You won’t have to do any heavy lifting or research because today we are here to offer the ultimate comparison between injection molding and 3D printing. My comprehensive analysis lets you look into every detail from cost to functionality.
Whether you are a manufacturer, designer, or curious mind, my detailed guide Injection Molding Vs. 3D printing will help you make an informed decision. So, let’s get started.
What is Injection Molding?
It is a traditional manufacturing process employed for the high-volume production of intricate and complex parts. In this method, molten material is injected into the mold cavity to create the desired shape. Once the material cools and solidifies, the finished part is ejected by opening the mold.
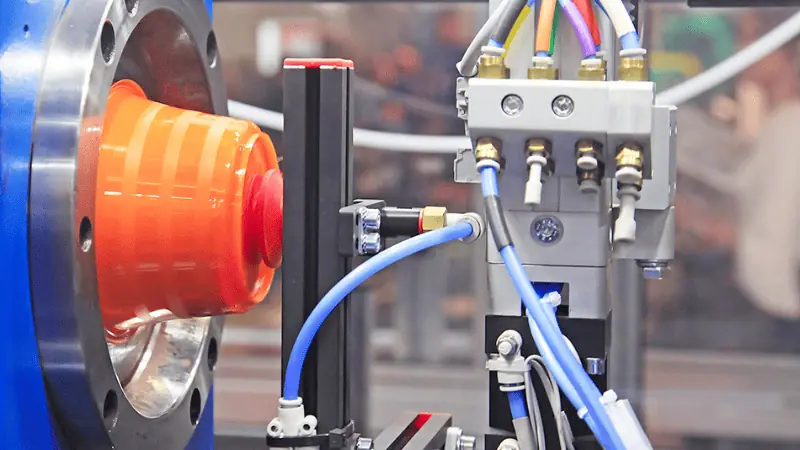
A big plus of plastic injection molding is that it is the most efficient process for large batch production of those parts which require outstanding surface finish and high precision. This additive manufacturing process is quite common for creating consumer goods, medical tools, automotive parts, etc.
What is 3D Printing?
It is an advanced technique used in the manufacturing industry. In this method, a manufacturer can create a three-dimensional object with the help of a digital file. This process is also popular as additive manufacturing.
Typically, traditional manufacturing processes require a manufacturer to remove material from a large piece. But in the case of 3D printing, it’s easy to build an object layer by layer. Therefore, this manufacturing technique is quite suitable for creating complex geometries and structures.
There are many different kinds of 3D printing technologies. For example, manufacturers utilize Fused Filament Fabrication(FFF) where they melt a plastic filament to create different layers. During Selective Laser Sintering (SLS), a manufacturer uses a laser to sinter powder material layer by layer.
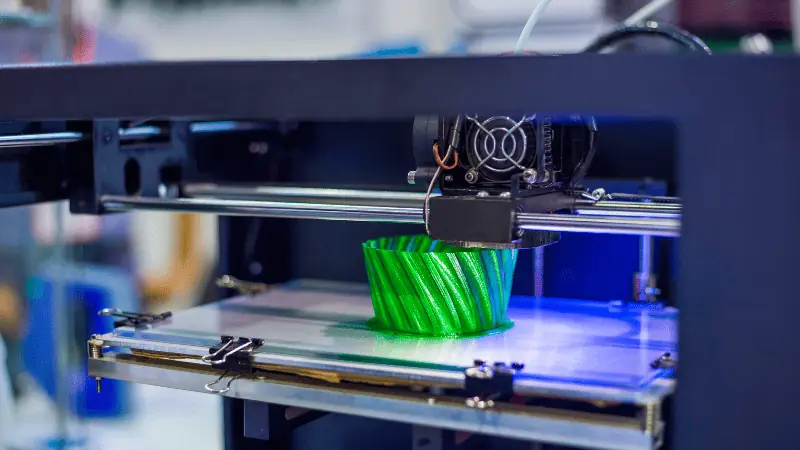

As far as the application of 3D printing in the manufacturing industry is concerned, you will be surprised to see how this method is employed in various applications. The most common uses of this method are custom manufacturing, medical implants, construction, and prototyping.
