TPE (Thermoplastic Elastomers) and PVC (Polyvinyl Chlorides) are two of the most flexible plastics used worldwide. Despite these two appearing to be the same, TPE and PVC behave chemically quite differently.
This article will provide a comprehensive comparison of the two materials, TPE and PVC, to enhance the reader’s knowledge about the differences and which material suits a specific application.
What Is TPE (Thermoplastic Elastomer)?
TPE is a new kind of plastic since it behaves like rubber, but on the other hand, it can be treated as a common thermoplastic.
TPE’s unique properties also arise from its hybrid form: softness and stretchability combined with recyclability.

TPE and silicone are very much in nowadays. TPE can be remelted and molded or remolded repeatedly with limited performance loss.
Common Types of TPE
- TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethane)
Strong and resistant to abrasion; used in cables, wheels, and protective cases. - TPO (Thermoplastic Polyolefin)
Low weight and weather-resistant; widely used in automotive parts. - SEBS (Styrene-Ethylene-Butylene-Styrene)
Soft and safe for skin contact; used for baby products and medical applications
Key Properties of TPE
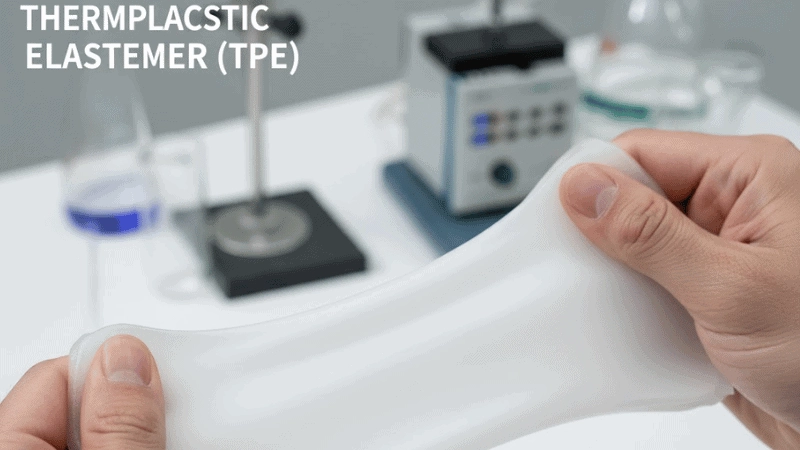

- TPE is soft and flexible, with good elasticity.
- They are recyclable and remoldable.
- These are latex-free and non-toxic.
- They have good weather and UV resistance.
- They have high comfort and are odourless.
Typical Applications
- Baby toys and teething products
- Medical tubing and stoppers
- Automotive seals and gaskets
- Tool grips, wearables, and sports equipment

TPE is preferred wherever long-lasting safety, comfort, and flexibility are concerned.
What Is PVC (PolyVinyl Chloride)?
PVC is a very popular plastic thermoforming due to its durability, low cost, and possibility of being processed into hard and soft modalities, depending upon the type of additives mixed with it. Nowadays, PVC and rubber are gaining similar attention from consumers.
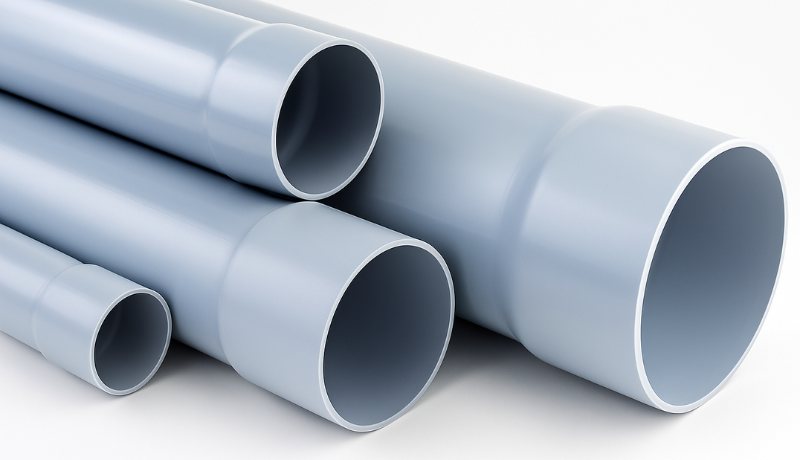

