As you embark on this journey, you’ll grasp the essence of cooling channel design, learn about the impact of coolant flows, and unravel the significance of mold temperature in ensuring top-notch plastic injection mold outcomes.
Join us as we unveil the nuances of injection molding machines and the pivotal role cooling plays in the manufacturing process.
What Is the Cooling System in Injection Molding
If you’ve ever marveled at the precision and consistency of plastic products, from everyday items to specialized components, there’s a good chance you’ve seen the handiwork of the injection molding process. But behind those polished products is a critical phase that doesn’t often get the limelight: the cooling system.
Now, you might wonder, why is the cooling phase so pivotal? Here’s the scoop: after the molten plastic is injected into the mold cavity, it needs to cool and solidify into the desired shape. It’s during this phase that the cooling system comes into play.
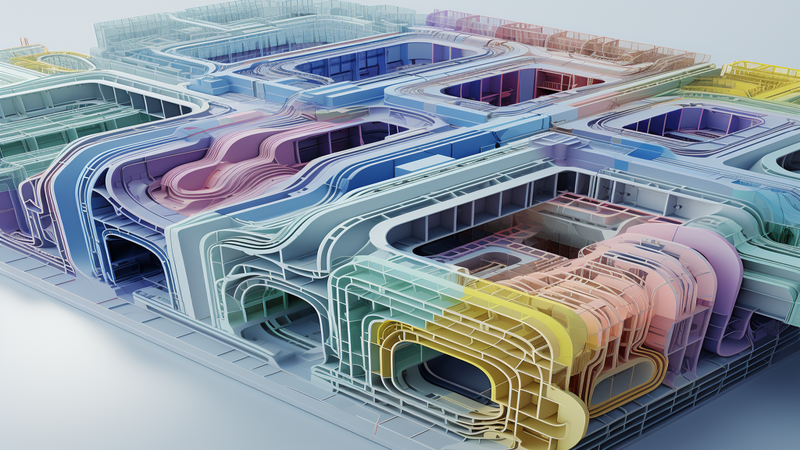
Comprising cooling channels through which a coolant flows, the system efficiently draws heat away from the molded part. The effectiveness of this cooling process dictates the quality, dimensions, and finish of the injection molded parts.
To put it in perspective:
- Proper cooling ensures reduced cycle time, translating to faster production rates.
- It mitigates defects like warping deformation and sink marks, ensuring the integrity of the finished product.
- A well-designed cooling channel optimizes temperature distribution, pivotal for the product’s structural strength.
In essence, the cooling system in injection molding isn’t just about chilling; it’s about precision, efficiency, and quality assurance in the manufacturing process.
Inquire About Our Silicone and Plastic Products!
Components of the Cooling System in Injection Molding
When it comes to plastic injection molding, the cooling system plays a pivotal role in ensuring the consistency, efficiency, and quality of the final product. But have you ever wondered what makes up these intricate cooling systems? Let’s break it down:
- Cooling Channels: These are the veins of the cooling system, guiding the cooling medium throughout the mold. Strategically designed and positioned, these channels ensure uniform cooling, preventing product defects and ensuring a faster cycle time.
- Cooling Medium: This is the lifeblood that flows through those channels. The most commonly used media are water and air. The choice of medium depends on the specific requirements of the molding process, with each offering its unique advantages.
- Heat Exchangers and Chillers: Acting as the heart of the system, heat exchangers and chillers manage the temperature of the cooling medium. They efficiently dissipate the heat absorbed from the mold, ensuring the medium remains at the desired temperature.
- Pumps and Flow Regulators: Think of these as the regulators of our system. They control the pressure and flow rate of the cooling medium, ensuring it reaches every nook and cranny of the mold uniformly.
