From automotive to consumer goods, all industries utilise the rubber mixing process. Read this guide to get an idea of what rubber mixing is, along with the techniques of rubber mixing and the factors that affect it.
What Is Rubber Mixing?
Rubber in its original form is too delicate for use in any product. Rubber mixing is done to make rubber fit for use in certain industrial applications.
Rubber mixing is a common process in rubber production and processing. In the rubber mixing process, raw rubber is blended with certain additives to enhance its properties. The raw materials used in this process include polymers (base rubber), fillers, plasticisers, curing agents, antioxidants, and pigments.

The purpose of rubber mixing is to make rubber durable and flexible, and to improve the resistance of rubber to heat and chemicals. To sum up, we can say that the rubber is made perfect for use in different products by undergoing a process called rubber mixing.
It is important to note that rubber mixing and compounding are not the same terms. Rubber mixing means using machines to blend the raw rubber with certain additives to give the rubber the desired properties.
Compounding, on the other hand, includes selecting the additives to give rubber the desired properties.
Types of Rubber Compounds
Rubber compound is a chosen blend of raw rubber and additives. In a rubber compound, the raw rubber and additives are selected based on the mechanical properties one wants the final product to have. There are several types of rubber compounds; the common ones include:

1. Natural Rubber (NR) Compounds
Natural rubber is derived from the latex material of the rubber tree. This rubber compound has excellent tensile strength, high abrasion resistance, and high elasticity.
This type of rubber compound is used where high elasticity is needed, like in conveyor belts, shock mounts, and vibration dampers.
2. Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (SBR) Compounds
This type of rubber compound is made from styrene and butadiene. Styrene gives rubber abrasion resistance, while Butadiene adds to rubber flexibility and elasticity.
The properties of the SBR compound include good abrasion resistance, cost-effectiveness, and consistent performance. This type of compound is easy to produce. SBR compounds are commonly used in car tires, shoe soles, and industrial mats.
3. Nitrile Rubber (NBR) Compounds
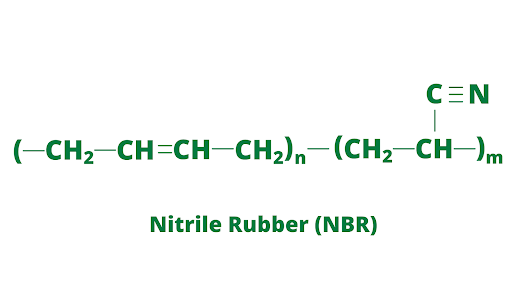
This compound is resistant to oil, chemicals, and fuels. NBR compounds are made from a copolymer of butadiene and acrylonitrile.
Products that come in direct contact with oils are made using this compound. O-rings, fuel hoses, and gaskets are popular rubber products made using this compound.
4. Neoprene (Polychloroprene) Compounds
Neoprene rubber offers excellent weather resistance, flame resistance, and some degree of oil resistance. Being weather-resistant, this compound is widely used for making wetsuits.
5. Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) Compounds
These compounds are UV and ozone-resistant. As a result, EPDM compounds are generally preferred in products that are subject to ozone exposure and used in outdoor applications. For instance, roofing membranes, window seals, and automotive weatherstripping all use EPDM compounds.
6. Butyl Rubber (IIR) Compounds

The key properties of these compounds include excellent air-tightness, water-tightness, and vibration-damping. Owing to these properties, sealants, inner tubes, and pharmaceutical stoppers use IIR compounds.
7. Fluoroelastomer (FKM) Compounds
This type of rubber compound is resistant to high temperatures and chemicals. Rubber products that are exposed to extreme temperatures and have to withstand heat for a long period of time are made using this compound.
8. Silicone Rubber Compounds
Silicone rubber mix is one of the most popularly used compounds. This compound can handle extremely high or low temperatures. The silicone rubber mix is widely used in food-grade and medical applications.
9. Acrylonitrile-Butadiene Rubber (NBR) Compounds
This compound is resistant to oil and fuel. Fuel hoses, oil seals, O-rings, gaskets, gloves, and other products exposed to oils and fuels use this type of compound.

