What is Injection Molding?
Injection molding is a manufacturing process where molten plastic is forced under high pressure into a mold cavity to form specific shapes. Raw material is fed through a hopper, then heated and pushed by a screw into the mold.
After injection, the material cools and solidifies inside the mold. Ejector pins then push the finished part out. This method is very precise, efficient, and ideal for the mass production of complex parts.
A typical injection molding machine includes a hopper, screw, heating system, clamping unit, and injection unit. They work together to ensure high consistency and accuracy in the final products.
Advantages of Injection Molding

- Rapid cycle times, which results in high volume output and lower production cost
- Excellent precision, especially for complex and intricate parts
- Strong and durable parts
- Tolerates a wide range of raw materials
Disadvantages of Injection Molding
- High cost of mold designs
- Not suited for manufacturing large parts
- Producing a small number of molded products can be quite costly
Applications of Injection Molding
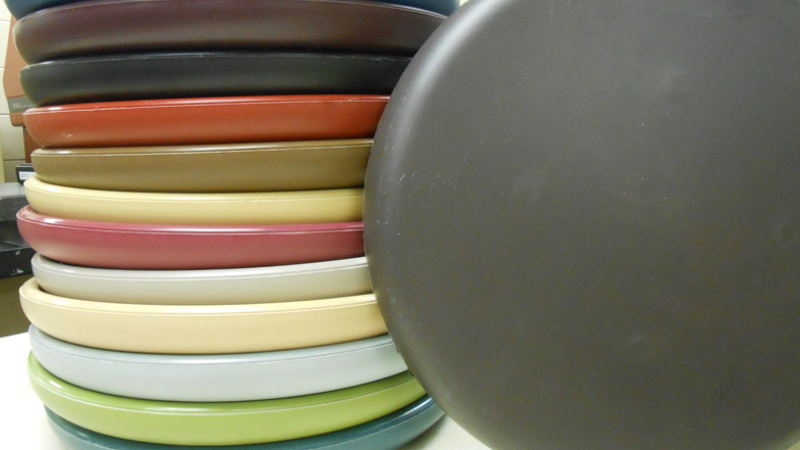

Injection molding can accommodate many materials and is suitable for producing complex parts. Consequently, this molding process is versatile and applicable in manufacturing.
- Automotive products like dashboard components, dials, and switches
- Computer and consumer electronics
- Window and door components
- Engineering prototypes
- Silicone cookware
- Plastic bottles
- Packaging for food storage
- Cable assemblies
- Medical and dental devices resistant to bacteria and corrosion
What is Compression Molding?
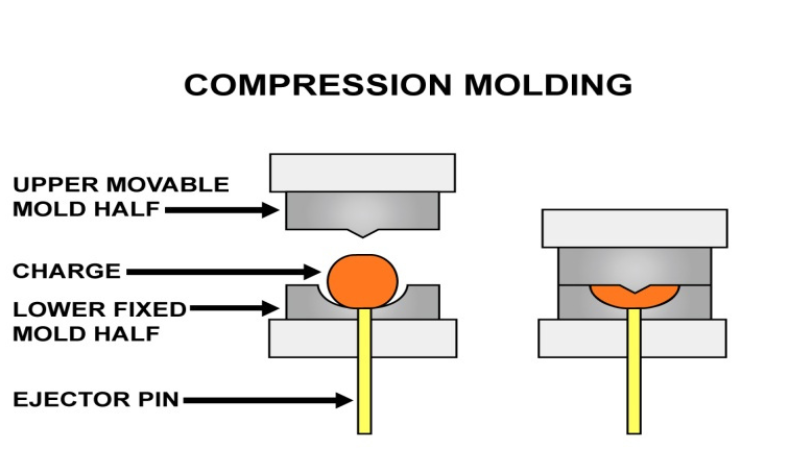
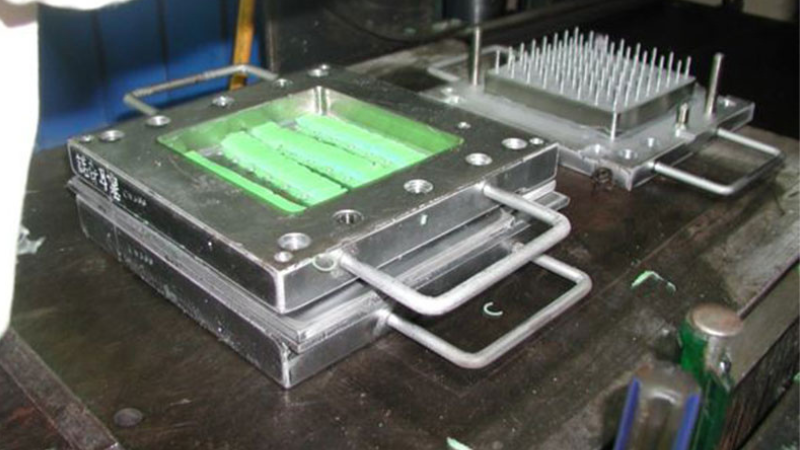
Unlike injection molding, compression molding heats and compresses a plastic material into its desired shape in the same mold. A compression molding machine has two parts, the upper and lower compression molds. While the lower half is stationary, the upper half is movable.
During the process, the lower mold is preheated before placing the plastic. After closing the mold, it presses the melted plastic and cures it. You can then remove your final product once it is cooled.
Advantages of Compression Molding
- The process is suitable for small production, which results in lower cost
- Compression molding is excellent for manufacturing products if varying thicknesses and lengths
- The process produces minimal waste
- The end products are sturdy and resilient
- The compression molding process preserves your raw material’s chemical and mechanical properties.
Disadvantages of Compression Molding
- Slower production time
- The process cannot produce complex parts
- Compression molding is not ideal for large-volume productions
- The end products may need extra processing to remove the overflow
Applications of Compression Molding

