Let’s unlock a comprehensive guide about prototype production for injection molding. It will help you understand the purpose and types of prototyping, while you can dig deep into the complete part design and material selection process.
Whether you are an injection molder, designer, or product specialist, this guide will offer you the most insights into the exciting world of prototype production for typical injection molding. Let’s begin!
What is Injection Molding Prototyping?
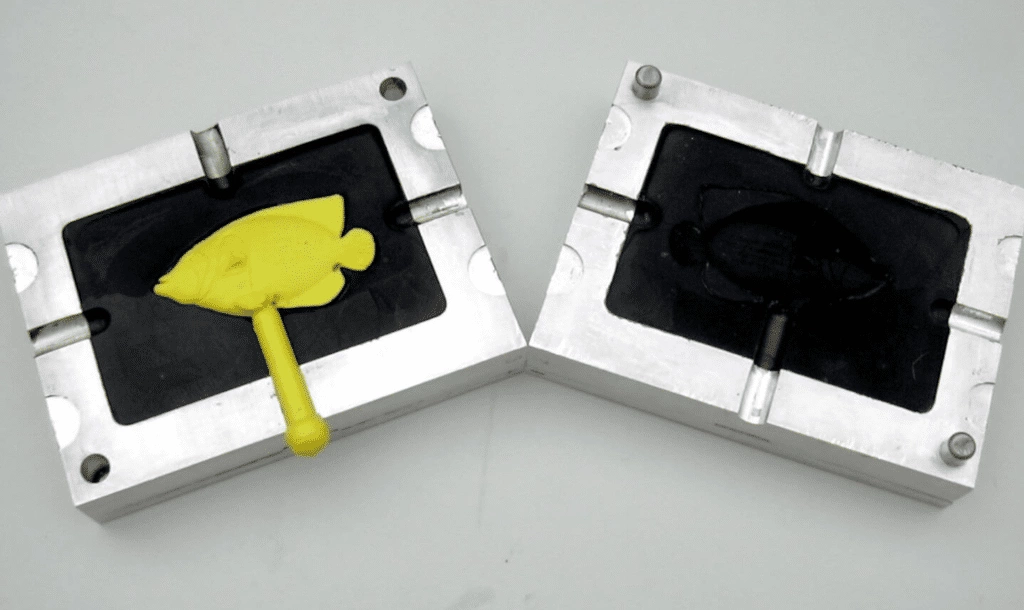
It is creating a preliminary version of part of the product by employing an injection molding technique. Injection molding is a manufacturing process during which molten material is injected into a mold cavity. This material cools and solidifies into the desired shape of the mold. The next step is to remove the plastic part of the mold
Purpose of Prototyping
You may be wondering why you must create a product sample before producing a part or product. Here are some main reasons:
- Testing and Validation
It allows you to test and validate a product’s design, function, textures, and manufacturability. During the test, if manufacturers can find some design flaws or injection molding defects, then they can rectify them before getting into full-scale production.
- Material Testing
Another purpose is to test the behavior and its behavior under different conditions. Manufacturers always need help to choose a suitable material for the finished product. Thankfully, Prototyping helps them choose other materials as a sample and then test their properties.
They can easily find the most suitable material for the final product by comparing different models and materials. It allows for testing other materials and their behaviors under various conditions. This helps in selecting the most suitable material for the finished product.
- Cost and Time Efficiency
You can save your time and money by producing prototypes. If you need to make any design changes, you can do that early. If you don’t create a sample, you may spend more money later on if any injection mold or design changes are needed.

- Market Testing
Before launching any product at an extended level, establishing new product samples is always a good idea. They let you test the market and evaluate the interests of potential customers and stakeholders.
Types of Prototyping
Here are four common types:
- Concept: Whenever you want to evaluate a product’s conceptual design and aesthetic, you create a prototype. They allow you to check the physical appearance and look of a design.
- Functional: You can create this type to test the function of a product in real-world conditions. Manufacturers make them with the material they want for the main product. The end goal is to test the strength, durability, and functionality of a part or a product.
- Presentation: You use high-quality materials whenever you need to use a sample product for presentation, marketing, or investor pitches. The purpose is to make the product highly appealing for display.
