In the world of medical devices and equipment, the choice of materials is critical. Silicone and Thermoplastic Elastomers (TPE) are two widely used elastomers that are characterized by their versatility and suitability for a range of medical applications.
In this blog post, we will delve into the key attributes of TPE and Silicone, comparing their strengths and weaknesses to help you make informed decisions when it comes to selecting the ideal elastomer for your medical projects.
What is a Thermoplastic Elastomer?
These TPE resins are characterized by their smooth blend of thermoplastics combined with elastomers, like the fusion of two polymers. Elastomers are the steadfast types; they stay put after they’re molded. But then, you’ve got super flexible thermoplastics like the gymnasts of the polymer world.
What makes TPEs seriously cool is that they last longer and are way more versatile than other materials. It’s like having the rubber’s resilience and plastic’s adaptability rolled into one!
What is Thermoplastic Elastomer Made of?
It is a fusion of plastic and rubber. It’s like a dynamic duo of polymers, one being the tough plastic and the other the flexible rubber. These two materials combine their powers to create a material that’s both strong and stretchy. So, in simpler terms, a thermoplastic elastomer raw material is a cool blend of plastic and rubber.
Thermoplastic Elastomer’s Melting Point
Thermoplastic Elastomer material injection molded and gets all comfy between 260-320 degrees Celsius, which is their sweet spot. If you crank up the heat beyond 150 degrees Celsius, TPE injection molding starts to throw a tantrum, getting all wrinkly and crackling with age.
What is Silicone?
Silicone, or polysiloxane, is super flexible and can handle crazy extreme and high temperatures too. It’s a champ against flames, won’t cause allergies, and doesn’t mess with chemicals. Think of silicone rubber as the bouncy superhero sidekick, made of a mix of silicon and organic stuff.

Silicone can’t handle steam, certain fuels, strong acids, or tricky chemicals. You’ll spot this versatile material in Hearing aid parts, ear tips-buds, or Respiratory masks. It is used for non-leaching uses as well.
What Material is Silicone Made of?
Silicone is man-made and can be a bit of both plastic and liquid silicone rubber parts. You can use silicone liquid injection molding, hard stuff, and squishy things. Silicon is an element, like a super-basic building block of stuff, while silicone is a big, fancy molecule that’s all about repeating patterns.
Silicone’s Melting Point?
It doesn’t melt, but it sure knows how to handle extreme heat well! When things get hot (around 200-450 degrees Celsius), the silicone molding and manufacturing process starts feeling a bit less flexible and turns a tad brittle. So, silicone’s comfort zone is between 200 and 300 degrees Celsius.
Why TPE and Silicone are Preferred for Medical Applications?
Why do doctors love using TPE materials and silicone in medical stuff? Well, here’s the lowdown in simple terms:
Take the First Step:
Requst for an Inquire
Quality Meets Affordability. Inquire Now for High-Quality Products at Low Volumes.
- Body-Friendly: the TPE materials and silicone don’t mess with your body. No weird reactions or immune system tantrums when they touch your insides.
- Super Bendy: They bend and stretch, which is perfect for medical gear like seals, tubes, and catheters.
- Chemical Toughness: They work well enough against most chemicals anyway. The cleaning staff in hospitals? They can handle it without losing their powers due to chemical resistance properties.
- Built to Last: TPE and the silicone material can take a beating, even from repeated sterilization, and still keep going strong.
- Easy to Shape: TPE and silicone can be used for injection molding lSR into all sorts of shapes and designs for medical gadgets.
- Allergy-Proof: Silicone won’t make your sensitive skin or allergies act up.