Overview of the Rubber Mixing Process
Given below are the rubber mixing equipment needed for efficient mixing, and a step-by-step rubber mixing process for engineers and production managers to conduct it easily.
Equipment Needed for Rubber Mixing
Before starting the rubber mixing process, it is important to have all necessary equipment ready. Below are the main equipment used for rubber mixing:
1. Mixing Machines
The first and most important equipment needed for rubber mixing is a mixing machine. There are different types of mixing machines; you need to choose the one that best suits your needs.
The common types of mixing machines include internal mixers (Banbury Mixers) and open mills (Two-Roll Mill).
2. Rubber Mixing Bowls
Mixing bowls with a rubber bottom are used to hold and mix the material before it is added to the machine. Bowls with a rubber bottom ensure a homogeneous blend and prevent slipping during the entire process.
For instance, as the KitchenAid stand mixer rubber feet keep a kitchen mixer steady, industrial rubber mixers use a similar rubber mixing bowl with rubber feet and vibration-damping pads to reduce movement and improve safety.
3. Temperature Control Systems
Overheating can contribute to premature curing and degradation of rubber. To prevent this, you need to have an efficient temperature control system.
After the mixing process, the temperature control systems cool down the rubber to prevent the issues that can be caused by overheating.
4. Weighing and Measuring Equipment
To achieve desired properties, one needs to accurately weigh and measure the additives. Even a slight error in measuring can impact the mechanical properties of the rubber. So make sure to get weighing scales to weigh all components.
5. Safety Gear
Just like other processes, the mixing silicone rubber process also includes an element of risk. To avoid risks associated with extreme temperatures, moving machines, and chemicals, operators need to have safety equipment.
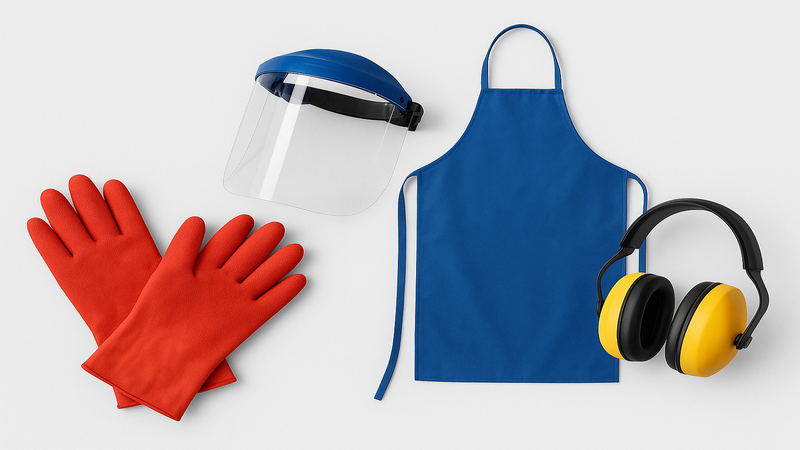

The safety equipment includes gloves, face shields, protective aprons, and ear protection gear.
6. Quality Testing Equipment
To determine the properties of the rubber mixing compound, production managers need to have certain quality testing equipment. Some of the common quality testing equipment includes rheometers (to measure curing behaviour), tensile testers (to check strength), and hardness testers.
Step-by-Step Rubber Mixing Process
To assist production managers with carrying out the rubber mixing process easily, a step-by-step mixing process is outlined below.
1. Raw Material Preparation
The first step in the rubber mixing process is to prepare the raw material. Sort and clean the raw rubber and additives to begin the mixing process.
2. Weighing & Measuring
The other crucial step is to measure and weigh the raw materials accurately. Before adding any additive to the mix, measure and weigh it to ensure that the final product is in accordance with the requirements.
3. Pre-Mixing
Occasionally, production managers need to mix the ingredients before adding them to the rubber mixing machine. This step ensures that the additives are mixed evenly and guarantees the proper formulation of the final product.
4. Mixing Stage
The fourth and most important step of rubber mixing is the main mixing stage. In this step, the raw rubber and additives are blended using either internal mixers or open mills.
5. Dispersion & Homogenization
This step is all about achieving a proper dispersion & homogenization of the additives. Fillers like carbon black and silica must be distributed evenly through the rubber mix.
6. Temperature Control
As mixing generates heat through friction, extreme heat can result in ruining the rubber by premature curing. To prevent this, one needs an optimal temperature control system.

