Whether you are a designer or a manufacturer, there is a need to understand the plastic thermoforming process, like what materials are used, how many types of this process are out there, what different choices of material are available for tooling, and much more.
By the end of this article, you will have a solid grasp of this process. So, let’s dive in and uncover the secrets behind this essential technique together!
Basics of Plastic Thermoforming
What is plastic thermoforming? It is a versatile method for shaping plastic pallets into different forms. This technique is helpful in crafting simple and complex designs. Thereby, this technique is applied in a multitude of industries from automotive to packaging, and beyond.
The biggest plus of this process is that it’s quite cost-effective for creating large and complex parts. It’s easy for you to craft both simple and complex shapes with it. If a project requires customization, you can meet and exceed this project’s requirements via this method effectively. Besides, it allows manufacturers to do quick prototyping.
As far as the application of this process is concerned in different industries, it’s good to know that this method is widely used in producing components for automotive interiors, manufacturing packaging goods, crafting displays, etc. Even this process makes it easy to produce medical device enclosures.
This process is flexible and efficient. Its adaptability and cost-effectiveness make it an ideal choice in modern manufacturing.
Types of Thermoforming
Here are the most popular types of thermoforming you should be aware of:
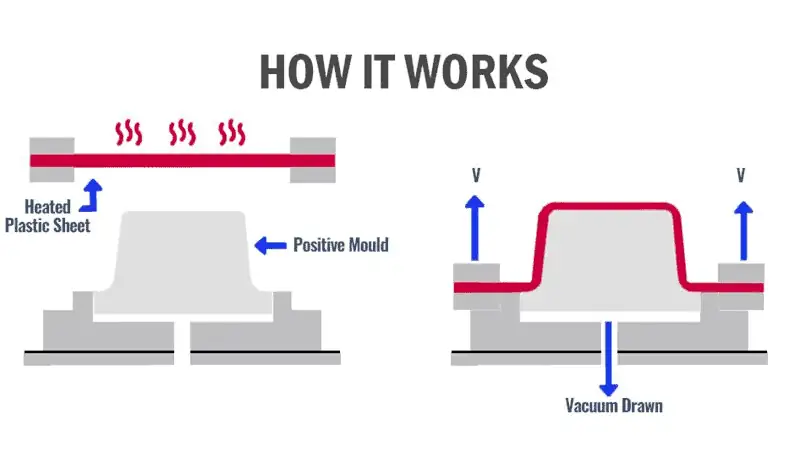
Vacuum Forming
Vacuum forming is the most commonly used thermoforming technique in producing bulk items like product packaging, custom-made signs, and trays.
In the vacuum forming process, a heated plastic sheet is set over a mold, and then a vacuum is applied to draw the sheet tightly against the mold surface. As a result, the desired shape of plastic is created.
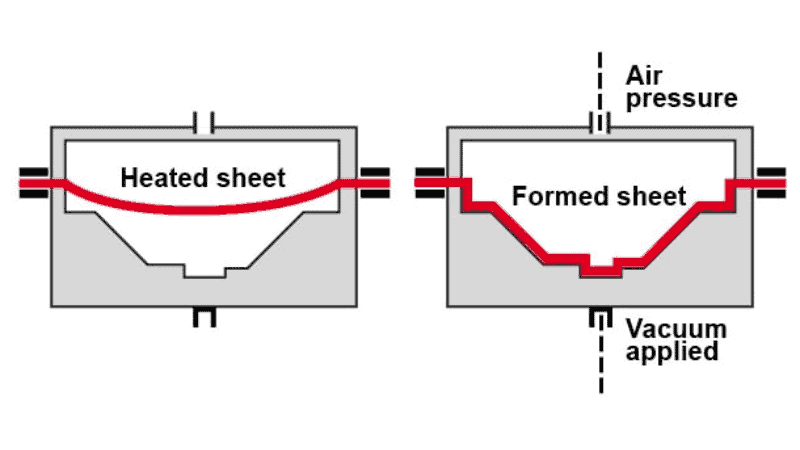
Pressure Forming
Another name for this technique is pressure thermoforming, which is used for different industries manufacturing parts such as electronics, aerospace, and automotive.