- Heat-Proof: Silicone and TPE are temperature resistant, can handle high temperatures, and are perfect for super-hot sterilization.
- See-Through Magic: Silicone can become invisible, which is great for medical tubes.
Real-World Applications in Medical Devices
Healthcare facilities are like a toolbox filled with different rubbery wonders. Two of the top picks are TPE and Silicone, and they’re chosen because they’re super clean, don’t leak much weird stuff, and get along famously with our bodies.
Now, let’s meet some of the medical devices that owe their existence to these rubbery heroes:
Medical Silicone Rubber
Imagine a material that’s like a chameleon but in a good way. Medical silicone rubber is just that. It’s cool with our bodies, doesn’t throw a fit when it gets hot or cold, and can be injection molded out into all sorts of shapes for medical gadgets. You’ll find it in things like airways, balloon catheters, and even fancy surgical instruments and handpieces.
Gloves
Remember those latex gloves doctors wear? They’re made from natural rubber – the kind that comes from trees. There are non-latex gloves made from elastomers, too. They’ve got your hands covered.
Implants and Prosthetics
Implants and prosthetics save the day when your body needs a helping hand. These are made from special elastomer plastic materials that can bend and flex.
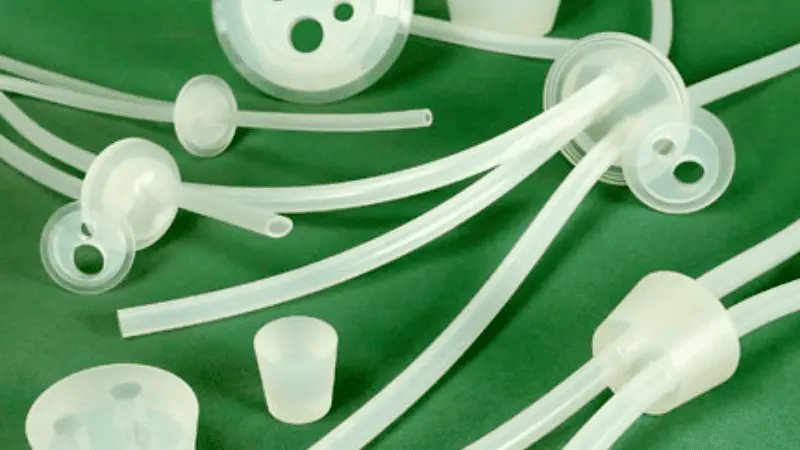
Medical Tubing
Medical tubing is used for all sorts of things, and lately, elastomers are making a big splash in this field. They’re FDA-approved, easy to keep squeaky clean, and they’re kind to the environment. Plus, they’re super slippery, clear, and see-through.
Take the First Step:
Requst for an Inquire
Quality Meets Affordability. Inquire Now for High-Quality Products at Low Volumes.
Syringe Gaskets
Have you ever wondered how your syringe doesn’t leak all over the place when you push the plunger? Well, you can thank elastomers for that. They make gaskets that snugly seal the syringe so no medicine escapes where it shouldn’t.
Oxygen Masks
Let’s talk about oxygen masks. They’re made from elastomers, too, and these materials are great because they’re super stretchy. This means the mask can mold comfortably to your face, making sure you get all the oxygen you need.
Head-to-Head: TPE vs. Silicone
Here’s a head-to-head comparison of TPE and Silicone based on key factors:
Mechanical Properties
- TPE: Offers a wide range of hardness options and has good tear resistance and elasticity. Suitable for various applications.
- Silicone: Known for its exceptional flexibility and elongation properties, maintaining these features over a wide temperature range.
Heat Resistance
- TPE: Generally less heat resistant, softening at lower temperatures around 100-150°C.
- Silicone: Outstanding heat resistance, capable of withstanding temperatures from -40°C to 230°C or higher.

Cost
- TPE: More cost-effective due to easier and less expensive manufacturing processes.
- Silicone: More expensive, largely because of the complexity of its manufacturing process and higher raw material costs.
Ease of Manufacturing
- TPE: Easy to process with standard thermoplastic manufacturing methods, no curing required.
- Silicone: Requires more complex manufacturing, including curing, which can increase production time and costs.
Chemical Resistance
- TPE: Good chemical resistance, but may not be as inert as silicone.
- Silicone: Highly chemically resistant, making it suitable for applications requiring this property.
Biocompatibility
- TPE: Can be formulated to be biocompatible for medical and food-contact applications.
- Silicone: Widely recognized for its biocompatibility, used extensively in medical and food-grade applications.
Durability
- TPE: Good durability, although long-term performance may degrade due to environmental factors and UV radiation.
- Silicone: Known for long-term durability and stability, even under harsh conditions.

