Abrasion resistance is essential for rubbers used in industries. In demanding environments, abrasion-resistant rubbers can maintain their performance and resist surface wear.
These rubbers are common in automotive and manufacturing industries, where they help reduce downtime. It is important to select the right rubber material for durable, efficient, and long-term functionality.
What Is Abrasion Resistance?
In simple words, abrasion resistance refers to a rubber material’s ability to withstand wear. Abrasion is often caused by mechanical movements. It is also caused by friction and repeated contact with surrounding equipment.
Abrasion resistance in any rubber material matters a lot because the abrasion problem is harmful to rubber. It slowly removes its outer layer, which leads to reduced performance and leakage.
Sometimes, it causes complete failure of the appliance. Hence, a rubber’s ability to withstand mechanical action is important.

In industries, rubbers with poor abrasion resistance often lead the setup to long downtimes. They also cause higher maintenance costs and frequent replacements. Abrasion occurs when a rubber comes into contact with rough materials, moving parts, or particles under pressure.
Friction between the rubber and other external materials accelerates wear. This also ruins the surface finish and damages the rubber.
Depending on how this friction is applied, abrasion can occur in different forms. Each of these types affects the durability and lifespan of the rubber.
Under abrasion testing, styrene‑butadiene rubber and polyurethane materials have shown 95% more resistance to material loss and wear compared to other materials. This highlights their effectiveness in wear-intensive applications.
The different types of abrasive conditions include sliding abrasion, rolling abrasion, and impact abrasion.
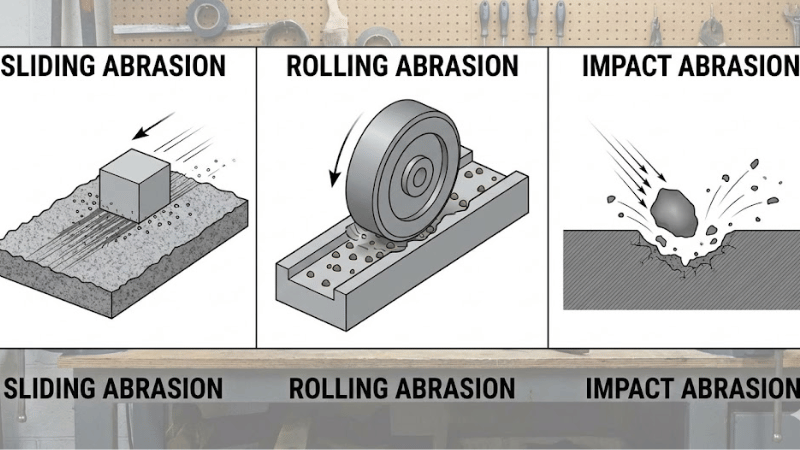
Sliding abrasion refers to the friction faced by rubber when it continuously rubs against another surface. Rolling abrasion is caused by the rotation or movement of rubber material while it faces high friction.
Impact abrasion results from sudden physical contact, vibration, or shock applied to the rubber material. Understanding all types of abrasion helps one choose a rubber with good abrasion resistance for their needs.
Common Examples of Abrasion Stress
There are several real-world examples where abrasion stress causes components to lose their properties and functionality. Some of these include the following:

