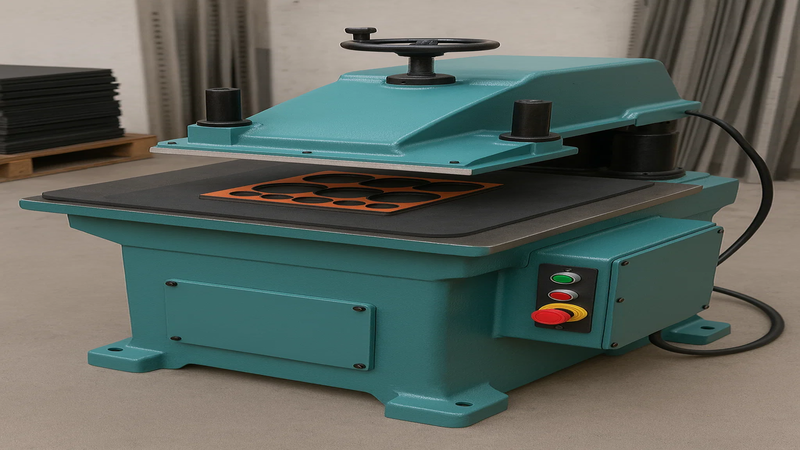

4. Production volume
Die cutting is great for medium to high-volume runs. Use CNC or digital cutting for mass production. For low-volume orders, use flatbed die cutters.
5. Material Performance
Every rubber component is designed for a specific environment. So choose materials based on requirements such as resistance to oil, temperature, chemicals, or abrasion.
6. When NOT to Use Die Cutting
Die die-cutting technique is not suitable if you are dealing with very tight tolerances or a short timeline. Also, avoid it for plastic or very thick materials with 3D features.
Die Cutting vs. Other Rubber Cutting Methods
| Method | Best For | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| Die Cutting | High-volume, 2D parts | Tooling costs, not ideal for 3D |
| Lathe Cutting | Washers, cylindrical seals | Only for symmetrical parts |
| Laser Cutting | Detailed cuts, prototyping | Slow, expensive |
| Waterjet | No heat-affected zones | Costly for large productions |
| Molding | 3D shapes, tight seals | High mold cost and lead time |
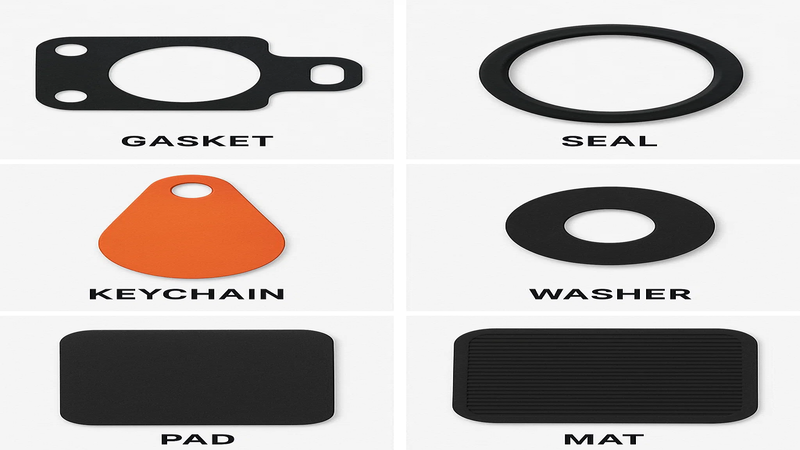
Common Die-Cut Rubber Parts & Use Cases
Die-cut rubber is everywhere. It is used in industrial machines and everyday products for sealing, insulation, and cushioning.
- Gaskets: Rubber gaskets are used to create a seal between two parts of a machine. It prevents leakage of gas and liquid. Commonly used in engines, pumps, and fluid handling systems.
- Washers: Washers are thin, flat rubber parts. It works as a seal or distributes pressure. Essential to use in plumbing, fasteners, and isolation mounts.
- Pads & mats: They are used to control vibration and reduce noise. Also used for safety and to reduce slips in various environments.
- Keychains & promotional items: Die-cut rubber is used to create various promotional and fun items. They are preferred for flexible and colorful branding items.
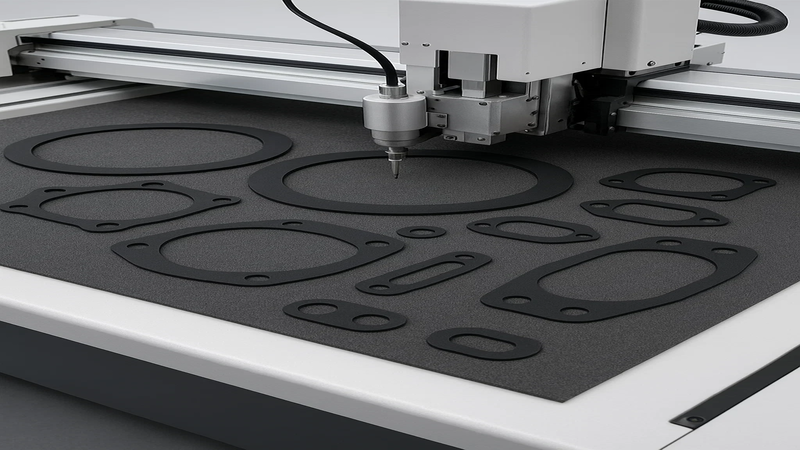