- Pre-Production: This type is created before high-volume production. The purpose of this prototyping is testing and validation.
Technique-Based Types
There are two common types of Prototyping Based on Techniques. One is a 3D Printing Prototype, and the second is an injection-molded prototype. Let’s unlock the details of each type one by one.
3D printing
It is a sample product created by utilizing a 3D printing production process. During this process, samples are built layer by layer using a digital model using 3d printed molds.
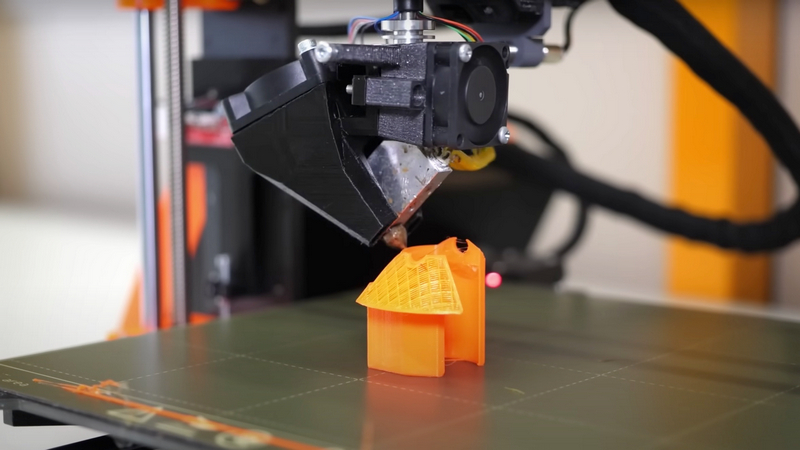
Here are some key benefits:
- It’s pretty tricky to produce detailed complex shapes through traditional manufacturing methods; 3D printing or additive manufacturing process is used to manufacture a sample.
- You can produce 3D samples quickly through this method. This one seems like a good idea when you want to save time in production.
- There is no setup or tooling cost, and it’s an ideal technique to produce small quantities cost-effectively.
Cons
- You can’t test the strength and thermal properties of 3D-printed parts.
- It is not a cost-effective prototyping technique because of slow production speed and high material cost.
- You can’t achieve a precise surface finish with 3D-printed parts.
Injection Molded Sample
It is a traditional method for high-volume products and prototyping. This method injects molten material into a mold cavity, where it cools and solidifies to form a prototype.

Pros
Here are the key benefits:
- It is the most effective technique to test strength and thermal properties.
- This technique is highly cost-effective for large quantities.
- You can produce high-quality samples with exceptional surface finish and fine details with injection molding. There won’t be any need for extensive post-processing.
Cons
Here are some shortcomings of prototypes:
- You need to spend more money first, as it requires you to create molds.
- It’s impossible or somehow challenging to create samples of complex designs through it.
- The lead time of Injection molding is higher than 3D printing because you need time to create the mold and tools.
Injection Molded Vs 3D Printing Parts
| Aspect | 3D Printed Prototype | Injection Molded Prototype |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing Process | It's an additive process, prototype builds layer by layer | It's a subtractive process, using a mold. |
| Design Flexibility | High temperatures can produce complex geometries | Limited by mold design constraints |
| Speed | Quick production of small quantities | At first it's, it's slow due to mold preparation. But, later it's faster for large production. |
| Cost for Low-Volume Production | More cost-effective | Less cost-effective for mold creation |
| Material Properties | Generally weaker than injection molding | Stronger and more consistent |
| Surface Finish | High temperatures can produce complex geometries | High-quality Surface finish, does not require post-processing |
| Cost for Low-Volume Production | Less Cost-Effective | More Cost-Effective |
Take the First Step:
Requst for an Inquire
Quality Meets Affordability. Inquire Now for High-Quality Products at Low Volumes.
What Makes Prototyping Vital?
Here are some reasons that make prototyping essential before committing to extended production.
1. Concept Validation and Refinement
Designers and stakeholders can visualize the products through prototyping. It allows designers to make vital changes and fine-tune a design before manufacturing the final product.
2. Functionality Testing
They make it simple for you to test the product’s functionality. If there are any functional flaws, you can make changes right away. You can prevent costly revisions after production.