In the pressure forming method, the heated extruded plastic sheet is placed in a pressure box and positioned over the mold. It is similar to vacuum forming but with an additional step where compressed air pressure is applied over the sheet against the mold.
The pressure forming method is super effective in the creation of intricate shapes with greater detail.
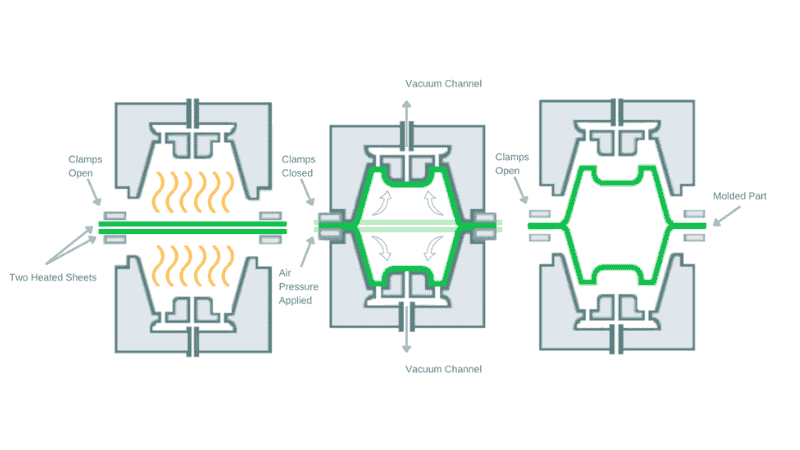
Twin Sheet Thermoforming
As the name explains a bit, this technique involves heating and forming two plastic sheets at the same time. These sheets are fused together to form a rigid plastic hollow, three-dimensional structure.
This process is widely used for creating storage containers, medical equipment housing, and automotive components.
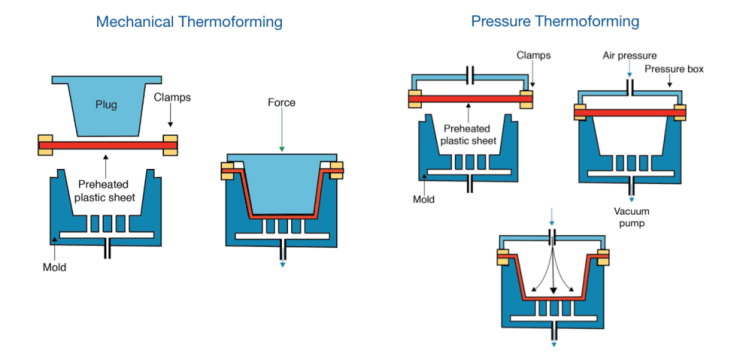
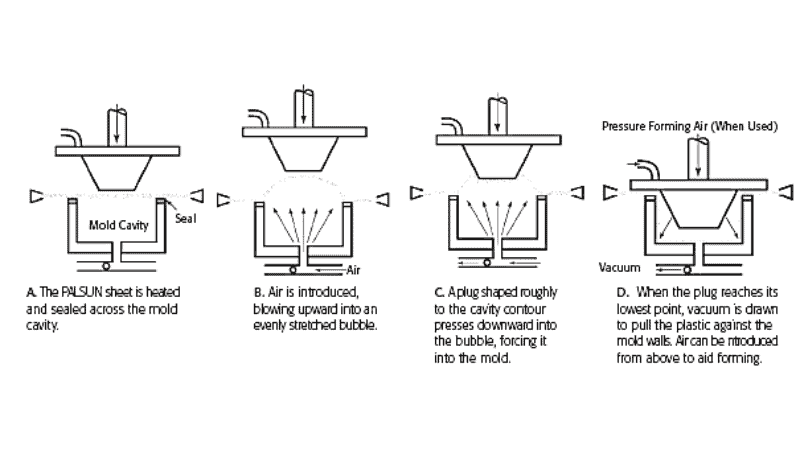
Plug Assist Forming
When it comes to producing complex and contoured-shaped objects such as appliance components, interior panels, and intricate packaging design, this type of plastic thermoforming is the best option.