- Rubber seals: Seals control the leakage, provide insulation, and protect from environmental factors. Usually used for automotive door seals, HVAC ducting, and various industries.
- Sheets & custom profiles: Used for sealing, vibration control, insulation, and more. Generally used in automotive, industrial machines, construction, and electronics.
Rubber Die Cutting Tolerances: What’s Achievable?
Rubber die cutting tolerance is based on rubber thickness, hardness, tool wear, and design complexity. Generally, it ranges from ±0.010″ to ±0.030″. For the production of critical parts, consult RMA tolerance charts or request CNC precision.
Design Tips for Engineers (Get Better Die-Cut Parts)
Follow these tips to improve your design and get an optimal die-cutting outcome:
- Keep the component thickness uniform. It helps to avoid material stress and deformation.
- Avoid ultra-thin or unsupported sections that can tear during stripping or use.
- Use internal radii instead of sharp corners. It will distribute stress evenly.
- Optimize nesting layout to reduce scrap and cost.

When Should You Use Rubber Die Cutting?
Rubber die cutting is most effective when you’re working with flat, two-dimensional parts. It can give consistent, repeatable results, which are ideal for components like gaskets, seals, pads, and washers.
This method excels when your part design is simple and the material thickness is within a suitable range of 0.065″ to 0.5″ inches.
Simple shapes which does not include 3D geometries benefit from the precision of steel rule dies. Square or 90-degree edge shapes can be manufactured quickly with minimal material waste.
However, rubber dies cannot be the best fit if your design demands molded radii and irregular 3D profiles. For very thick or compressible rubber materials like foam, die cutting can fall short in accuracy or durability.
In these cases, use alternative methods like molding, waterjet cutting, or CNC machining for better results.
In short, die cutting should be your go-to method when you need fast, affordable, and precise production of flat rubber parts. These rubber cut dies are used in various industries such as automotive, aerospace, HVAC, and medical manufacturing.

Custom vs OEM Rubber Die Cutting: Which Is Better?
The selection of custom vs OEM rubber die cutting depends on the project’s needs. Custom rubber die cutting gives full design freedom, but with upfront tool costs. It is best for branded or function-specific parts.
OEM(Original Equipment Manufacturer) is cost-effective. It is suitable for projects where you need consistency with moderate performance. It is ideal for standard washers, gaskets, or seals.
MOQ(Minimum Order Quantity) depends on whether you choose Custom or OEM. Small businesses should prefer stock tooling initially.
Conclusion
Rubber die cutting turns raw sheets into precise, functional components. It is fast, accurate, and cost-effective, ideal for industrial parts across multiple sectors.
Now that you understand how the process works, ready to plan your next product run or prototype with confidence. Use this knowledge to reduce waste, improve quality, and streamline production.
Need Custom or OEM Rubber Components? Let’s Get Started
We at Hongju Silicone are ready to assist you in delivering exceptional rubber parts for your projects. From providing custom silicone rubber to designing high-quality rubber components, we can handle everything if you want.
You can explore our products page and contact us today for a free consultation to get a perfect solution for your business.
FAQs About Rubber Die Cutting
Q1: Can I die-cut rubber at home?
No, the die-cut rubber method requires a specific machine that cuts accurately. Home methods lack precision, pressure, and you cannot handle the die safely.
Q2: What’s the minimum order quantity?
Minimum order quantity is the number of items a supplier sets to deliver in one order. It can be 100+ items or more. Manufacturers set these requirements for profitability and resource management.
Q3: What thickness can you cut?
Rubber die cutting works best with thinner sheets, usually up to 1/4 inch (6.35mm) or 3/8 inch (9.5mm) thick.
Q4: What’s the turnaround time?
Usually 7–14 days after design approval. Custom tooling, complex product design, and production volume can extend lead times.
Q5: Is die cutting better than laser for rubber?
Die cutting is an efficient and cost-effective way to create high-volume, simple designs. For detailed, complex designs and prototypes, a laser is better.