Key Differences: Injection Molding vs. 3D Printing
Although both techniques are used to create objects, here are some key differences between them:
1. Process
During the injection molding process, melted plastic is injected into a specified mold to achieve a specified shape and size. Once the material is solidified and cooled down, it is ejected. As far as the additive manufacturing process is concerned, it requires no mold. Manufacturers can build an object layer by layer directly from a digital file.
Send Your Inquiry Now!
Quality Meets Affordability. Inquire Now for High-Quality Products at Low Volumes.
2. Cost and Speed
Cost is always a crucial factor in the manufacturing industry. So, when comparing injection molding with 3D painting, it’s vital to look into it.
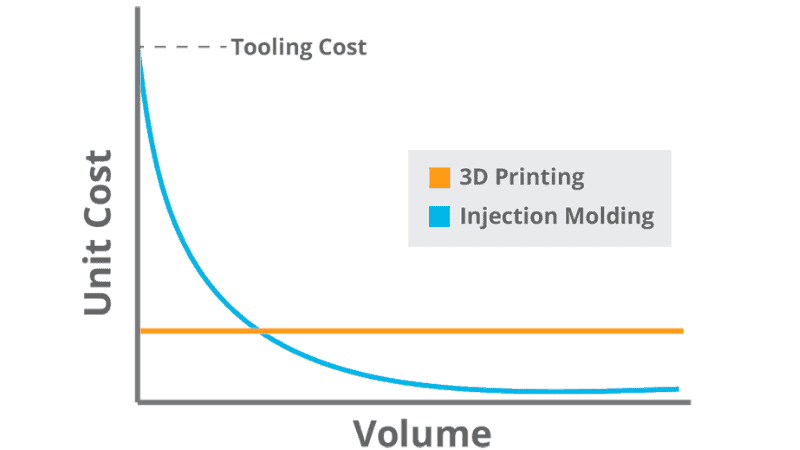
The initial cost of injection molding is high because a manufacturer needs to create a mold. But once the mold is created, you can enjoy lower per unit cost. Therefore, it is considered the more economical option for mass production.
3D printing doesn’t have a high initial cost. Therefore, you can consider this process for small runs or prototypes. However, its per-unit cost is significantly higher than the traditional method.
The next thing to look into is the speed of production. When you want to produce large quantities of an object, injection molding lets you achieve this goal faster than 3D printing.
3. Material Options
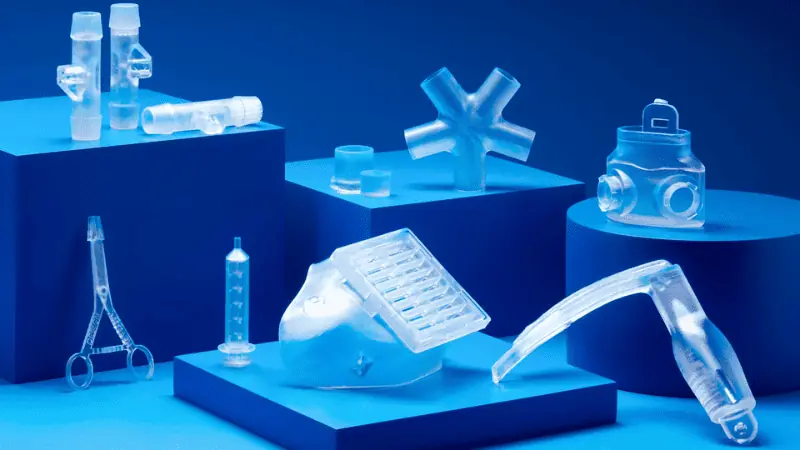

When your project has material diversity such as plastic, metals, ceramics, etc. then you certainly can handle this project well with 3D printing. This advanced technique offers greater material diversity. You can handle limited materials such as metal, glass, plastic, etc. with injection molding.