- In conveyor belts, constant sliding and material load on the belt cause abrasion, leading to surface wear and damage.
- Wheels and rollers that are under a lot of motion and face consistent friction. Working against friction continuously leads to gradual abrasion and heat fatigue.
- Gaskets face repeated compression, vibration, and movement. The mechanical motion faced by gaskets increases their wear over time.
How Is the Abrasion Resistance of Rubber Tested?
There are a few standardized laboratory tests that help evaluate the abrasion resistance of any rubber material. These tests simulate friction and mechanical wear on rubber under controlled conditions. The purpose is to check if the rubber can resist wear.
These tests are also meant to accurately check the level of resistance that a certain rubber material shows. These laboratory tests allow accurate comparison between different kinds of abrasion-resistant rubbers.
Using the results of such testing, one can easily pick the right rubber material according to real-world uses.
Common abrasion-resistant testing methods include the following.
- DIN abrasion test: This test measures material loss by rubbing rubber material against an abrasive surface under a fixed pressure rate.
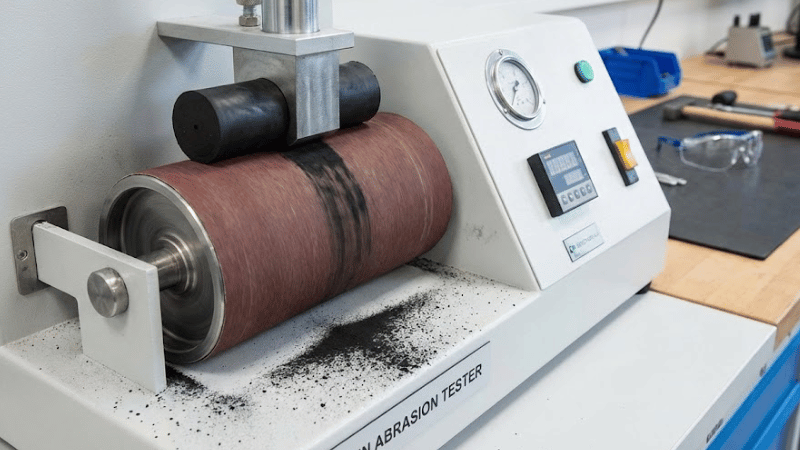

- Taber abrasion test: In this test, rotating abrasive wheels are exposed to repeated friction to test surface wear.
- Rotary drum abrasion method: In this method, a rotating rubber is subjected to heavy-duty wear. This test is conducted by rotating the rubber inside an abrasive-lined revolving drum at high speed.
Under each of these tests, the volume loss of the rubber material is assessed. This is then comparatively rated with a number called the wear index. This number ranks the performance of that rubber material under abrasion.
Several standards act as benchmarks when evaluating different rubber materials to ensure a consistent test for each.
High-Abrasion-Resistance Rubbers

Several types of rubbers often pass abrasion tests and are ranked as highly resistant when it comes to friction against abrasive materials.
One of the finest examples of abrasion-resistant rubber is natural rubber, which comes with high resilience and tensile strength. This rubber performs exceptionally well even under repeated friction due to mechanical stress and continuous rotation.
Such features make natural rubber ideal for heavy-duty industrial applications. Hence, it is used in conveyor belts, tires, vibration mounts, and other flexible components.
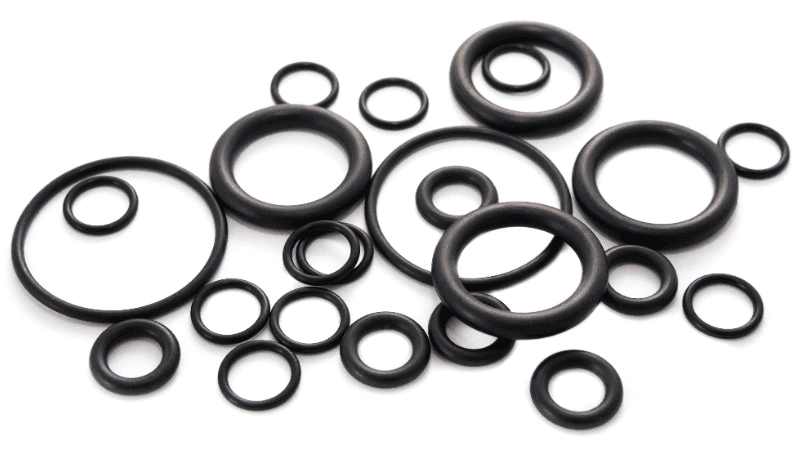

NBR, or nitrile rubber, is another rubber with excellent abrasion resistance. It works excellently despite being in repeated contact with oils and fuels. This makes it ideal for use in automotive and other industrial systems for the manufacturing of gaskets and O-rings.
It is also ideal for use in many applications where friction and fluid exposure are common, such as construction rollers and hoses.
Neoprene rubber, or CR, also provides reasonable abrasion resistance along with stability against external factors and chemicals. It is not as resistant as natural or nitrile rubber, but it is quite reliable when it faces mixed environmental conditions.
Neoprene rubber is commonly used in industrial belts, protective covers, and mechanical pads.
EPDM rubber is a moderately abrasion-resistant rubber that shows excellent resistance to heat, ozone, UV, and other forms of weathering. It is suitable for outdoor use, especially for components that are exposed to mechanical applications.
Viton, or FKM, delivers high abrasion resistance along with exceptionally strong chemical resistance properties. It also remains stable under extreme temperatures.
It is, therefore, suitable for applications where chemicals, fuels, and high heat are common.