Types of PVC
Rigid PVC: uPVC for plumbing, doors and windows, and construction works
Flexible PVC: soft form mixed with the help of plasticizers for cables, flooring, bags, and toys.
Here are additions normally used with the PVC material
A number of additives improve PVC properties. PVC can be made flexible and soft by adding plasticizers. Stabilisers are incorporated to inhibit degradation and lengthen the life of PVC products. Those colours are rendered by pigments that allow PVC to be more visible in a number of hues.

Key Attributes of PVC
PVC has many useful properties. It offers excellent durability and it is able to withstand physical wear for long periods. Chemical resistance is another characteristic of this material, which makes it ideal for those environments that contain exposure to chemicals.
Regular Applicative Use
PVC is used in a range of items. Water pipes quite frequently rely on PVC for its ability to withstand corrosion and its strength. Floor tiles and wall covers include it for durability and easy cleaning. Electrical cables apply this for insulation, as a result of their safe electrical properties.

TPE vs PVC: An All-Inclusive Comparison Table
| Property | TPE (Thermoplastic Elastomer) | PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Blend of rubber and plastic polymers | Vinyl polymer dependent on additives |
| Flexibility | Extremely elastic and soft | Moderate flexibility based on plasticisers |
| Temperature Range | -50°C to 125°C | -10°C to 60°C |
| Durability | Maintains properties without aging issues | Can harden or crack as plasticisers migrate |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to oils | Good resistance but weak to some solvents |
| Toxicity / Safety | Non-toxic and latex-free | May release chlorine or VOCs |
| Recyclability | Fully recyclable | Difficult to recycle |
| Cost | Slightly more expensive | Very low cost |
| Typical Uses | Baby products, medical devices, automotive parts | Pipes, flooring, cables |
Key Differences between Properties

1. Flexural Properties
The main reason why TPEs resemble rubber is that they can be stretched, bent, or twisted with injection molding and yet will return to their original form. This gives TPE its suitability for applications such as handles, soft touch products, and other moving parts.
As for PVC, its softness is due to the use of plasticizers. When added, they may evaporate or migrate from the host material, eventually making it hard or sticky.
2. Heat Resistance
TPE holds a good range of temperatures, from very hostile cold to very high heat. They remain flexible during winter and maintain shape during warm conditions. PVC is more temperature-sensitive. It becomes stiff when cold and soft when overheated.

3. Long-term Endurance and Ageing Resistance
TPE, naturally, is resistant to UV rays, ozone, and oxidation, thus retaining its color and softness for long periods. PVC can acquire a yellowish tan by compression molding and become hard when exposed to sunlight. Flexible PVC may crack after prolonged exposure due to the loss of the plasticizer.
4. Health, Safety, and Toxicity
TPEs are free from phthalates, BPA, and chlorine and are therefore safe to use for baby products, food-contact items, and medical equipment.