In this process, a plug is used to help shape the heated plastic sheet into a complex and contoured shape.
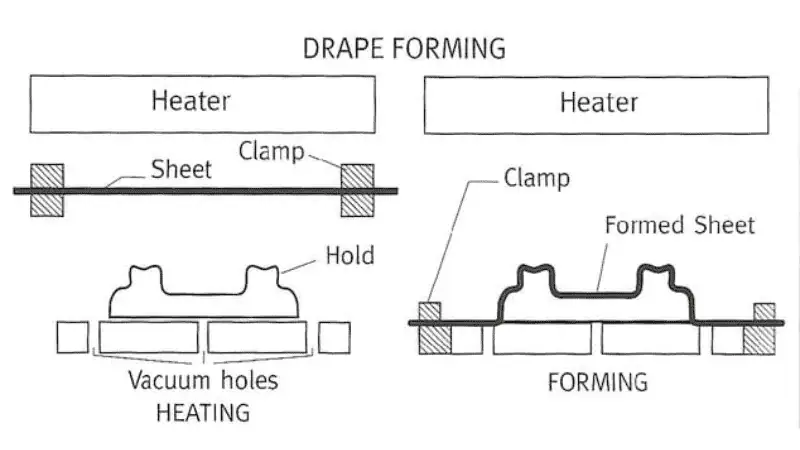
Drape Forming
It is the simplest type of thermoforming process. Its common applications are disposable food containers and interior trim components. In this process, the heated plastic sheet is draped over the mold to create shallow, gently curved items. Shapes are created without using any pressure or vacuum.
Send Your Inquiry Now!
Quality Meets Affordability. Inquire Now for High-Quality Products at Low Volumes.
Materials Commonly Used in Thermoforming
This versatile process can be used with a wide range of plastic materials, such as:
- ABS: It stands for acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene. When your project is all about automotive parts, consumer goods, and electronic enclosures then you can go with ABS. Because this material contains top-level durability and impact resistance properties.
- Polystyrene: It is a good choice for packaging, disposable tableware, and medical care because of its ease of thermoforming and clarity properties.
- Polyethylene: PE is a versatile material that is available in different forms such as high-density polyethylene (HDPE) and low-density polyethylene (LDPE). This material is employed to create containers, toys, and packaging.
- Polypropylene: This lightweight and durable material is commonly used in plastic thermoforming for the creation of consumer goods, automotive components, and packaging.
- Polyvinyl Chloride: This material is applied in producing construction materials, signage, and packages because of its top-level rigidness and chemical resistance.
- Polycarbonate: It is a suitable material option for safety shields, eyewear, and medical devices due to its optical clarity and impact resistance properties.
- PET: The common application of Polyethylene Terephthalate is food packaging, thermoformed tray, and food packaging. Because this material possesses properties of recyclability and transparency.
- Acrylic: This is a common material used for plastic thermoforming. It is known for UV resistance and optical clarity. Thereby, the common applications of acrylic are display cases, lighting fixtures, and signage.
- Polyurethane: PU offers flexibility and resistance to abrasion and chemicals. It’s used in automotive interior components, footwear, and protective gear.
- High-Impact Polystyrene: Due to its enhanced impact resistance, HIPS is commonly used to manufacture interior trim of automotive and point-of-purchase displays.