Low-Abrasion-Resistance Rubbers
Compared to the above highly abrasion-resistant rubbers, a few rubber materials are not abrasion-resistant. These often fail in abrasive environments.
One such rubber is silicone rubber with its soft and flexible nature. This rubber wears out quickly under friction or when exposed to repeated mechanical movements.
This makes it unsuitable for dynamic and high-wear applications. Silicone is best used in static seals where temperature stability and flexibility are required.
Butyl rubber, or IR, offers low abrasion resistance. However, it provides excellent chemical resistance and low gas permeability. Additionally, it is commonly used in sealing, insulation, and other applications where friction exposure is extremely low.

Comparison Table: High vs Low Abrasion Rubbers
Below is a table comparing high-abrasion versus low-abrasion rubbers based on their common uses, durability, and the temperatures they can withstand.
| Rubber Type | Abrasion Rating | Temperature Range | Durability Under Wear | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Natural Rubber (NR) | Very High | -50°C to +80°C | Excellent | Conveyor belts, tires, couplings |
| Nitrile Rubber (NBR) | High | -30°C to +100°C | Very Good | Seals, hoses, rollers |
| Neoprene (CR) | Medium–High | -35°C to +100°C | Good | Industrial belts, covers |
| EPDM | Medium | -50°C to +150°C | Moderate | Outdoor mechanical parts |
| Viton (FKM) | High | -20°C to +250°C | Excellent | Chemical & fuel handling systems |
| Silicone | Low | -60°C to +200°C | Poor | Static seals, insulation |
| Butyl (IIR) | Low | -40°C to +120°C | Poor | Gas seals, liners |
How to Choose the Best Rubber for Abrasion Resistance

Choosing the right rubber that offers abrasion resistance is not hard. Simply start by identifying the application. See whether the rubber will roll, slide, or be at risk of impact wear. For sliding abrasion, go for natural rubber, and for rolling, go for NBR or neoprene. Impact abrasion demands rubbers that have better elasticity and tensile strength.
Next, evaluate the environmental factors in which the rubber equipment has to perform. This includes considering whether the rubber will be exposed to high temperatures, chemicals, oils, fuels, water, or other elements. Depending on these environmental factors, you can choose between Viton, nitrile, or EPDM.

Finally, match the material to the functionality expected from it. You can go for natural rubber when maximum abrasion resistance is required in clean and non-oily environments.
However, nitrile is a better choice when you need abrasion resistance along with oil compatibility. Similarly, Viton is worth investing in when the application involves harsh chemicals and extreme temperatures.
Conclusion
Rubbers that can withstand abrasion, like natural rubber, nitrile, Viton, and others, are reliable partners for your industrial needs. Choose the right material for your needs, evaluating your needs, environment, and operational requirements. Don’t forget to source only from a reliable rubber manufacturer and supplier.
Source Rubbers With High Abrasion Resistance from Hongju!
With Hongju Silicone, you can enhance your industrial operations and minimize downtime. Our expertly crafted rubber materials provide chemical, heat, and abrasion resistance like none other.
Benefit from our rapid prototyping abilities, expert craftsmanship, and low MOQ.
Whether you want bulk volumes or want to place an individual order, reach out to us today.
FAQs
Q1: What if I need both abrasion and chemical/oil resistance?
In that case, it is best to go either for Nitrile (NBR) or Viton (FKM). Both of these rubbers provide a balanced combination of chemical and wear resistance.
Q2: How do I choose the right abrasion-resistant rubber for my application?
For that, we suggest you consider factors like contact surface, pressure, temperature, presence of chemicals, and dynamic movement. Our engineers can recommend optimized materials based on real-world testing, ensuring longevity and cost-effectiveness for your specific use case.
Q3: What is your production time?
The average production cycle for our products is 9-15 workdays, but this can vary according to the quantity of orders, the complexity of our products, and the different seasons.
Q4: What certifications does your factory have?
We are ISO 9001 certified silicone rubber products manufacturer. And we have CE and FDA certificates for our products. We can also apply for you if you have specific certification needs for your market.