Compression molding is suitable for producing durable and robust parts. This process is therefore applicable in:
- Automotive parts
- Electronic components
- Circuit breakers
- Clothing fasteners
- Plastic dinnerware
Common Traits Between Compression Molding & Injection Molding

Although compression molding and injection molding have significant differences, they are alike in some ways. The table below summarizes the common traits between compression and injection molding.
| Compression Molding | Injection Molding | |
| Material Form | Thermoplastics or thermosets (often preheated) | Thermoplastics or thermosets (molten state) |
| Mold Usage | Uses a two-part mold | Uses a two-part mold |
| Production Efficiency | Suitable for medium to high volume production | Suitable for high-volume mass production |
| Process Type | High-pressure forming process | High-pressure forming process |
| Part Complexity | Capable of producing complex parts | Suitable for highly complex and detailed parts |
| Uniformity & Consistency | Provides good part consistency | High consistency and dimensional accuracy |
| Common Applications | Automotive, electrical, appliance components | Automotive, consumer electronics, medical parts |
Differences Between Compression Molding and Injection Molding

| Compression molding | Injection molding | |
| Material | Elastomers, thermosets, and sheet molding compound (SMC) | Rigid thermoplastics, urethanes, elastomers |
| Product size | Large parts, varying thickness | Smaller parts, tight tolerances |
| Production time | Slower process, longer cycle time | Faster process |
| Production capacity | Low-volume production | High-volume production |
| Process | Simple process, fewer components required | More complex, requires more components |
| Precision | Less precise, may require post-processing | Highly precise, consistent results |
| Model complexity | Suitable for simple parts | Ideal for complex designs |
How to Choose Between Injection Molding and Compression Molding

The choice of a suitable molding process depends on your application, techniques, the cycle time, and product complexity.
If you want to manufacture products for complex parts quickly, injection molding is ideal. And if your application requires simple products, compression molding may be excellent.
Nevertheless, before choosing a suitable molding process, you can discuss the details of your application with your manufacturer.
What are the Alternatives to Injection Molding?
There are several alternatives to injection molding for producing high-quality parts. These alternatives include 3D printing, blow molding, extrusion, thermoforming, and rotational molding.
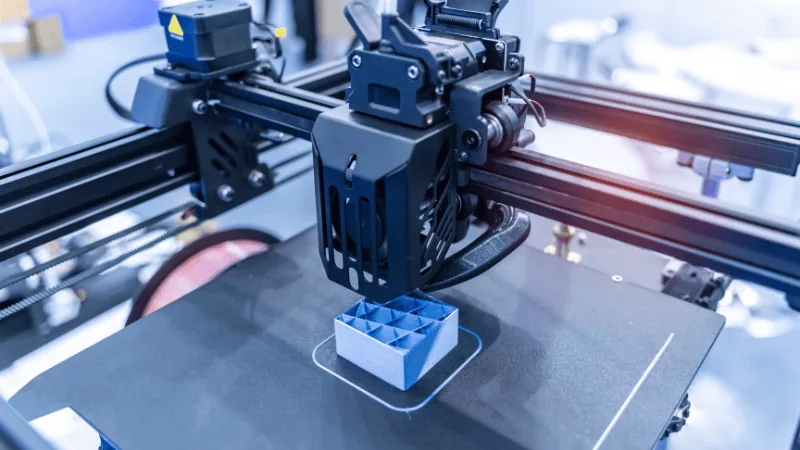
- 3D printing
3D printing creates parts by printing layer upon layer of material, while injection molding uses a mold to create a desired part out of molten material.
Although both methods are ideal for creating complex designs, injection molding has minimal wastage and is suitable for high-volume production.
3D printing, on the other hand, has a slower cycle time but a faster setup.