Applications of Plastic Thermoforming

Plastic thermoforming has diverse applications due to its flexibility, low cost, and ability to produce both simple and complex shapes. Let’s dig into some common applications of plastic thermoforming methods in different industries.
1. Consumer and Food Packaging
In the packaging industry, plastic thermoforming is commonly used to create various packaging items such as cosmetics, toys, and electronics. You can manufacture high-quality products such as trays, food clamshell containers, and blister packaging items with this technique as well.
2. Automotive Industry
This process is used to create both internal and external parts in the automotive industry. For example, you can manufacture wheel covers, body panels, bumpers, dashboard door panels, and trim pieces through it.
3. Medical Equipment
In the medical equipment industry, plastic thermoforming is used to create products that hold medical devices. It is also used to produce housing and enclosures for medical equipment to maintain hygiene and durability.
4. Aerospace
In the Aerospace industry, thermoforming is used to create lightweight and durable interior panels, while it is also employed to craft cabinets, galley components, and storage bins.

5. Retail and Point of Purchase (POP) Displays
When it comes to boosting the visibility and sales of your product, display matters a lot. It’s good to know that thermoforming helps you craft custom displays as per your product shape.
This process is used to create POP displays in retail superstores and supermarkets to showcase products properly.
6. Electronics
In the electronics industry, this process is employed to create plastic accessories for electronic gadgets. For example, smartphone cases and keyboard covers are usually thermoformed.
Besides, this technique is helpful in producing protective enclosures of electronic devices to ensure that they remain durable and functional for a long time.
7. Recreational and Sports Equipment
It’s unsafe to go cycling, motorcycling, or skiing without using a helmet. So, when it comes to creating safety equipment, thermoforming plays a big role. It is used to create helmets and golf club heads.
Watercraft parts need top-notch strength and buoyancy. Fortunately, thermoforming is here to create solid kayak shells and paddleboard decks.
8. Construction and Building Materials
The Aesthetic appeal of architectural design depends highly on decorative elements and panels, which are thermoformed. This technique is employed to manufacture diffusers and covers for light fixtures as well.
The Process of Plastic Thermoforming
It’s time to explore the step-by-step process of Plastic thermoforming below:
Step 1- Material Selection: In the first step, you need to pick an ideal thermoplastic material. Several factors affect the choice of material, such as project requirements, application, budget, and required properties.
Step 2- Heating the Plastic Sheet: Once you select the material, the next step is to place the selected plastic sheet in either the oven or a heating chamber. It is heated to a specific temperature until it becomes pliable but not melted. Pliable forming temperature varies from one material to another.
Step 3- Placing the Mold: A mold for the thermoforming process is made of materials like aluminum, wood, or composite material. Once the plastic is heated, mold is positioned inside the thermoforming machine. Generally, the mold has the inverse shape of the desired final product you need.

Step 4- Forming the Plastic: Once the plastic sheet has reached its specified temperature, it is transferred to the forming station. The sheet is placed over the mold and then different types of plastic thermoforming are used to shape it.
Step 5- Cooling the Formed Parts: Once the shape is all set, the formed parts are cooled to solidify. The cooling process is quite important because it ensures that plastic maintains its desired form. The cooling process may involve fans, water jets, or other cooling methods.
Step 6- Removing the Formed Product: The final products are removed from the mold. The removal process can be manual or automatic.
Step 7-Trim Station: It is a step to create a specific shape. So, if there is any excess plastic material or flash around the material, then it is trimmed through an automated trimming machine or cutting tools to get the desirable finished shape.
Step 8- Quality Control: The final product undergoes a quality check process to ensure that it meets the specifications and standards. The purpose of this check is to ensure that it has a surface finish and dimensional accuracy.
Step 9- Packaging and Distribution: If a product passes the quality control process then it is ready for packaging and distribution.
Send Your Inquiry Now!
Quality Meets Affordability. Inquire Now for High-Quality Products at Low Volumes.
