What is Silicone Rubber?
Silicone rubber is a type of elastomer or rubber-like material. Its main composition is silicone, which in itself is a type of polymer. Manufacturers use different formulations to mix this silicone with other materials like oxygen, carbon, and hydrogen. This results in several types of silicone rubber ideal for various applications.
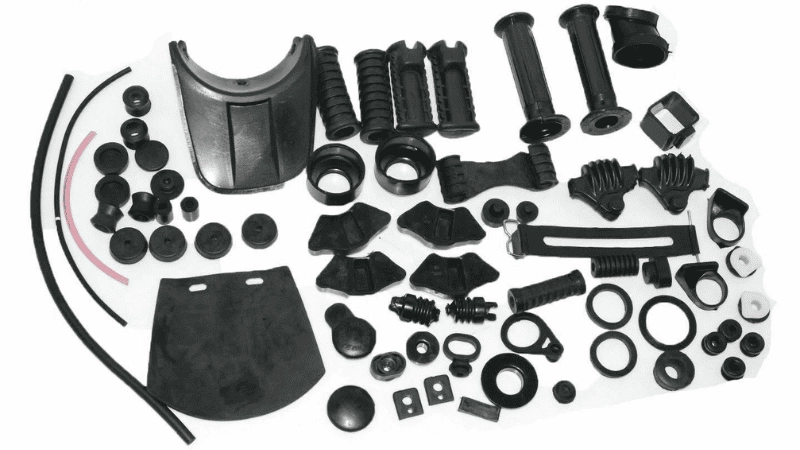

The unique composition and versatility of silicone rubber provide many advantages. By adjusting its fillers and other properties, it is possible to decrease costs without sacrificing quality.
This flexibility also allows for the development of customized silicone rubbers that meet the strict requirements of food-grade and medical-grade standards. This combination of adaptability, flexibility, and regulatory compliance makes silicone rubber an optimal material for a range of applications in various industries.
Its versatility is only one of the many qualities that make silicone rubber popular today. It’s also valuable because of its durability, stability, and non-reactive state, even after extreme temperature and chemical exposure.
It can withstand temperatures from −55 to 300 °C (−70 to 570 °F) without losing its most important properties.
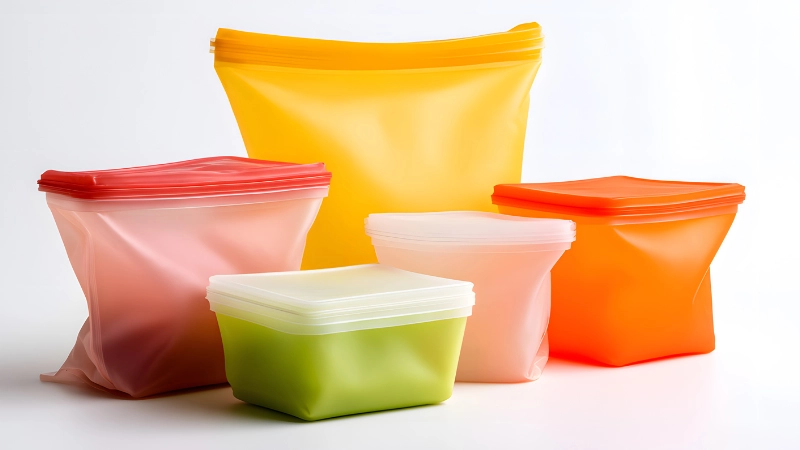

Injection molding silicone rubber is also very easy. This is why you can see it in various shapes and sizes. You can add color and adjust the transparency to suit design requirements.
Silicone can meet every requirement for automotive applications, home repair, seals, food storage, cookware, or even medical-grade requirements.
How did Silicone Rubber Come to be?
The very first silicone elastomer was initially for electric motors and generators. The intention was to search for a better insulating material that could replace resin-infused glass fibers that were popular then. The problem they were trying to solve was the inability of phenolic resin to withstand exposure to high temperatures that were common among smaller electric motors.