3. User Feedback
Prototyping is essential for the survival of new products in the market. You can assess market potential and have an insight through consumer feedback before committing to full-scale production.
4. Cost and Risk Reduction
Prototyping helps manufacturers identify and address risks and flaws in the early development stages. It reduces expensive errors and redesign. Besides, you can manage your resources well by making an informed decision by selecting the suitable material for a part or product.
5. Stakeholder Engagement and Funding
It is the most important thing to have for securing funding from stakeholders. Investors can check the potential and viability of a product through sample products.
6. Regulatory Compliance and Certification
Many times, you need product samples for testing and certification purposes. Regulatory authorities can only review the product and issue the certificate when it complies with industry standards or regulatory requirements.
Designing Prototypes for Injection Molding
Here is a step-by-step process of designing prototypes for injection molding.
Step 1: Prepare Product Design
In the first step, plastic product design is created. A design must be doable. Typically, plastic experts or 3D prototyping experts generate the design by considering proper wall thickness. You must work with design experts or make the most of CAD software to craft a feasible design concept.
Step 2: Product Engineering
Once a design passes functionality standards and is considered doable, it is sent to the production engineering stage. It’s where the material is selected for the prototype, and experts monitor the plastic injection molding process so that if any adjustments are required, they can tackle them readily.
Typically, steel mold is used for plastic prototyping services, and tapered material is used so it can be ejected quickly.
Step 3: Mold Creation or 3D Printing
If you have a complex design, you can tackle it with 3D Printing without creating a mold. However, plastic plates are used in the process of plastic injection molding.
If a design has complicated geometries, you need a new steel tool because more than two halves of the mold will be required. Prototype mold can be made of softer steel than regular injection molding because this material will be easier to carve out.
A complex and relatively expensive test mold is used for simple and small quantity plastic products. Technological advancement has made the process of plastic prototypes simple.
Thanks to mold flow analysis, you can easily see the flow of plastic material into the mold, and it’s not a challenge anymore to determine gate locations. It has become easy to check the gas traps and areas that won’t be filled with material.
Step 4: Take advantage of the Injection Mold Machine
Once the mold is ready, it will be set into the injection molding machine, which is then injected with plastic material.
The molten plastic is injected into the mold and cooled by the water lines. After the cooling process is done, the clamp pressure will be released. The mold opens up, and you can have your plastic design in physical form.
Take the First Step:
Requst for an Inquire
Quality Meets Affordability. Inquire Now for High-Quality Products at Low Volumes.
Materials for Prototype Production
Here are the common materials used:
Different Types of Plastic
Commodity plastic is a cheap option when your design is in the initial stages, and you must create a sample. But its major shortcoming is that it will have different properties than your intended material for mass production.
Engineering plastic costs more than polymers, but they are a good choice for crafting medical device samples. It would help to use the injection molding technique to create samples for the first article inspection. Polyphenylsulfone PPSU is a cost-effective material choice for the production of functional types.
Although you can use engineering plastic material and make a prototype with 3D Printing, remember that this sample will be stronger than the one created with injection molding.
| Aspect | Commodity Plastics | Engineering Plastic |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanical properties | Higher strength, stiffness, and heat resistance.Ideal for low-stress application | Lower strength, stiffness, and heat resistance. Ideal for demanding applications. |
| Cost | Cost-effective, suitable for budget-friendly prototyping | Expensive due to specialized formulations |
| Chemical Resistance | Limited chemical resistance, more prone to degradation due to chemicals and solvents | High chemical resistance, suitable for harsh environments |
| Thermal Properties | Lower melting points, not suitable for high-temperature applications | Higher melting points, Ideal for high-temperature applications |
Steel and Aluminum
Prototype mold can be created with either steel or aluminum. There are many different grades of both materials:
| Aspect | Aluminum | Soft and Semi-Hardened Steel |
|---|---|---|
| Weight | Lightweight, 1/3 of steel weight | Soft, easy-to-machine |
| Strength | Low | High tensile strength, especially in semi-hardened varieties |
| Machinability | Soft, easy to machine | Hard, hard to machine |
| Corrosion Resistance | Natural corrosion resistance without surface treatment | Less corrosion resistance, coatings, and treatments for protection |
| Cost | Less Expensive, cost-effective for lightweight applications | Less corrosion resistance, coatings, and treatments for protection |
- Aluminum: If you want to spend less, aluminum is the right choice. You can use this material when tight tolerances aren’t required in an injection molding project.
