This article breaks down the 10 most popular materials for gaskets and their properties. It also introduces 5 rubber alternative materials for gaskets to help you compare them in detail and choose the right material for your gaskets. Let’s dive in!
What is a Gasket?
Silicone rubber gasket seals are flexible, non-porous components that seal tiny gaps between surfaces and joints. Surfaces can have microscopic imperfections, invisible to the naked eye. These imperfections prohibit proper contact between two surfaces and result in poor sealing. Gaskets are squeezed between two surfaces, filling these microscopic cavities and gaps.
Rubber gaskets seal smartphones, electronics, automotive applications, and many more. Plastic and rubber-hybrid gaskets are less common and limited to particular applications.
10 Rubber Gasket Materials
Rubber can be categorized into two main groups: natural and synthetic. Synthetic rubber materials are polymers with specific properties, like heat, ozone, or water resistance. Here are the ten most popular rubber gasket materials.
Natural Rubber
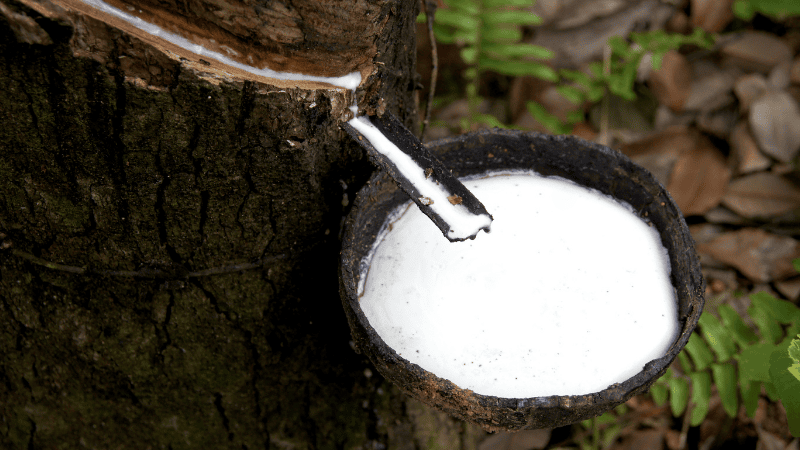

Natural rubber exists as a sticky, milky sap trapped inside rubber trees. This sap is cured and processed over several days into a usable state. It has excellent material properties, including good tensile strength and impact resistance. But it is weak to temperature changes and susceptible to chemical damage.
Natural rubber gaskets can be deployed in most environments with zero issues. They are water-resistant and can be easily incorporated into any plumbing and hydraulic applications. The same can be said for several other sealing applications like electronics and automobiles.
Unfortunately, you cannot deploy it in car engines due to natural rubber’s weak thermal properties. Vulcanization can help with some of these shortcomings, but it is better to stick with synthetic rubber for demanding applications.
Silicone Rubber
Silicone rubber is by far the best gasket material on this list. It is the most versatile option, applicable to nearly all sealing applications. Silicone rubber is specifically designed for high-performance applications and harsh environments.

It has an extensive operating temperature range, going from 500° F to -75° F. Silicone rubber gaskets also have excellent resistance to ozone, UV, water, and flame.
But the benefits of silicone rubber products don’t stop with excellent resistance and properties. Silicone rubber gaskets are also biocompatible, medical-grade, and FDA-approved. They are utilized in medical equipment, surgical instruments, automotive applications, food packaging, and aerospace applications.
Neoprene/Chloroprene Rubber (CR)
Chloroprene rubber, i.e., neoprene, is a synthetic elastomer known for its excellent mechanical properties and decent chemical resistance. Though neoprene gaskets can be deployed in several industries, they are primarily used in the industrial and automotive sectors.

Oils, acids, and grease are present in most industrial spaces and can easily make their way to other parts of a factory.
A leaking gasket can halt the entire production line and result in a severe loss of work. Neoprene gaskets can significantly reduce machine and tubing failures. The one shortcoming of neoprene is its poor heat resistance.
Nitrile Rubber (NBR)
Nitrile rubber is known by several names in the industries, including Buna-N and NBR (nitrile butadiene rubber). Nitrile can be seen as a jack of all trades for gasket materials. It has great mechanical properties on par with natural rubber. It also has good chemical and environmental resistance, further increasing its versatility.
Nitrile gaskets are best suited to harsh environments where acid, alkaline, and gasoline damage is likely. Nitrile is also an FDA-approved rubber material and can be used for food container gaskets. The only shortcoming of nitrile gaskets comes from poor heat and flame resistance.