PVC and antimicrobial plastic contain chlorine and may release harmful gases when overheated or burned. Some types of PVC use phthalate plasticizers, which are restricted in many countries.
5. Environment Considerations
TPEs are recyclable and do not give off toxic byproducts while being disposed of. Scrap material, in many cases, can be directly reused in the manufacturing process.
PVC is not an environmentally friendly material because of the additives. It can release dioxins and chlorine compounds.
6. Cost and Process-Ability
PVC is one of the cheapest materials and a cost effective material , therefore, very easy to process, which is why it is a favorite in construction and mass manufacturing.
TPE is a bit more expensive, but its recyclability and safety benefits often outweigh the costs, especially in high-end or consumer-oriented goods.
TPE Versus PVC in Practical Applications
Consumer Goods
TPE is used for baby toys, toothbrush grips, headphone parts, and wearable accessories. The soft feel and safe formulation of TPE make it suitable for all products that contact skin or the mouth.
PVC provides shoes, flooring, rain gear, and cheap cables. Cost consciousness is the factor behind its adaptation into household goods.
Automobile
TPE is used very widely in weather strips, bumpers, dashboards, and other soft-touch interior parts. It boasts excellent weathering and UV resistance.
PVC is used for wire insulation and dashboard skins, but is being gradually phased out for concerns related to weight and safety.
Medical and Food
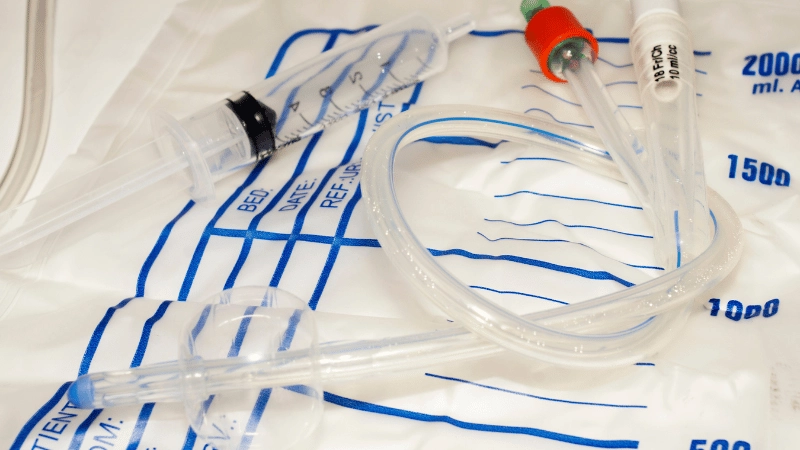
TPE is ideally suited for medical tubing, syringe stoppers, and food-contact seals, increasingly becoming the first option because it is free from toxic substances.
Plastic is still used for food containers, and PVC is in use for certain blood bags and IV lines, but is in declining demand due to the restriction on DEHP and chlorine.
Industrial
TPE is commonly used to replace rubber in the housing of connectors, hoses, andprotective coatings.
PVC is still favoured for pipes, heavy-duty insulation, and construction materials because of its rigidity and cost.
Future Trend – TPE Replacing PVC

The new trend around the world is to move toward sustainable materials, of which TPE fits perfectly into this category since it is recyclable, has no smell, and is hypoallergenic.
Countries have also banned PVC and phthalates in baby and medical devices. The more stringent regulations become, the more TPE is used as a material of choice for safer and greener manufacturing.
Conclusion
Though TPE and PVC seem to be quite alike, they differ largely as regards performance and safety. TPE makes a smarter choice if you look for modern, eco-friendly consumer or medical products, though certified, non-toxic grades will always guarantee product quality and safety.
Choose Hongju Silicone When Comparing TPE vs PVC
If you are evaluating TPE vs PVC for safer, cleaner, and more advanced product performance, Hongju Silicone delivers high-purity TPE solutions tailored to medical, consumer, and industrial manufacturing.
Get TPE solutions perfect for medical and consumer uses with fast 3-5 day prototyping, low MOQs, and 20+ years of expertise.
Contact Hongju Silicone for samples, recommendations, and project-specific guidance.
FAQs
Q1: Is TPE safer than PVC?
TPE is free from chlorine, phthalates, and other harmful chemicals contained in PVC, hence the widespread use in baby and medical products.
Q2: Why is TPE more expensive than PVC?
More pure, high-quality raw materials and clean processing result in TPE being more costly than PVC; however, these factors also add to TPE’s recyclability, durability, and safety, leading to savings in total cost, lessening costs in the long run.
Q3: Can TPE replace PVC in medical tubing?
Yes, many hospitals and manufacturers already utilize TPE tubing due to its toxic-free, flexible structure and compliance with strict medical safety standards.
Q4: Between TPE and PVC, which one is better when it comes to outdoor usage?
TPE is better because it resists UV rays, weathering, and temperature changes. PVC may become brittle or hard after prolonged outdoor exposure.