- Extrusion
Extrusion is a comparatively new plastic molding process. Both extrusion and injection molding inject molten material through a machine to mass-produce parts.
However, unlike injection molding, extrusion is more suitable for creating two-dimensional products. In addition, extruded products are not as strong are injection-molded details.
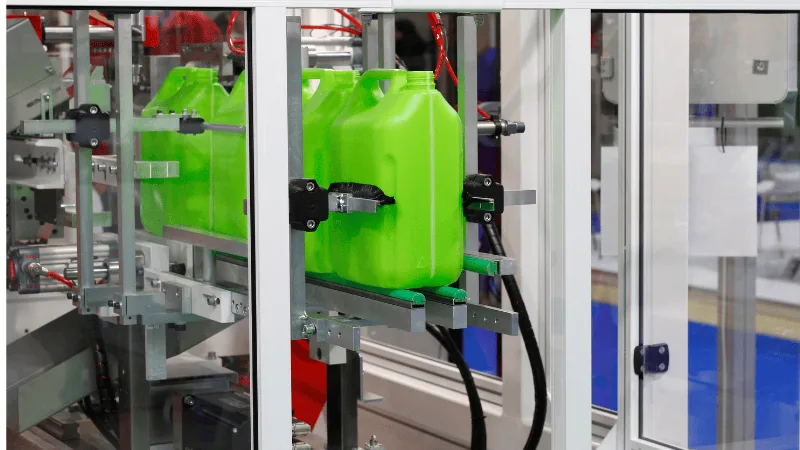
- Blow molding
Blow molding is a high-volume production molding process. Although this process is suitable for most thermoplastics, it is used explicitly in molding hollow products like bottles and beakers. In contrast, injection molding is used to mold solid parts.

- Thermoforming
Thermoforming and injection molding are repeatable processes that produce high-quality parts from thermoplastic materials.
The difference between these two methods is that thermoforming molds a heated flat sheet of plastic using suction and pressure, while injection molding injects molten material into a mold.
- Rotational molding
Injection molding and rotational molding use preheated plastic injected into a mold. The difference, however, is that rotational molding rotates the mold on two axes in an over to create a uniform coating of the molten plastic.
How to Maximize Value When Choosing a Molding Process
Beyond the molding methods’ technical differences, companies often need to evaluate molding methods based on cost, sustainability, and scalability. Adding these perspectives helps you make more informed choices.

1. Cost Breakdown Over Time
- Injection molding: High upfront tooling cost (tens of thousands of dollars) but extremely low per-part cost when producing hundreds of thousands of products.
- Compression molding: Lower investment but higher per-part cost, making it more economical for low to medium runs.
2. Sustainability Factors
- Injection molding often creates more sprues and runners, causing higher waste unless using recycling systems.
- Compression molding generates less scrap, but cycle times are slower. Companies aiming for green manufacturing may favor compression for short runs or invest in closed-loop recycling with injection molding.
3. Part Performance Considerations
- Injection-molded parts achieve tight tolerances down to ±0.05 mm, critical for medical and electronics applications.
- Compression-molded parts maintain material integrity well, especially for fiber-reinforced composites.

Practical Buying Guide for Businesses
- Define volume needs: Choose compression molding for fewer than 10,000 units; injection molding for more than 50,000 units.
- Check certification requirements: Medical, food-grade, or automotive parts often mandate injection molding for precision.
- Ask about recyclability: Confirm whether your manufacturer recycles materials to reduce waste.
- Evaluate total cost of ownership: Consider both tooling and parts cost, not just initial investment, to save cost in the long run.
FAQs
Q1: Why is Injection Molding Preferred?
Injection molding allows high-volume production of complex parts. The process is highly efficient and compatible with a wide range of plastic and thermoplastic materials.
Furthermore, there is minimal waste and a faster cycle time, which saves you money.
Q2: What Can Plastics Go through Compression Molding?
Thermoplastics and thermosets are raw materials that can go through compression molding. These plastics are flexible and can be easily molded into desired parts. Besides, sheet molding compound (SMC) and bulk molding compound (BMC) can also be compression molded.
Q3: Why choose compression molding?
Ideal for large parts, lower tooling cost, and compatible with thermosets or fiber-reinforced materials.
Conclusion
Injection and compression molding both deliver high-quality plastic or silicone parts. Injection molding excels for complex designs and high-volume production with fast cycle times. While compression molding offers lower initial costs and excels with large, sturdy components.
Each method can provides unique advantages in precision, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness for applications.
Hongju – Your One-Stop Custom-Molded Rubber Products Manufacturer
Hongju is a leading manufacturer in the rubber industry. We offer custom-molded products at fast turnaround times and competitive prices. Our process is simple, effective, and dedicated to providing value to our customers.
We also have efficient capabilities of compression molding and injection molding. We create many kinds of silicone rubber products, including keypads, o-rings, rubber grommets, and gaskets.
Contact us today to achieve your rubber molding projects!