Beyond Mechanical Properties: Sealing and Sterilization
When it comes to making sure medical devices are safe and work as they should, choosing the right materials is super important. Two popular picks in the medical world are Thermoplastic Elastomers and Silicone. Let’s break down their various sealing properties and sterilization superpowers:
Sealing
TPE: TPEs are great at sealing because they can bend and squeeze into all sorts of shapes, making them perfect for medical tubing, gaskets, and O-rings.
Silicone: Silicone is the most powerful in terms of heat resistance and sealing. It can create a rock-solid seal even when things get super hot or cold. It’s the go-to for implantable medical devices and important medical equipment gaskets.
Sterilization
TPE: Thermoplastic rubber can handle various methods, like gas, radiation, and steam, but the specifics might vary depending on the exact type of TPE and what’s mixed into it.
Silicone: Silicone laughs in the face of autoclave steam and is best buddies with gas and radiation methods. It can handle being sterilized over and over without breaking a sweat, making it a top pick for devices that need frequent cleaning.
Choosing The Right Materials: TPE vs. Silicone
LSRs and TPEs – two different materials with perks. Picking the right material for one? Well, it’s like choosing a car: it depends on your ride, your wallet, and how fast you wanna go!
When is LSR the Best Choice?
When you’re in a hot-and-cold situation, LSR is the superstar. It can handle pressure molded in both scorching and chilly environments. This makes LSR the top choice for pressure-sensitive gigs, like medical devices that deal with fluids, fancy surgical gear, and health gadgets.
It’s skin-friendly, so there’s no need to worry about irritation when using it in stuff like respiratory devices and those cool glucose-monitoring wearables. It’s got a whole bag of tricks, like making duckbill valves, hearing aid parts, and even baby bottle nipples.
The uses of liquid silicone rubber, LSR, are not limited. Liquid silicone rubber has many medical applications, such as:
- Duckbill valves, membranes, and diaphragms
- Hearing aid parts/ear tips-buds
- Respiratory masks
- Baby bottle nipples / Pacifiers
When are TPEs the Best Choice?

Now, when you want to save some bucks and still get good performance, TPE is your choice. It’s cheaper than LSR and plays well with heat – it can handle a bit of a hot temper.
You’ll find TPE in things like baby bottles, bottle caps, and even impact-resistant gizmos. It’s also a smart pick in the medical world, especially for gloves. Plus, it’s recyclable, which is Earth-friendly.
Depending on your requirements, uses of TPEs include items such as:
- Baby bottles
- Bottle caps
- Closure liners
- Seal rings
- Seals
- Impact-resistant devices and component housing
If you start throwing in things like plasticizers, anti-oxidants, and processing boosters, you might end up with some extra volatile stuff that you don’t want. Especially if your gizmos are going into medical gadgets and sciency stuff, you have to keep a close eye on those levels.
Safety and Regulatory Considerations for TPE and Silicone

Creating safe medical devices with materials like Thermoplastic Elastomers and Silicone is no simple feat. Here are the key things to keep in mind in the TPE and Silicone injection molding and manufacturing process:
- Biocompatibility Check: Ensure that the materials won’t make your body throw a fit. We follow ISO 10993 rules to be sure.
- Material Detective Work: Investigate the chemical makeup and purity of the materials.
- Germ Warfare: Make sure these materials can stand up to common sterilization methods. We don’t want any nasty surprises.
- Material’s Longevity: Check if they can go the distance without falling apart. We want materials that can keep up with the marathon, not sprinters.
- Hidden Chemicals Alert: Investigate if these materials have any secret chemical interactions with our human body or other drugs.
Take the First Step:
Requst for an Inquire
Quality Meets Affordability. Inquire Now for High-Quality Products at Low Volumes.
- Follow the Rules: We have to stick to the rules set by the FDA (in the U.S.) or the EU MDR (in Europe). There’s paperwork and tests involved, just like any medical industry or other serious business.
- Risk Management: Identify and tackle any potential risks that might come with using these materials.
- Quality Control: Keep up the good work by following ISO 13485. It’s like maintaining your gear – always in top shape.
- Market Watch: Even after our product is out there, we need to keep an eye on it.
Conclusion
In conclusion, when it comes to choosing elastomers for medical applications, TPE and silicone are two fantastic options, each with its strengths.
Remember, TPE offers versatility and cost-efficiency, while silicone boasts excellent resistance and biocompatibility. So, the next time you’re designing a medical device or product, weigh these factors carefully.
Transform your Medical Device Business with Hongju’s Specialized Material
Hongju is a trusted name in the medical industry for producing eco-friendly silicone products. Whether you’re developing surgical instruments, diagnostic equipment, or implantable devices, Hongju’s expertise and innovative materials can elevate your product’s quality and functionality.
Contact us now and get a free consultation for your needs. Our team is ready to support your project with customized solutions, fast turnaround times, and reliable performance every step of the way.