With the aid of advanced molding machines and expert craftsmanship, these silicone molds come to life. Their ability to withstand extreme conditions makes them a go-to choice across industries.
So why settle for anything less than top-notch quality when it comes to your custom molded rubber products and parts? Explore the fascinating realm of rubber moldings today!
Understanding Different Types of Rubber Molding Processes
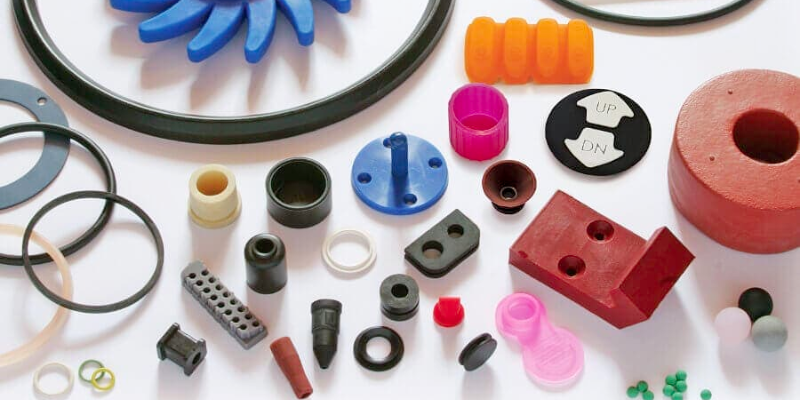

Rubber molding is a manufacturing process in which a rubber compound is pressed or injected into a mold, creating a custom-shaped part with excellent characteristics such as high-temperature resistance, excellent durability, high abrasion resistance, and more.
Rubber moldings are widely used in various industries for their flexibility, durability, and ability to withstand extreme conditions. The general act of creating a custom molded rubber or silicone product requires a mold to be made from scratch. Depending on the method used, the rubber mold itself will be made differently.
There are three main types of rubber molding processes: injection molding, transfer molding, and compression molding. Each process has its own advantages and is suitable for different applications.
Injection Molding
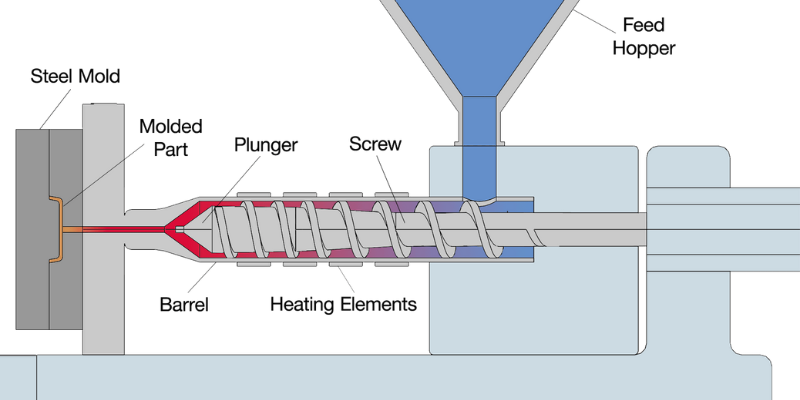
Injection molding is a widely used rubber molding process that involves injecting molten rubber into a mold cavity under high pressure.
This process offers several benefits, including high production efficiency, precise control over the final product’s dimensions, and the ability to create complex shapes with intricate details. Injection molding is commonly used for mass production of rubber parts such as seals, gaskets, and O-rings.
In the injection molding process:
- The raw rubber material is heated until it becomes molten.
- The molten rubber is then injected into a closed mold cavity.
- The rubber cools down and solidifies inside the mold.
- The mold opens, and the finished product is ejected.
Transfer Molding
Transfer molding is another popular method for producing rubber moldings. This process involves placing pre-measured amounts of cured and uncured rubber into a chamber called a pot or plunger assembly. The assembly then transfers the material into a heated mold cavity where it undergoes curing.
In transfer molding:
- A pre-measured amount of uncured rubber is placed in a pot or plunger assembly.
- Heat softens the material inside the chamber.
- Pressure forces the softened material to flow through channels into the heated mold cavity.
- Curing takes place as heat causes vulcanization (cross-linking) of the rubber.
- The mold opens, and the finished product is removed.
Compression Molding
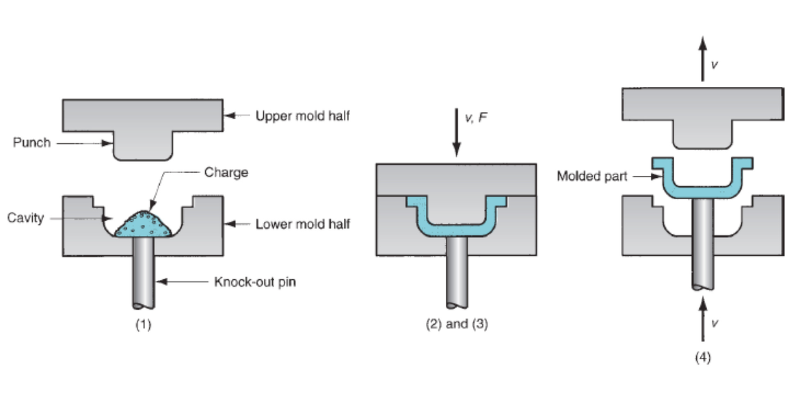
Compression molding is a versatile rubber molding process that involves placing pre-measured amounts of uncured rubber into an open mold cavity. The mold is poured and then closed, and heat and pressure are applied to the mold to release from the shape and cure the rubber.
In the compression molding:
- Pre-measured amounts of uncured rubber are placed in an open molding cavity.
- The mold closes, applying heat and pressure to shape the material.
- Curing occurs as heat causes vulcanization (cross-linking) of the rubber.
- The mold opens, and the finished product is extracted.
Choosing the Right Rubber Molding Process
When choosing a suitable rubber molding process, several factors should be considered, including complexity, volume requirements, and cost considerations.
Custom rubber molding, especially, custom rubber injection molding, is a very popular choice with customers because, while it is more costly than standard molding, custom molding is still less expensive than alternative rubber manufacturing methods.
Injection molding is ideal for high-volume production runs with complex designs, while transfer molding offers faster cycle times and minimal flash formation. Compression molding is a cost-effective option for low-volume production or larger parts with simpler designs.
Exploring the Advantages and Disadvantages of Rubber Moldings
So far, we have discussed three different kinds of rubber molding processes. To keep things simpler, we will discuss each rubber molding process’s advantages and disadvantages separately.
Injection Molding
Injection molding is a widely adopted technique that involves injecting molten rubber into a closed mold under high pressure. This process allows for fast production cycles due to its ability to fill complex molds with precision.