EPDM Rubber
EPDM stands for Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer. EPDM rubber is a complex elastomer made from an ethylene and propylene mixture. Gaskets made from EPDM are favored for outdoor deployment, where sunlight, oxidation, and environmental corrosion are prevalent.
EPDM has excellent chemical and environmental resistance, including protection from acids, alkalines, ozone, sunlight, and hydraulic fluids. For hazardous environments, EPDM is the ideal rubber gasket material.
Viton (FKM)
Viton is the trademarked name for fluoroelastomers, also known as FKM. This material was specially designed to be used in vehicle engine blocks. As such, it has exceptionally high tensile strength and outstanding resistance to chemical and thermal effects.
Viton is a versatile material that can be adapted to various environments. But Viton rubber is more cost-effective to use Viton gaskets for automotive applications.
Butyl Rubber (IIR)
Butyl is another complex elastomer made from isobutylene and isoprene. This material stands out for its shallow gas, air, and moisture permeability. Additionally, it also has industry-standard mechanical and chemical properties.
Butyl gaskets are insanely customizable and flexible in applications. You can also get pressure-sensitive adhesive backings for your butyl gaskets.
Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (SBR)
SBR rubber is a standard synthetic elastomer that is a low-cost alternative for most applications. It has average properties across the board, except for abrasion resistance and durability. Like many other rubber materials, SBR is weak against high temperatures.
SBR gaskets come with a nylon insert option for added strength. They can be deployed in most general applications.
Polyurethane Rubber (PU)
Polyurethane is an incredibly tough and resilient material. In terms of natural properties, it can outperform most rubber and some metal materials. Other than poor heat resistance, polyurethane has excellent chemical and environmental damage resistance.
Polyurethane gaskets are best suited to applications where strength and durability are critical. And it is often used in food-grade gaskets and seals.
Foam Rubber
Elastomers can be whipped with additional components to create a rubber foam filled with tiny air pockets. Foam rubber properties are dependent on the base elastomer component. However, the properties of foam rubber gaskets will be significantly lower than those of pure rubber gaskets.
Foam rubber gaskets provide a cushioning effect as well as insulation advantages. Foam rubber gaskets are also used for sound and vibration dampening.
5 Non-Rubber Gasket Materials

Rubber is generally the preferred material for gaskets and mechanical seals. But for some applications, you will benefit from plastics and cloth gaskets. Additionally, some gasket materials are hybrid mixtures of non-rubber and rubber materials.
Here are the five rubber alternatives materials for your gaskets.
Felt
Felt is a wool-based cloth product. It is full of air pockets and is incredibly absorbent. Felt gaskets are generally preferred for their sound absorption properties. But they can be used for several other applications as well.

Cloth Inserts
Cloth materials are other inserted into rubber gaskets for additional reinforcement of mechanical properties. Cloth inserts can significantly raise the tear resistance of a rubber gasket.
The cloth base can be made from several materials, including cotton, nylon, polyester, etc. In contrast, the co-ingredient rubber is mainly limited to EPDM, neoprene, or nitrile.
Cork Additive
Cork is shredded tree bark encased in cellulose. It is a lightweight and buoyant material impermeable to air and water. Cork is a flexible and compressible material that gains additional properties once combined with a rubber base.
Neoprene and nitrile cork gaskets are fuel, oil, and solvent-resistant.

PVC
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) is a common material for plastic gaskets. PVC gaskets provide good shock absorption, leading to cushioning and sound-dampening properties.
It produces low-cost transparent gaskets that are used in various commercial applications.
PTFE
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a unique material that exhibits rubber and plastic properties. It is officially a thermoplastic but shares many properties with elastomers.
PTFE has excellent chemical resistance and a wide thermal operating range. You will mostly see PTFE gaskets in chemical industries.
Gasket Material Selection Chart
Following is a simple comparison chart of different gasket materials and their advantages and disadvantages.
| Material | Advantage | Disadvantage |
|---|---|---|
| Natural Rubber | Good Mechanical Properties | Poor Chemical & Thermal Properties |
| Silicone | Excellent Thermal & Mechanical Properties | Weak Chemical and Oil Resistance |
| Neoprene | Decent Properties in all Aspects | Poor Heat and Flame Resistance |
| Nitrile | Good Mechanical Properties and Good Chemical Resistance | Poor Heat and Flame Resistance |
| EPDM | Good Environmental Resistance | Poor Fuel & Oil Resistance |
| Viton | Excellent for Automotive Applications | Higher Cost |
| Butyl | Low Fluid Permeability | Poor Fuel & Oil Resistance |
| SBR | Good Abrasion Resistance and Durability | Poor Heat and Flame Resistance |
| PU | Excellent Mechanical Properties | Poor Heat and Flame Resistance |

| Material | Advantage | Disadvantage |
|---|---|---|
| Felt | Good Sound Absorption Properties | Weak Mechanical Properties |
| Cloth Inserts | Excellent Tear Resistance | Higher Cost |
| Cork Additive | Low Fluid Permeability | Higher Cost |
| PVC | Low Cost and Transparency | Poor Elasticity |
| PTFE | Excellent Chemical Properties | Poor Elasticity |
Conclusion
Rubber gaskets stand out as the most versatile sealing solution, offering superior temperature resistance, durability, and FDA approval. From automotive to medical applications, they ensure long-lasting protection where other materials fail, making rubber the top choice for critical gasket needs.
Why choose Hongju for your Rubber Gaskets?
Hongju is an experienced manufacturer of innovative and sustainable custom-molded rubber products. We offer several high-quality and precision OEM and ODM services. Our silicone rubber gaskets are water, weathering, and oxidation resistant. And they are completely food-safe, complying with the latest FDA food safety regulations!
Contact us now! Don’t miss out on this chance to avail our low MOQ, expert craftsmanship, and lightning-fast delivery!