7. Monitoring & Testing
Throughout the mixing process, engineers and product managers need to test the quality of rubber samples. The testing equipment mentioned above helps determine whether the rubber samples meet the required specifications.
8. Cooling & Storage
Once the mixing process is done, you need to cool down the rubber compound and store it. Storing the rubber compound appropriately is important to keep its quality optimal for a long period of time.
9. Further Processing
Depending upon the requirements of the final products, the rubber compound is shaped, moulded, or processed in this step.
10. Quality Assurance
In this step, the rubber compound is tested for stability, flexibility, and strength. Only the rubber that is up to the mark and meets certain quality specifications is selected for further processing. This step also ensures batch consistency.

11. Cleanup & Maintenance
The last step is to clean the tools and machines to avoid contamination in future batches. Maintaining the equipment extends its life and guarantees consistent performance, so you need to maintain the equipment after every use.
Rubber Mixing Techniques
There are different techniques used for rubber mixing. The production managers need to choose the one that is based on their batch size, end product requirements, and the material type.
The commonly used rubber mixing techniques, along with their advantages and limitations, are mentioned below:
1. Open Mill Mixing
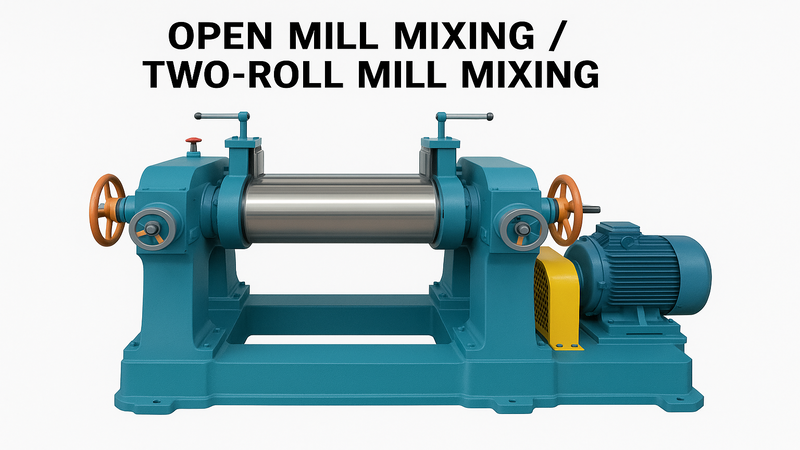
Open Mill Mixing is the most common rubber mixing technique. It is also known as two-roll mill mixing, as it uses two counter-rotating rolls that blend rubber with additives.
In open mill mixing, the raw materials are weighed and added to the rubber mixing machine. The material passes through the roll gaps, where it is shredded and kneaded to blend with additives.
The rubber compound is then compressed and spread onto a thin sheet. The sheet is consistently folded and fed back into the roll gap to ensure uniformity. Once uniform, the compound is collected as a sheet, which is then cut and stored for use.
The advantages of open mill mixing are that it is cost-effective, simple, and ideal for custom formulations. However, there are a few limitations of this rubber mixing technology as well. The limitations are that this method is labour-intensive and is a bit slower as compared to the other methods.