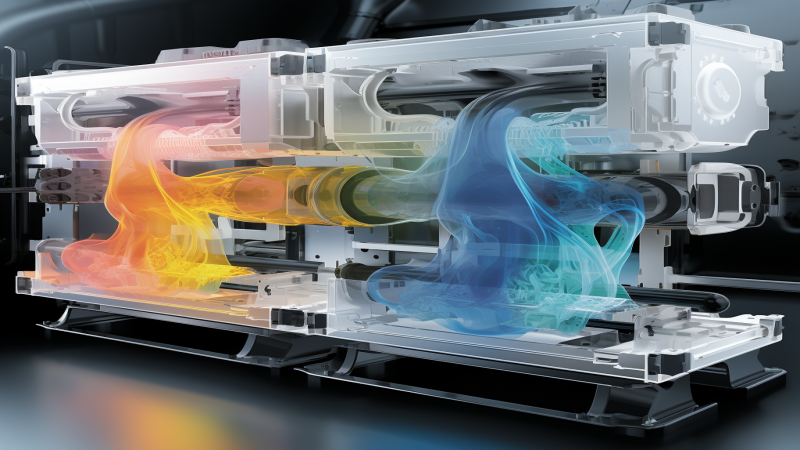
Each component, though distinct in function, works harmoniously to ensure the mold cools down efficiently and uniformly. The next time you hold a perfectly molded product, remember the symphony of these components that played a part in its creation.
Different Types of Injection Mold Cooling Systems
The art of injection molding hinges heavily on the choice of cooling system employed. If you’ve ever pondered over the mechanics of it, you’d know there are primarily two contenders in this arena: air and water cooling systems. Let’s demystify these for you:
Air Cooling System in Injection Molding
Among the diverse cooling methods employed in the injection molding process, the air cooling system stands out for its unique approach. As the name transparently suggests, this system harnesses the potential of air, typically in a compressed or forced state, as its principal cooling medium within the injection mold cooling process.
Strengths:
- Air’s inherent characteristics offer several advantages. Its lower density, compared to water, remarkably diminishes the possibility of mold corrosion. This ensures a more extended mold lifespan, a crucial aspect when considering long-term manufacturing investments.
- The simplicity of the air cooling system is another undeniable merit. It offers a relatively straightforward cooling system setup, which, in turn, translates to reduced maintenance hassles. This can be particularly beneficial for manufacturers who prioritize ease of use and maintenance in their injection molding service.
Drawbacks:
- However, every coin has two sides. Air, despite its benefits, falls short when it comes to heat conduction efficiency, especially when juxtaposed with water. Consequently, the cooling times under this system can be extended.
- This elongation in cooling duration might impede the desired production rate, especially in high-demand scenarios.
Water Cooling System in Injection Molding
This system, a popular choice among many manufacturers, leverages water’s intrinsic properties. It adeptly circulates water through the designated cooling channels within the injection mold, ensuring optimal temperature distribution.
Strengths:
- Water’s prowess as an outstanding heat conductor is universally acknowledged. This property ensures prompt cooling and fosters accelerated injection molding cycles. For manufacturers chasing deadlines, this rapidity can be a game-changer.
- Water’s versatility is another commendable trait. It effortlessly accommodates a spectrum of additives, enhancing the cooling efficiency manifold. This adaptability can be a boon in scenarios demanding customized cooling solutions.
Drawbacks:
- Yet, water cooling isn’t devoid of challenges. One glaring concern is the potential for mold corrosion, especially if there’s any laxity in maintaining water quality. Such corrosion can compromise the integrity of the injection mold, leading to subpar finished products.
- The water cooling system, while efficient, demands a comprehensive infrastructure. The water in cooling lines can be chemically treated to avoid mold and bacterial growth as well as waterline pollution. However, this includes the integration of pumps, intricate heat exchangers, and chillers, which can elevate the initial setup costs.
In the realm of injection molding, the choice between air and water cooling systems isn’t black and white. It’s a nuanced decision, pivoting on specific manufacturing needs. Whether it’s the allure of rapid production cycles or the charm of minimal maintenance, understanding these cooling systems’ intricacies is paramount.
Such knowledge empowers manufacturers, allowing them to tailor their injection molding service, ensuring a harmonious blend of efficiency and product quality.
Inquire About Our Silicone and Plastic Products!