- Soft and Semi-Hardened Steel case tight tolerances are required; you can machine steel molds and produce parts with high tolerances, such as within +/-0.001 inches. It would be best to consider soft and semi-hardened steel for sample products, as experts can create a mold with this material in less than two weeks. Although you spend twice as much on semi-hardened steel, it’s worth it when you need to inject molded parts with tight tolerances.
- Hardened Steel: Using hardened steel is always a good idea if you need tight tolerances in prototypes for aerospace, medical, or other demanding applications.
| Aspect | Aluminum Molds | Hardened Steel Molds |
|---|---|---|
| Durability and Lifespan | Easier to machine, let you produce molds fast and more cost-effectively | High durability, long lifespan. Ideal for large-scale production. |
| Machinability | Less expensive, cost-effective for low-volume production and prototyping | Tougher to machine, requires more time and cost for mold preparation |
| Heat Transfer | Excellent thermal conductivity, faster cooling time, and quicker cycle time. | lower thermal conductivity, slower cooling time, and higher cycle time. |
| Cost | High due to machining and material costs. Cost-efficient for high volume production due to the durability factor. | High due to machining and material costs. Cost-efficient for high volume production due to the durability factor. |
Multiple Mold Materials
You can use multiple materials for your mold. For example, create its base with soft steel or aluminum, and then you can make an insert with hardened steel. The choice of material depends on your project requirement, though.
MUD
You can also use master unit die (MUD) inserts, which work well with standard mold frames. The best thing about MUD mold is that it decreases tooling costs by 66 percent. You can use this material when you need a prototype with complex and intricate design patterns.
Take the First Step:
Requst for an Inquire
Quality Meets Affordability. Inquire Now for High-Quality Products at Low Volumes.
When Do You Need Prototype Injection Molding?
When creating a prototype, you can save time with 3D Printing and machining, especially when you have a complex or intricate design to form. But there are many times when you use injection molding prototypes before opting for mass production:
1. Economic
You can produce large quantities of prototypes at high speed with injection molding. When you need to produce more than 30 quantities, you should always go with injection molding as it is more cost-effective than 3D Printing. Spend a little on a sample mold and then replicate as many parts as you need at a lower price than 3D Printing.
2. High Precision

You can’t achieve high precision and a smooth finish with 3D Printing or machining. It’s when you need an injection molded part.
3. Versatility
The injection molding technique lets you try a wide variety of plastics. So, when selecting the suitable material for your product, this technique is better than 3D painting.
Sample parts made via injection molding are highly resistant to wear and tear. Therefore, injection-molded prototypes are widely used for medical testing and clinical trials.
4. Faster Production Time
Typically, prototype molds for injection molding have a single cavity, depending on the design. Thereby, this mold can be produced in one to two weeks.
Once the prototype tool is ready, you can create a rapid prototype with injection molding compared with CNC Machining or 3D Printing. The cycle time is 45 to 60 seconds in injection molding. Therefore, it’s one of the quickest methods of producing prototypes at a large scale.
Take the First Step:
Requst for an Inquire
Quality Meets Affordability. Inquire Now for High-Quality Products at Low Volumes.
Conclusion
Prototype production for injection molding is the most critical part of a successful product development process because it helps you reduce the risk of design or product failures. You enjoy a deep understanding and foresight of materials and methods through prototyping.
Prototype production is essential because it helps you prevent the risk of design failure and lets you refine your vision and test the feasibility and functionality of a product. This initial step of product development saves you from expensive errors and mistakes in the post-production stage.
Make Exceptional Prototypes at a Blazing Speed with Hongju
Hongju experts are specialized in the injection molding process, and we are listed among the well-known injection molding manufacturers. Whether you need a new prototype for market testing, design evaluation, or any other purpose, we will stand by your side every step of the way.
We can bring your design to life through our streamlined prototype injection molding process. Let’s join hands and make your product design an ultimate success!