Advantages
- Fast production cycles: The high-pressure injection ensures quick filling of the mold cavities, resulting in shorter cycle times.
- Enhanced accuracy: The controlled injection process allows for precise control over material flow, ensuring consistent dimensions and accurate replication of intricate details.
- Resistance properties: Rubber injection molded products exhibit excellent resistance to heat, chemicals, and wear.
Disadvantages
- The injection molding machines have high maintenance costs
- The whole production setup also requires more expensive injection molding machines and tools
- Injection molding allows limited design capabilities on the device as well as the finished product
Transfer Molding
Transfer molding utilizes a plunger system to force the rubber into the mold cavity through channels. This method provides precise control over material flow and is often preferred when intricate designs or specific material placement is required.
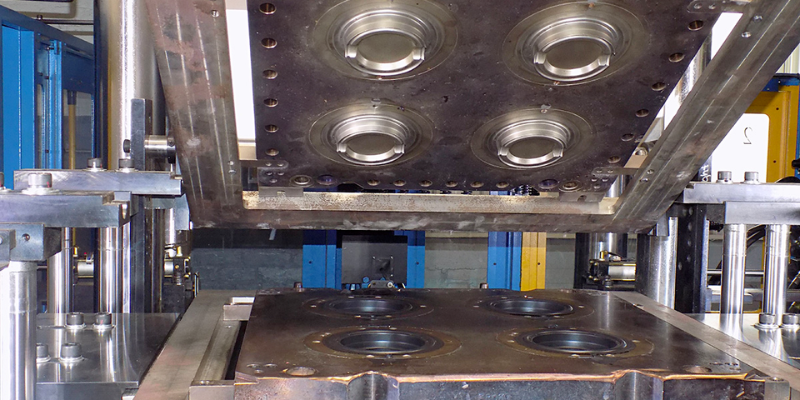