Comparison between Air and Water Cooling Systems
Selecting the right cooling system for injection molding can seem daunting. But, by comparing the two primary systems side-by-side, the choice becomes clearer. While both air and water cooling systems have their respective merits, understanding their differences is crucial to optimize molding processes.
| Criteria | Air Cooling System | Water Cooling System |
|---|---|---|
| Efficiency | Moderate (due to air's lower thermal conductivity) | High (water rapidly conducts heat) |
| Setup Complexity | Simpler (fewer components needed) | Complex (requires pumps, chillers, etc.) |
| Maintenance | Lower (less prone to corrosion) | Higher (regular water quality checks needed) |
| Cooling Speed | Slower (due to lower efficiency) | Faster (efficient heat conduction) |
| Cost | Generally lower initial costs | Might be higher (due to complex setup) |
| Lifespan of Mold | Longer (less corrosion risk) | Can be shorter (if water quality isn't maintained) |
The choice between air and water cooling doesn’t boil down to one being universally better than the other. Instead, it’s about aligning with your specific requirements, production goals, and available resources. Weigh the pros and cons, understand the demands of your process, and let this guide aid in your decision-making journey.
Significance of Cooling Systems in Injection Molding
Within the realm of injection molding, the cooling process often seems like a passive phase – a mere wait for the molten plastic to solidify inside the mold cavity. However, the cooling system is a linchpin that can make or break the quality of the finished product.
Why is the cooling system so essential?
- Quality and Precision: The cooling channels within the mold ensure uniform cooling. This is pivotal to prevent defects like warping deformation, sink marks, and uneven cooling in the plastic injection mold. Proper cooling also ensures the molded part comes out as intended.

- Efficiency and Cycle Time: In the injection molding process, a significant portion of the cycle time is devoted to cooling. An effective cooling system can dramatically reduce this time, ensuring faster production rates. This is especially true when the mold design incorporates optimal cooling channel design.
- Mold Longevity: Uneven temperature distribution within the mold can lead to thermal stresses. Proper cooling, especially with coolant flows designed for the mold, ensures the injection mold has a longer lifespan, safeguarding the investment in the mold.
So, the next time you see a perfectly shaped plastic product, remember the silent yet crucial role the cooling system played. Whether it’s air cooling or water cooling, the choice and design of the cooling system can profoundly impact the injection molding service.
Key Considerations for Selecting the Right Cooling System
Selecting an optimal cooling system for your injection molding process isn’t just about choosing between air cooling and water cooling. It’s about aligning the cooling system intricacies with the specific requirements of the molded part. So, how does one make this crucial decision?
Here are some pivotal considerations:
- Mold Design and Complexity: Analyze the mold design. Complex designs with intricate features may benefit from high thermal conductivity solutions like water cooling.
- Material Used: Different materials have varying cooling needs. For instance, some plastics might require rapid cooling, while others need a more gradual process to avoid defects.
- Cycle Time: If you’re aiming for a shorter molding cycle, a cooling system that can quickly remove heat from the mold cavity becomes essential.
- Budget Constraints: While initial setup costs might favor air-cooled systems, consider the long-term operational costs, especially if water quality checks and maintenance become frequent.
- Environmental Factors: In hotter climates, water cooling systems may offer more effective cooling. Conversely, in cooler environments, air cooling might suffice.
Remember, it’s not just about the immediate benefits. Consider the long-term implications on product quality, mold lifespan, and operational costs.
Inquire About Our Silicone and Plastic Products!
Conclusion
In the intricate dance of the injection molding process, the cooling system plays a pivotal role. As we’ve journeyed through its significance, components, and the factors influencing the choice between air and water cooling, it’s evident that an effective cooling system is not just about temperature regulation.
It’s about quality, efficiency, and precision in delivering impeccable plastic products. As you venture forward in your molding endeavors, remember to give cooling its deserved attention, ensuring optimal results every time.
Unlock the Power of Optimal Cooling with Hongju
Ready to elevate your injection molding game? Hongju‘s expertise is just a click away now, and get the professional solution. Dive deeper into the world of precision molding, explore our array of eco-friendly silicone products, or engage directly with our team of experts.
Let’s collaborate to ensure you’re equipped with the right cooling system for unparalleled results.