Tooling Options for Thermoforming: Fiberglass vs. Wood
Before you start the thermoforming process, you need to choose between two common tooling options used for the methods such as Fiberglass and wood. Each material has its specific advantages and disadvantages. A quick comparison will help you choose the right tool as per your project requirements.
| Feature/Aspect | Fiberglass | Wood |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | High: Resistant to wear and tear | Moderate: Can wear over time |
| Detail Resolution | High: Can capture fine details | Moderate: Less detailed |
| Weight | Moderate to heavy | Light to moderate |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Low to moderate |
| Thermal Conductivity | Moderate | Low |
| Life Span | Longer lifespan | Shorter lifespan |
| Surface Finish | Smooth, can be glossy | More porous, may need sealant |
| Maintenance | Low: Requires less upkeep | Higher: Needs regular care |
| Lead Time | More porous, and may need sealant | Shorter, easier to machine |
| Suitability for Prototypes | Often preferred for production runs | Good for prototypes |
Fiberglass tooling for thermoforming boasts durability and fine detail capture, ideal for consistent production runs. However, it’s pricier and has longer lead times.
Wood, being more affordable and faster to machine, is great for prototypes but lacks the durability and precision of fiberglass. In choosing between the two, considerations should be made based on the project’s scale, budget, and desired output quality.
Challenges and Limitations of Plastic Thermoforming
Just like any other process, Plastic thermoforming has certain challenges and limitations. It’s time to uncover all those challenges and limitations below.
- Material Restrictions
The biggest limitation of the plastic thermoforming process is that it is only limited to thermoplastic, which can be heated or formed repeatedly. You can’t employ Thermosetting plastics for this process because they don’t soften when heated.

- Thickness Variability and Limitations
This method is suited for producing parts with consistent thickness. However, it will be a big challenge for you to achieve uniform thickness in complex or deep-draw parts as variations may occur
- Precision and Detail Compared to Injection Molding
When you compare plastic thermoforming with injection molding, you realize that it’s a challenge to achieve good tolerances and precision with it. So, if your project requires tight tolerances and complex geometers, then injection molding is the best option.
Whenever you need to replicate fine details and intricate surface texture or undercuts in complex parts, you can’t do that with thermoforming; only injection molding helps you create intricate patterns and finish in this scenario.
- Tooling Costs and Lead Times

You need to spend high on mold development for thermoforming, especially when you use fiberglass material as a precise tool. When you have a tight project deadline with a large and intricate mold, you may find it hard to meet the deadline. It’s because the fabrication of tooling for intricate models has high lead times.
- Limited Material Options for Certain Applications
Certain industries or applications need specialized material, thermoforming process can not be used there.
- Size Limitations
Some thermoforming equipment has size limitations as well. So, when a project involves large and complex parts that exceed the size capabilities of equipment then you need to go for other manufacturing processes such as large-scale injection molding or rotational molding. You need very large production machines to meet the requirements of big items.
Send Your Inquiry Now!
Quality Meets Affordability. Inquire Now for High-Quality Products at Low Volumes.
Conclusion
Finally, you have explored an illuminating journey of plastic thermoforming with a clear picture of this versatile manufacturing process, its diverse options, its high-volume applications, and even available tooling options.
The key takeaway of this guide is to help you understand the basics of plastic thermoforming such as what is plastic thermoforming, and how it is a cost-effective method for shaping tons of products in various industries.
The adaptability of plastic makes it a star player in the plastic thermoforming process as you can mold it to either simple or complex shapes.
Why go to Hongju for your Thermoforming Manufacturing needs?
Do you want to harness the power of plastic thermoforming for your next project? If yes, you should schedule a consultation with Hongju‘s experts, who will help you revolutionize your manufacturing process.
Contact us now and let our technology to improve your business well. It’s time to discover how plastic thermoforming can elevate your product design while improving overall performance and reducing costs. You can unlock Innovation with Plastic Thermoforming.