General Electric and Corning Glass chemists started looking for better heat-resistant materials to solve this issue. This eventually got them to try out silicone polymers. The new material has proven that its structure can withstand extreme temperatures.
After this discovery, the chemists found a way to produce silicone material commercially. They decided to call this discovery silicone, which is a misnomer.
The -one was to denote the substance with oxygen’s double-bonded atom as its backbone. This is because the chemists initially erroneously thought that the atoms of oxygen bond differently in silicone. But after further studies, silicone rubbers should have the name polysiloxanes.
As silicone rubber grew in popularity, it could be used for more applications. By the early 1950s, the mass production of silicone had become more prominent.
Types of Silicone Rubber
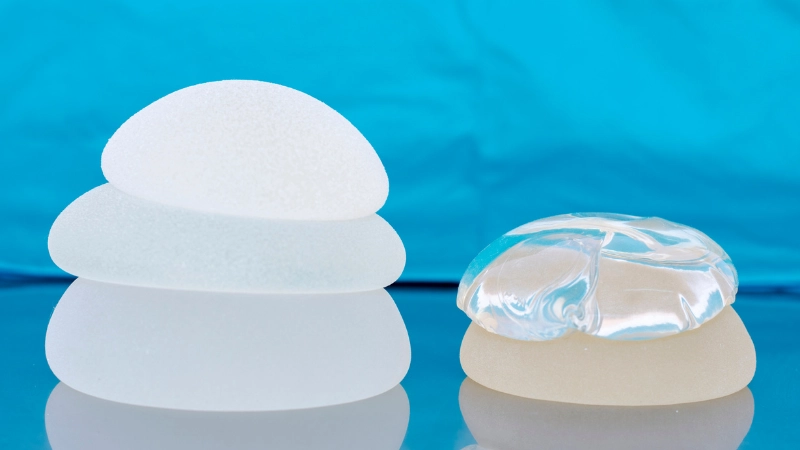

There are two ways to classify silicone rubber. One is through its molecular structure, and the other is through its primary form.
Classification through composition
Silicone rubber is so versatile that you can create it using different organic groups. It can be methyl, phenyl, vinyl, or other groups. Usually, the choice will depend on the specific application of the silicone rubber.
Based on the ASTM D1418 standard that officially classifies rubber, silicone rubber has these classifications depending on its molecular structure.

- Methyl Group. This group carries other identification, including dimethyl silicone elastomer, methyl silicone rubber, or the shortest reference of MQ. It’s the base and simplest structure of silicone.
- Methyl and Vinyl Group. This group also has other names, like vinyl methyl silicone elastomer. It can be identified as VMQ. These are ideal for both high and low-temperature applications. It’s non-toxic, can retain its original structure despite sunlight exposure, and is highly resistant to fungal decay.
- Methyl and Phenyl Group. This carries the name methyl-phenyl silicone elastomer. A more common name is phenyl silicone rubber. Also, going by the name of PMQ, this composition is excellent for low-temperature applications.

- Methyl, Phenyl, and Vinyl Group. This also carries the name PVMQ, known for its ability to perform well over low temperatures. With the introduction of phenyl, the silicone rubber’s thermal properties undergo significant enhancements – allowing it to keep its structure despite exposure to frigid temperatures.
- Fluoro, Vinyl, and Methyl Group. The fluorosilicone rubber, fluorinated rubber, or FVMQ, has properties that make it highly resistant to chemicals like oil, fuel, acids, alkaline, and other non-polar solvents. It is a long-lasting type of elastomer that’s relatively stable and resistant to compression across extreme temperatures.
Classification through viscosity and processing method
The classification of silicone rubber can also be done by its viscosity and the processing method that it goes through.
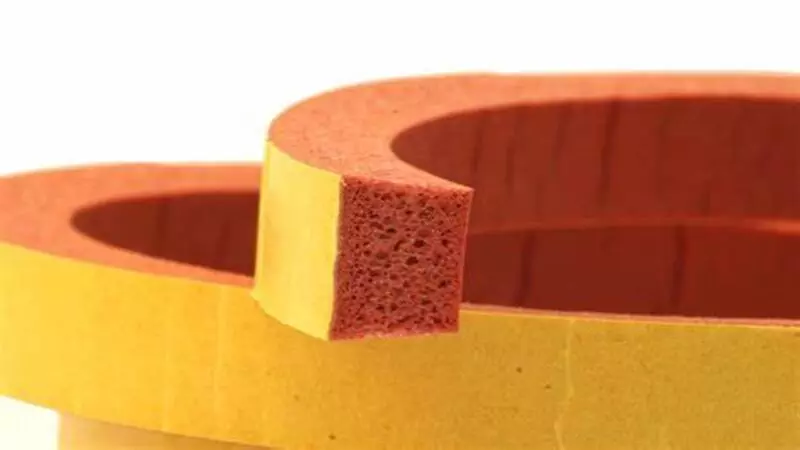
- High-Temperature Vulcanized Solid Silicone Rubber (HTV): This type of silicone rubber has a composition that includes polymers with high molecular weight and long polymer chains. These are usually uncured in form and use traditional techniques in processing organic rubber.
- Liquid Silicone Rubber (LSR): Liquid Silicone Rubber (LSR) is made of polymers with shorter chains and lower molecular weight, giving it better flexibility. It’s produced by injection molding or extrusion, and maintains its strength across a wide temperature range. Heat-cured LSR is transparent, durable.
- Room Temperature Vulcanized Silicone Rubber (RTV): This silicone rubber has two types of composition: RTV-1 (one-part) or RTV-2 (two-component) systems. This affects the hardness range of the silicone, from being very soft to a little bit harder. This makes it ideal for sealing, potting, or encapsulation applications.