4. Complexity and Design
3D printing can handle complex design projects effectively because it lets a manufacturer create an object layer by layer without needing any additional molds or tools. However, Injection molding can sometimes struggle with very complex geometries. Undercuts and internal structure are real challenges with this process.
5. Customization
During the injection molding process, the manufacturer creates a mold, and then production begins. Customization becomes limited after mold creation.
On the flip side, you can get custom items with 3D printing because you can change the design in the digital file if you like. There won’t be any need to create new tools or molds.
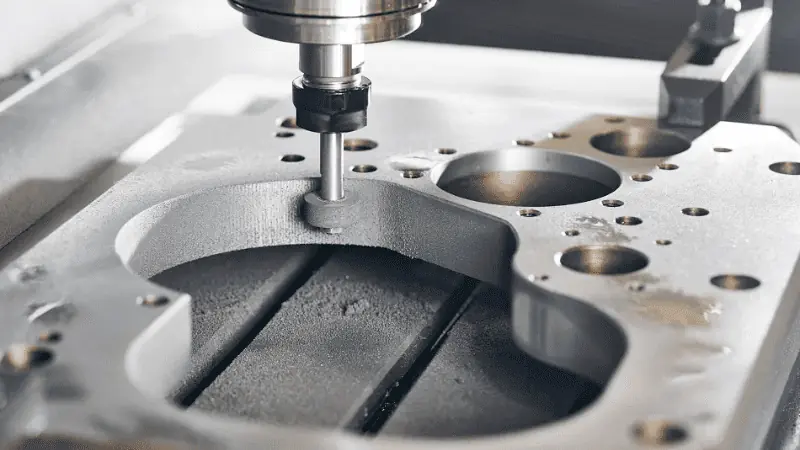

6. Scale and Volume
Injection molding is the best manufacturing technique when a project requires high-volume production. You can handle mass production with utmost speed and low per-unit cost. Contrary to this, 3D printing is a good choice for low to medium-run production.
7. Surface Finish
The surface finish of parts is different in both methods. Normally, the injection molding process brings a next-level surface finish, so you won’t need to go for post-processing. However, 3D-printed parts may have a layered surface finish, so you need to plan a post-processing step to get smooth production results.
8. Application Areas
Injection molding is a traditional manufacturing method used in the mass production of medical devices, automotive parts, and consumer devices.
Send Your Inquiry Now!
Quality Meets Affordability. Inquire Now for High-Quality Products at Low Volumes.
Since 3D printing is an advanced technique with no need for mold, it is an effective process used to create a wide range of applications such as custom manufacturing, architectural models, prototypes, etc.
Core Technologies Explained
Before you know when to use both techniques, it’s a good idea to understand how these processes actually work. So, continue reading and get this info.
How does Injection Molding Work?
Let’s look into this process step by step.
STEP 1 Material Preparation: In the first step, raw material pellets are loaded into the injection molding machine.
STEP 2 Melting: This machine has a heated barrel with a rotating screw that melts the material. The solid material is converted into a molten one.
STEP 3 Injection: The molten material is injected into a mold cavity under high pressure by employing a mechanical system.
STEP 4 Cooling and Solidifying: Once melted material is injected into the mold, water circulation begins around the mold. The purpose is to cool down the molten material. This cooling process solidifies the material that takes the shape of the mold.
STEP 5 Ejection: In this step, the mold opens to remove the injection molded parts.
STEP 6 Post-Processing: In this step, excess material is trimmed off. If a part requires additional finishing, then it will be executed as needed.
STEP 7 Cycle Repeat: The mold closes again and the whole process is repeated for the creation of the next unit.
How Does 3D Printing Work?
Here is a step-by-step guide to the 3D Printing process:
STEP 1 Design: The first step of this process is the creation of a digital design. A designer uses CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software to create a design. Once the design is finalized, its digital file is downloaded.
STEP 2 File Conversion: The downloaded digital file is converted into a format that a 3D printer supports.