Advantages
- It is more consistent and accurate as compared to compression and injection moldings
- The use of multiple cavities in transfer molding takes less time compared to compression molding
Disadvantages
- The transfer molding process leads to a lot of waste.
- Transfer molding tools require high maintenance since they need time for removal and resetting
- Designing precise molds can cost a lot
Compression Molding
Compression molding involves shaping preheated rubber directly in the mold cavity using heat and pressure. It is a versatile technique suitable for both simple and complex designs.
Advantages
- Cost-effective for low-volume production runs.
- Suitable for large parts with simple designs.
- Can accommodate various types of rubber compounds.
Disadvantages
- The finished products aren’t as consistent as in injection molding
- The whole process is time taking
Some Common Uses of Rubber Moulded Products
Rubber products are widely used in various industries for their versatility and reliability. From gaskets and seals to hoses and bushings, rubber moldings find numerous applications in a wide range of fields. Let’s explore some common uses of these rubber-molded products.
Fluid Sealing Applications
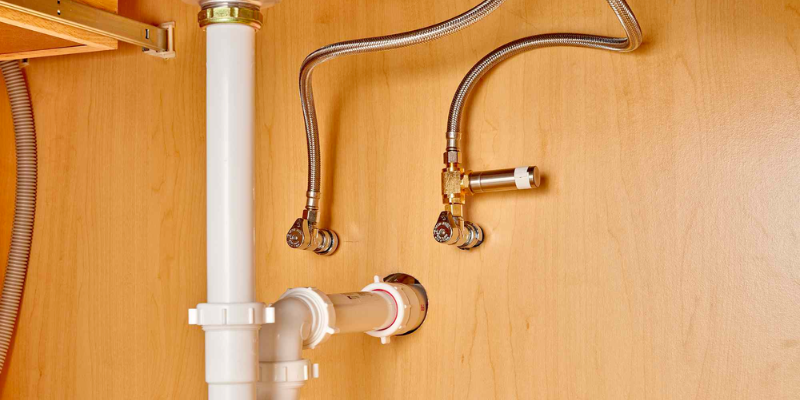

Rubber molded products such as gaskets, seals, and O-rings play a crucial role in fluid sealing applications. These custom molding components are designed to prevent leakage and ensure tight seals in systems that handle liquids or gases.
Whether it’s an industrial pipeline or a simple household plumbing system, rubber moldings provide effective sealing solutions. Their flexibility allows them to conform to irregular surfaces, creating a reliable barrier against leaks.
Automotive Industry
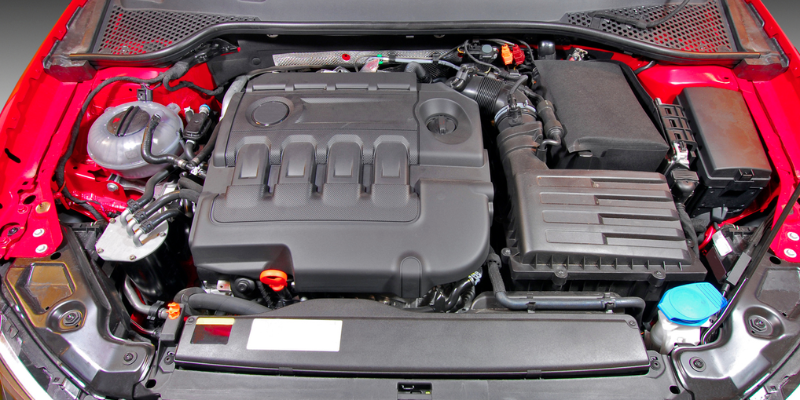

In the automotive industry, rubber molded parts find widespread use due to their unique properties. Hoses, bushings, mounts, and other rubber components are employed for various functions ranging from noise reduction to vibration isolation.
For example, rubber hoses facilitate and protect the flow of fluids like coolant or fuel within the vehicle’s engine. Rubber bushings help absorb vibrations between different car parts, enhancing ride comfort and reducing wear on mechanical components.
Electrical Industry
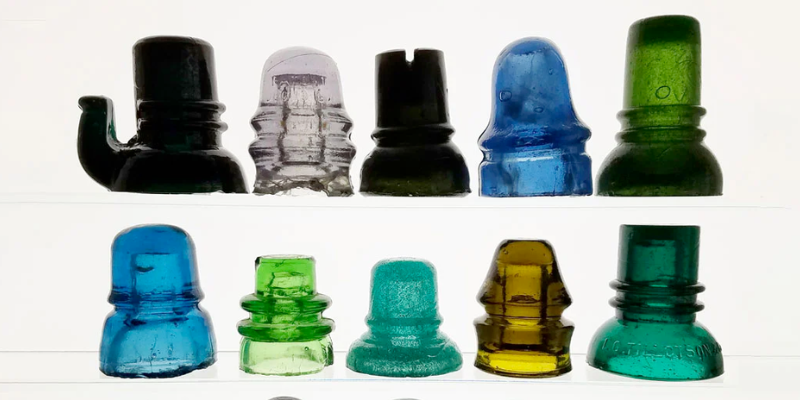