Key Properties & Characteristics of Silicone Rubber
Silicone is the primary reference for a class of inorganic polymers. It has remarkable properties and characteristics that make it ideal for various industrial purposes. You can change its properties by attaching different methyl groups to its molecular chain.
That means it’s possible to make silicone rubber more flexible, soluble, or chemical or temperature resistant by adding a suitable material.
But what are these properties? Let’s explore them individually so you can understand them better.
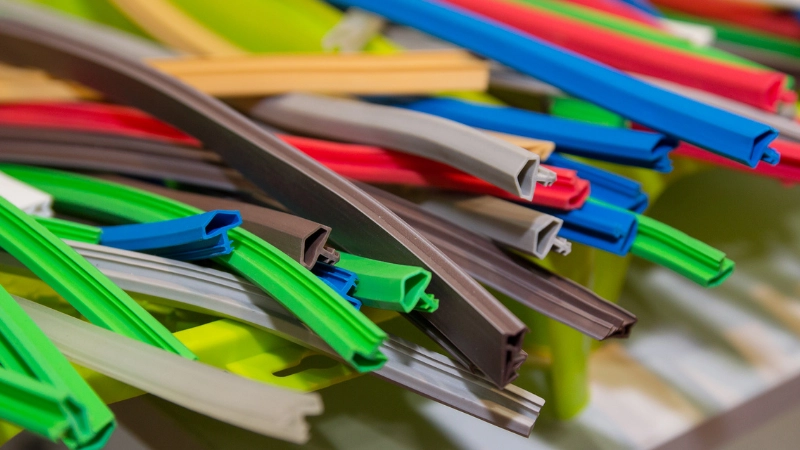

General properties of silicone rubber
Here are the general properties that you can find in silicone.
- It’s very soft and pliable. Its durability allows it to retain its original structure without cracking, hardening, and fatigue. This makes it ideal for high-pressure applications that include repetitive loading and unloading.
- It has hydrophobic properties that can repel water. This ensures that specific parts or areas have protection against leakages. This makes silicone rubber an effective sealant, waterproof coating, or insulation. It can do this without restricting breathability.
- Its molecular chains have low rotational energy barriers. This allows it to move with high flexibility when even a small amount of energy is applied.
- It’s highly resistant to aging. The durability of silicone rubber is thanks to its ability to resist UV radiation, extreme temperatures and chemical exposure.
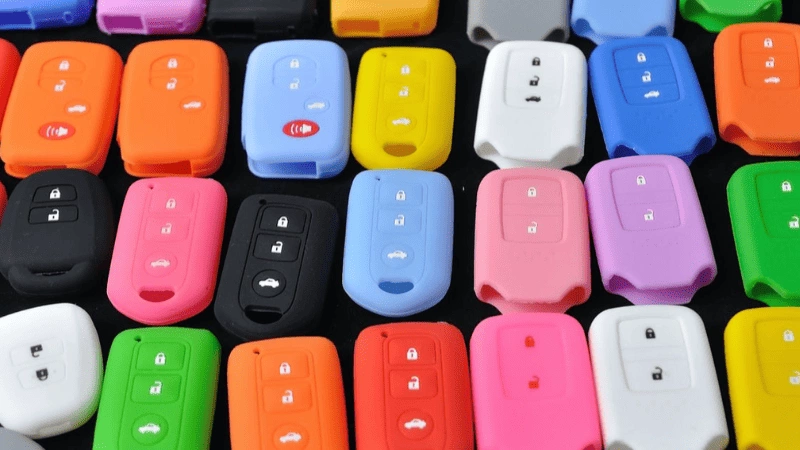

Physical properties of silicone rubber
The exact composition of silicone allows it to be used in different processes to create various sizes and shapes, from tubing, sheets, gaskets, etc. Despite this, it won’t compromise its valuable physical properties. These properties include the following:
- Flexibility: The combination of silicone and oxygen in the chain backbone gives the material incredible flexibility. It can move, fold, bend, and twist even after setting and molding without damaging its original structure.
- Hardness: Silicone hardness is measured using two scales: Shore OO for soft, sponge-like silicone, and Shore A for denser types. A common range for thicker silicone is 30A to 70A, while high-performance grades can be as low as 10A or as high as 90A.
- Color and Finish: In its original state, silicone is translucent white. But depending on the design, the silicone product can appear in various colors and textures.