STEP 3 Slicing: Specialized software is used to slice the 3D model into thin layers. The purpose here is to define a complete roadmap for printers to follow.
STEP 4 Printer Setup: In this step, a designer will prep the printer by calibrating the print bed and loading the material.
STEP 5 Printing: Printing begins, and the printer will create the object layer by layer.
STEP 6 Monitoring: These days, advanced printers offer real-time monitoring. You can check external computers from time to time. If there is any error or issue during printing, you can fix it right away.
STEP 7 Post-Processing: After printing is done, the post-processing stage begins. It requires you to remove the support structure and cure so that the material solidifies.
STEP 8 Quality Check: Once the injection is ready, the quality check begins. The purpose of inspection is to ensure that the object is made according to specified quality standards.
Send Your Inquiry Now!
Quality Meets Affordability. Inquire Now for High-Quality Products at Low Volumes.
When to Use 3D Printing vs. Plastic Injection Molding
It’s time to know about all those scenarios when you can use these techniques.
When to Use 3D Printing?
You can use the 3D printing technique when you:
- Are in the product development phase. Therefore, you need to create different versions of a prototype. 3D printing will help you develop multiple iterations with minimal setup cost.
- Need to deliver small batches or customer orders. This process makes this specific production run quite cost-effective. Since you don’t have to spend money on expensive mold creation.
- Have a project with complex designs such as geometries, internal structures, and undercuts. It becomes easy to handle complexities with 3D printing.
- Have to deliver customized or personalized products.
- Plan to do material testing. It becomes easy for you to test different materials with 3D printing.
- Have a tight deadline for the initial production run or prototype. It will be easier to meet this requirement quickly with the 3D printing method.
When to Use Plastic Injection Molding?
You can use plastic injection molding when you:
- Need to create thousands and millions of identical plastic parts. This process will help you achieve economies of scale.
- Have to deliver consistent quality.
- Are handling a project that needs specific mechanical properties of a material, such as temperature resistance, high tensile strength, etc.?
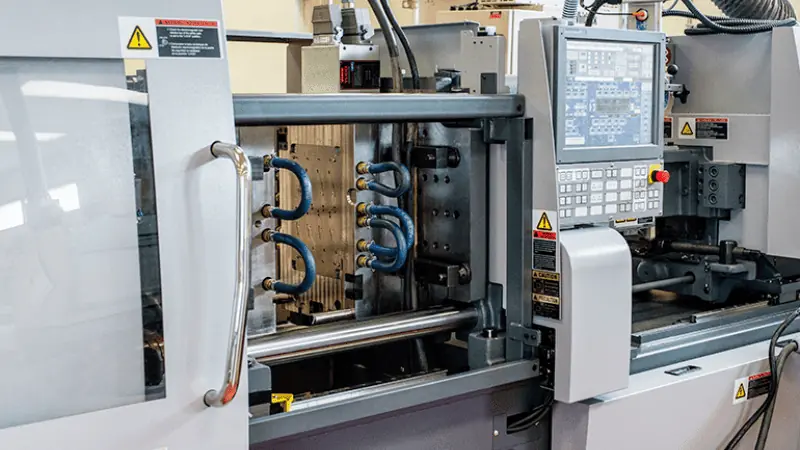

- Want to reduce labor costs for large runs? Once you set up the injection molding machine, it is easy to manage the whole operation.
- Need a smooth finish of the product parts.
- Are you looking for an efficient production run? After its initial setup, this technique lets you produce parts more quickly than 3D printing.
- Need to achieve economies of scale. The per-unit cost drops when you increase the production volume, making it an ideal option in mass production.
Cost Factors
When looking into 3D printing vs. Injection molding, it’s common to think about the cost factor. Are you wondering which method is cost-effective? Well, it is time to take a quick look at the cost factors of both processes.
| Upfront Cost Factor | Injection Molding | 3D Printing |
|---|---|---|
| Design | The initial mold creation cost is high. | A license cost is required for CAD software or advanced slicing software. |
| Machinery | Specialized injection molding machines are required. | The cost of a 3D printer is high |
Generally speaking, the Material cost is cheaper in bulk with injection molding, but it varies from one material to another. Once you are done with the mold setup, labor costs are reduced. If you go for high-volume production, then you can achieve a low per-unit cost.