The electrical industry heavily relies on rubber molded components for their excellent electrical insulation properties. Insulators made from rubber materials are essential for protecting electrical wires and cables from damage caused by contact with conductive metal surfaces or air. Rubber connectors also play a vital role in joining electrical circuits and wire together securely while preventing short circuits or electric shocks.
Other Applications
Apart from the aforementioned industries, there are several other areas where rubber moldings find application:
- Medical Sector: Rubber moldings are used extensively in medical devices such as catheters, syringes, and surgical instruments due to their biocompatibility.
- Consumer Goods: Rubber is utilized in everyday consumer goods like kitchen utensils (e.g., spatulas), toys (e.g., rubber ducks), and various household items.
- Food Industry: Rubber moldings are employed in food processing equipment to ensure hygienic and safe operations. They can be found in seals, gaskets, and conveyor belts used in food production facilities.
Choosing the Right Rubber Material for Moldings
Selecting the right rubber material is crucial. Different rubber materials possess varying properties such as hardness, temperature resistance, chemical compatibility, and elasticity.
Considering factors like application requirements, environmental conditions, and budget will help you choose the appropriate rubber material for your project.
Understanding Rubber Materials

There are several common rubber materials used in moldings, each with its own unique characteristics:
- EPDM (Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer): EPDM is known for its excellent weather resistance and durability. It can withstand extreme temperatures ranging from -40°C to 120°C (-40°F to 248°F) without losing its elasticity. This makes it suitable for outdoor applications such as automotive weatherstripping and window seals.
- Nitrile (NBR): Nitrile rubber offers exceptional oil and fuel resistance, making it ideal for applications involving contact with petroleum-based substances. It also exhibits good compression set properties and works well in sealing applications where resistance to abrasion is required.
- Silicone: Silicone rubber has a wide temperature range of -60°C to 230°C (-76°F to 446°F), making it suitable for both high and low-temperature environments. It provides excellent electrical insulation properties and is commonly used in electrical connectors, gaskets, and medical devices.
- Neoprene (CR): Neoprene is a versatile synthetic rubber that offers good resistance against ozone, sunlight, oxidation, and chemicals. Its temperature range varies from -45°C to 115°C (-49°F to 239°F). Neoprene is often used in industrial applications where moderate oil resistance is required.
- Natural Rubber (NR): Natural rubber exhibits high tensile strength and tear resistance while maintaining flexibility over a wide temperature range (-50°C to 80°C / -58°F to 176°F). It is commonly used in applications that require vibration isolation, such as engine mounts and conveyor belts.
Considerations for Choosing Rubber Materials

When selecting the appropriate rubber material for your moldings, it’s essential to consider the following factors:
- Application Requirements: Determine the specific performance characteristics required for your application. Consider factors such as flexibility, durability, resistance to chemicals or oils, and temperature range.
- Environmental Conditions: Evaluate the environmental conditions in which the rubber moldings will be exposed. Take into account factors like temperature extremes, UV exposure, moisture levels, and potential contact with harsh chemicals.
- Budget Constraints: Consider your budget constraints while choosing a rubber material. Some materials may be more cost-effective than others while still meeting your application requirements.
By carefully considering these factors and understanding the properties of different rubber materials available, you can confidently select the right rubber material for your moldings.
Whether you opt for liquid silicone rubber used for EPDM for its weather resistance or neoprene rubber blend for moderate oil resistance, choosing the appropriate material ensures optimal performance and longevity of your rubber trim moldings.
Conclusion
In conclusion, rubber moldings offer customers a wide range of benefits across various industries. By understanding the different molding processes available and considering factors such as material selection and international shipping options, you can ensure the successful implementation intended application of rubber moldings for your specific needs.
Get Top-Of-The-Line Products From Hongju
Still unsure about rubber molding? Talk to our experts at Hongju Silicone. We are professional rubber molding experts with years of experience in the industry. Contact us if you’re ready for a mix of adventure, professionalism, and reliability for your custom rubber parts.
Send Your Inquiry Now!
Quality Meets Affordability. Inquire Now for High-Quality Products at Low Volumes.