2. Internal Mixer
An internal mixer, also known as a banbury mixer, consists of multiple components for blending raw rubber with additives. These components include a mixing chamber, rotors, a door drop, and a cooling system.
In an internal mixer, you first load the material into the mixing chamber. After the material is loaded, the rotors begin to rotate. The rotation generates heat and friction, which soften the rubber and ensure dispersion.
The temperature control system keeps the temperature under control, and once the mixing is done, the door of the drop chamber opens, and the final product is collected.
The advantages of the Banbury mixer are that it is ideal for large-scale production, is automated, and delivers consistent results. The limitations include a higher initial investment and unsuitability for small batch production.
3. Continuous Mixing

Continuous mixing, as the name indicates, carries out the rubber mixing process without stopping. Continuous mixing usually comes as either a single or twin screw extruder.
A single screw extruder has one screw and works best for simple mixes. A twin screw extruder has two screws and is best for better and faster mixing. A twin extruder can handle more types of materials than a single screw extruder.
In both single and twin screw extruders, material is loaded into a hopper. The continuous rubber mixing mill process is ideal for high-volume production and guarantees a uniform mix. The con associated with this type of mixing is that it is complex to set up.
| Technique | Batch/Continuous | Ideal For | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Open Mill | Batch | Small batches | Low cost, allows custom formulation | Labour-intensive, slower |
| Internal Mixer | Batch | Large-scale production | Consistent quality, automated | High initial cost |
| Continuous Mixer | Continuous | High-volume production | High efficiency, uniform mixing | Complex setup |
Applications of Rubber Mixing

Rubber mixing is widely used in various industrial applications. The common applications of rubber mixing are:
- In the automotive industry, for manufacturing durable seals, gaskets, and hoses
- In construction, for making rubber roofs, in waterproofing, and in certain outdoor applications
- For making the soles of shoes
- In consumer goods, including swimming caps, utensils, rubber bands, and toys
- In the medical sector, for making medical devices, gloves, and tubes.
- In electronics, for making insulating jackets
Factors Affecting Rubber Mixing Methods
There are several factors affecting the mixing process. The factors include:
- Raw material quality: The low-quality raw material results in low-quality final products.
- Mixing time & temperature: Overmixing can generate more heat, which can degrade the rubber product.
- Chemical reactions & curing: Chemical reactions and curing can affect the rubber mixing method by affecting how the rubber will harden, set, and gain its final properties.
- Operator skills & training: If the operator is not trained or lacks the skills needed, the final product might not be fit for use
- Environmental factors: Certain environmental factors, like humidity and temperature, can also affect the rubber mixing methods.
Luckily, by taking proper measures, you can prevent the defects and achieve the desired rubber properties easily.
Best Practices for Optimising the Rubber Mixing Process

To optimise the rubber mixing process, make sure to develop the right compound formulation. Choose the type and quantity of additives that are as per your requirements.
Make sure that the raw material you are using meets the quality standards. Another practice for optimising the rubber mixing process is to weigh and measure the raw materials accurately.
Also, ensure that the equipment in use is well-maintained. Additionally, monitor the mixing process in real time to identify defects in the final rubber product.
Final Verdict
Rubber mixing’s ultimate goal is to make the rubber durable, sturdy, and flexible. When conducted carefully, rubber mixing makes rubber ideal for use in various industrial applications.
To get benefits in the long term, it is always advised to partner with experienced and reputable names in the market.
Hongju Silicone – Your Trusted Rubber Solutions Partner
Having more than two decades of expertise in offering custom rubber solutions, Hongju Silicone is a name you can trust.
Our certified team is always ready to assist you with all your needs. Also, our products are CE and FDA approved, so you don’t need to worry about safety while partnering with us.
Contact us today for a consultation or to obtain a quote for your bulk requirements.
FAQs
Q1. What is the mixing time for rubber?
In an internal mixer, mixing time ranges from 8 to 18 minutes per batch. In open mills, the timing can be 20-40 minutes. It is essential to note that the timing varies depending on requirements, formulation, and complexity.
Q2. What is the fill factor for rubber mixing?
The fill factor means the ratio of the volume of material to the total volume of the mixing chamber. Ideally, the fill factor ratio for rubber mixing ranges from 75% to 80%.