However, when you go for 3D printing, the Material cost is expensive per unit. You need to incur high labor costs for setup, monitoring, and post-processing. Cost doesn’t decrease when you produce a large volume. The cost of each item remains the same.
| Hidden Cost Factor | njection Molding | 3D Printing |
|---|---|---|
| Maintenance | Regular printer maintenance cost increases over time. | Reqular printer maintenance cost increases over time. |
| Customization | Any change to the design requires additional mold cost. | None |
| Operational Cost | Post-processing cost is high because it requires curing, painting, and smoothing the printed object. | Regular printer maintenance cost increases over time. |
3D Printing vs Injection Molding- Which One is Cost-Effective?
Injection molding is cost-effective when you need to produce a high volume of objects. The initial cost of the project will be amortized over a large number of units. It’s how you will be able to enjoy lower per-unit costs.
On the other hand, when you have a customized or complex design project, you can achieve cost-effectiveness by going with the additive manufacturing process. The low setup cost and flexibility will outweigh the higher per-unit cost in the small production run.
Send Your Inquiry Now!
Quality Meets Affordability. Inquire Now for High-Quality Products at Low Volumes.
How to Choose: Injection Molding or 3D Printing?
Do you want to choose between 3D printing and injection molding techniques? If yes, then here are some considerations you need to make:
1. Project Volume
You should choose injection molding for high-volume production. It’s when you can easily offset high upfront costs with low per-unit costs.
Unlike injection molding, 3D printing will be an ideal choice when you need to run low to medium-volume production, especially with a rapid prototyping project.
2. Design Complexity
Another thing to look into is the design of the product. If a product has a simple design, you can achieve economies of scale with injection molding. This process isn’t ideal for complex design because intricate shapes require multiple molds and manual assembly. As a result, costs will increase.
3D printing lets you handle complex designs without any challenges because you won’t have to spend money on additional tools or molds.
3. Material Requirements
Always choose the injection molding process for a project with a specified material like high tensile strength plastic. You may have fewer material options with this entire process but it will help you achieve top-quality results.
In case your project involves diverse materials, such as ceramics, resins, and other specialties, then you should opt for 3D printing.

4. Time Constraints
When you need to deliver a prototype or initial production quickly, you can achieve this goal with 3D printing. Mold creation is a time-consuming process, and you can’t speed up the initial run. However, when you need to deliver a high volume of products, then certainly the molding process is quicker than 3D printing.
5. Budget
The Initial cost of injection molding is higher than a 3D printer. But when you need to produce large quantities of an object, the former method is more cost-effective.
6. Customization Needs
In case a project requires customization, always go with 3D printing. Because injection molding has limited flexibility for design changes or personalized design.
7. Environmental Considerations
When you are concerned about the environment, an advanced technique like 3D printing is your best mate. In this process, material is added to the structure only when needed. Injection molding, on the other hand, produces more waste due to excess material from each run.

You can evaluate all these factors carefully and decide what method to choose. It’s also a good idea to consult with experts to get detailed insight into your business needs.
Conclusion
Finally, you have explored the ultimate comparison -Injection molding vs. 3D Printing. When it comes to making a choice, you should know that there isn’t a one-size-fits-all scenario.
You need to consider many different factors, such as design complexity, project volume, budget, and other considerations. Certainly, both methods have their advantages and drawbacks. There is a need to compare them with utmost care and consideration.
Call to Action
Are you still unsure whether injection molding or 3D printing is the right choice for you? If yes, then it’s time to speak with one of Hongju‘s experts. Now you can get personalized advice tailored to your specific manufacturing needs.
We are always here to make that happen for you. Contact us and take your manufacturing to the next level.