- Electrical properties: Silicone boasts excellent electrical insulation properties, with a dielectric strength typically between 20 and 30 kV/mm, making it ideal for high-voltage applications. Silicone can also accept conductive fillers, making it an effective sealant for electronic devices. You can use it as EMI O-rings or heat transfer pads.
- Thermal properties: Silicone rubber is both a thermal insulator and conductor, depending on its formulation. Its thermal conductivity typically ranges from 0.2 to 0.3 W/(m·K). This makes it suitable for low-heat transfer products, such as tubing for oven applications or other food-related devices.
- High melting point: Since silicone is a thermoset elastomer, it won’t melt. It can maintain its mechanical structure even in temperatures up to 300°C.
Benefits of silicone rubber
Thanks to the previous list of properties, silicone rubber possesses the following incredible benefits.

- Steam resistance and flame retardancy: The general resistance of silicone rubber to steam, flame, and heat makes it an ideal material for high-temperature applications like food prep situations. This also makes it suitable for industrial applications that use heat-inducing machinery and processes.
- High resistance to compression set: Due to its curing process, silicone rubber has a low compression set, generally below 10% at 150°C. So, it can maintain its original shape and sealing force over a long time after being compressed.
- Food-grade and medical-grade ratings: Among the other rubber materials, silicone rubber can withstand the rigorous testing requirements to declare a material acceptable for food or medical applications. It also doesn’t use harmful materials like plasticizers or chemicals like BPA.

- Inertness: This is one of the properties that make silicone rubber ideal for medical purposes. It does not react even if it interacts with biological and chemical elements. That means it won’t trigger allergic reactions even upon skin contact.
- Resilience and rebound: Silicone rubber is flexible and will always return to its original shape even after twisting, bending, or folding. But this will still depend on the original hardness measure of the silicone before its application.
- Tensile strength: The tensile strength of standard silicone rubber is between 5 and 10 MPa. Some high-grade types can reach up to 1,500 psi. And its elongation at break can be anywhere from 200% to 700%.
Applications of Silicone Rubber Products
The properties of silicone rubber products make them ideal for various applications. The typical applications include the following.

Automotive
This is probably the most common application of silicone rubber. Because of its temperature, chemical resistance, tear strength, electrical insulation, etc, the automotive industry uses it for multiple parts.
Among the uses are gaskets, seals, sealants, spark plug tires, heat exchangers, engine covers, radiators, valve covers, and many more.
Food and Consumer Products
Silicone rubber is safe to come into contact with food. Its ability to repel fungal decay and practical sealing qualities ensure that leakages won’t happen and bacteria can’t grow. This is why it’s an excellent material for food packaging, prep equipment, trays, baking molds, and other kitchen appliances.
Electronics
The electrical properties of silicone rubber make it the ideal material or component for connectors, insulators, or control units, etc. It’s also applicable for lighting applications like diffusers, reflectors, floodlights, lens mold, etc.
Silicone rubber is effective in these applications because its aging properties and temperature resistance make it resistant to vacuum collapse.
Healthcare
Silicone rubber can achieve a medical-grade rating because of its inertness. It gives the material biocompatibility properties that make it safe as medical tubing, seals, catheters, o-rings, gaskets, membranes, masks, and more.
The biocompatibility property also makes silicone safe for any application that comes into contact with human skin. This includes mouthpieces, goggles, bands, etc.
Conclusion
Silicone rubber is versatile, durable, and safe, making it the ideal choice for reliable and custom product solutions. With outstanding temperature resistance, flexibility, and biocompatibility, it outperforms many other materials. Thus, it is commonly used across automotive, medical, food, and electronic industries.
Ready to Bring Your Custom Silicone Project to Life?
Whether you need a custom design or already have one, Hongju Silicone is your go-to partner. We specialize in producing high-performance silicone rubber products. And we offer a wide range of high-quality OEM and ODM services.
Contact us to leverage our low MOQs, rapid prototyping (3-5 days!), and decades of molding expertise to bring your project to life!