The oil spill looks terrible, right? This is mainly due to wear and tear of the oil seal.
What are they, and how do they work? These seals may appear small but are vital to the mechanical system. They prevent fluid leaks that often cause equipment failure.
Our comprehensive guide explains the functions of oil seals through basic diagrams and explores various types of seals. Follow our step-by-step installation guide with professional maintenance tips.
What is an oil seal and why does it matter?
These are simple components that prevent lubricating oil leakage in machinery and equipment. They work by sealing the space between the fixed and moving parts of the machine. At the same time, the seal prevents foreign matter, such as dirt, from entering the machine.
Lubrication is essential for the smooth operation of machinery, machines, or automotive engines. The oil seal keeps the lubricant in the machine. If fluid leaks due to a broken seal, the machine will experience extreme wear and tear.
In addition, various types of oil seals are widely used in automotive engines, transmissions, and pumps. They are also present in all hydraulic machinery and mechanical systems that require fluids to operate.
Parts for Oil Seals
Oil seals are not very complex components. Let’s explore the different parts of the seal. We will learn more about their functions on this basis.
Shell
The enclosure is designed to provide a secure fit. It is made of metal to strengthen the seal. Other types of oil seals also have rubber-coated housings for added durability. Housing allows you to easily install and maintain the seal inside the housing.
Seal lip
The sealing lip consists of two parts: the main lip and the dust lip. Each part has a different function, but both are crucial. The main lip is in direct contact with the rotating portion to provide a sealing effect. It prevents liquid leakage under high-pressure conditions.
In addition, the dust lip can block external contaminants. The oil is sandwiched between the two lips, creating a sealing effect. The sealing main lip can be made of rubber, elastomer, or PTFE. The choice of material depends on the need, as these materials vary in performance.
Spring
The garter spring supports the seal lip to ensure contact with the rotating part. It exerts continuous pressure on the sealing lip to achieve a tight seal. The springs are made of stainless steel to maintain durability and long life. It also reduces wear and tear on the main lip.
Now that you know this, let’s discuss how it works.
How does an oil seal work?
The diameter of the oil seal is smaller than the shaft in order to surround it tightly. When the seal is installed on the rotating shaft, it forms a barrier that prevents the lubricating oil from leaking and blocks contaminants.
The spring ensures continuous contact with the shaft by applying a radial force, resulting in a strong sealing effect. The springs are adapted to different operating conditions. For example, during high-performance operation, the pressure on the seal rises.
The performance and efficiency of this seal depend on several key factors. Select the right seal size for perfect alignment and fit. You must know the shaft diameter, slot width, and slot diameter. In addition, look for compatible sealing materials based on the intended application.
Types of Oil Seals
There are many available. You should pay attention to their applications to choose the best one.
1. Lip Seal (Single and Double Lips)
These seals are mounted directly on the shaft. They produce a suction seal effect to prevent leakage and contamination. The spring is wound around the seal, applying maximum pressure to enhance the sealing effect.
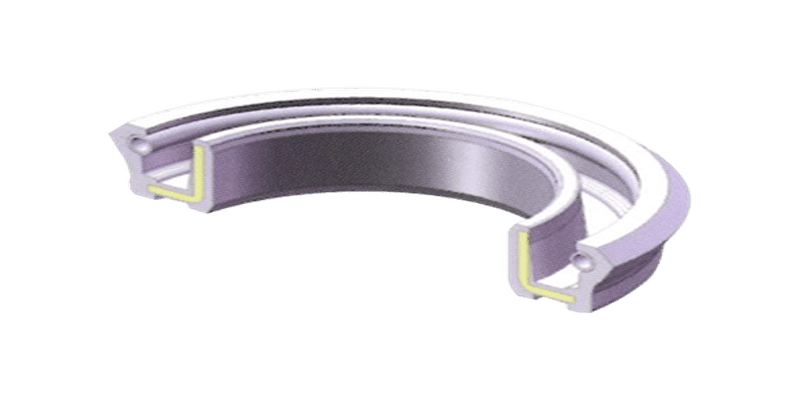
Single lip seal and double lip seal are different in design. The single lip seal has a rubber element attached to the shaft. It’s recommended for low-pressure applications only, as it is as it is ineffective in preventing contaminants.
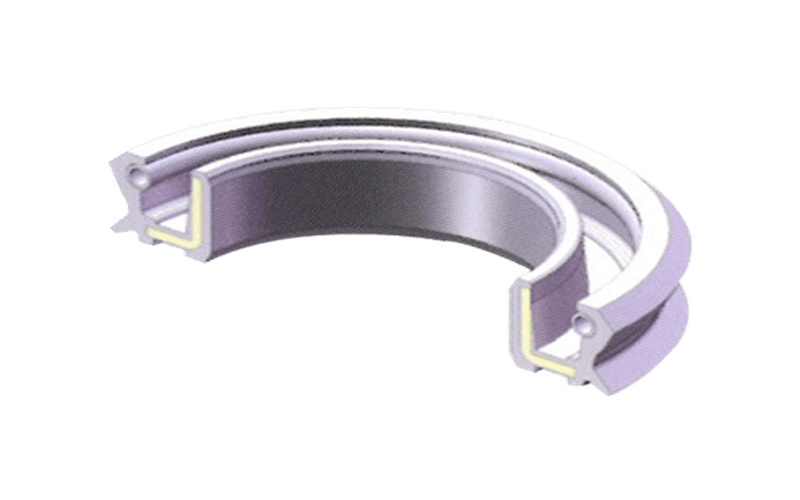
In addition, the double seal has two rubber elements fixed to the shaft. One element holds the liquid and the other keeps the air and contaminants from sliding inside. It provides better protection.Gases and pollutants. However, higher levels of friction cause hysteresis.
2. Rotary shaft seal
Rotary shaft seals are designed for low-pressure and high-speed applications. They provide relatively little friction and are ideal for motors and pumps. Seals prevent water, oil, and other fluids from leaking while maintaining the required pressure.

The rotary shaft is encapsulated in hub bearings, differential gears, engine crankshafts, fuel pumps, and water pumps. They keep the fluid within the system for seamless operation.
3. Radial oil seal
Radial oil seals have special applications on rotating shafts, crankshafts, and camshafts. They prevent oil leakage by sealing the gap between the rotating shaft and the machine housing.The seal is mounted on the shaft. The inner rubber portion of the seal is wrapped around the shaft.
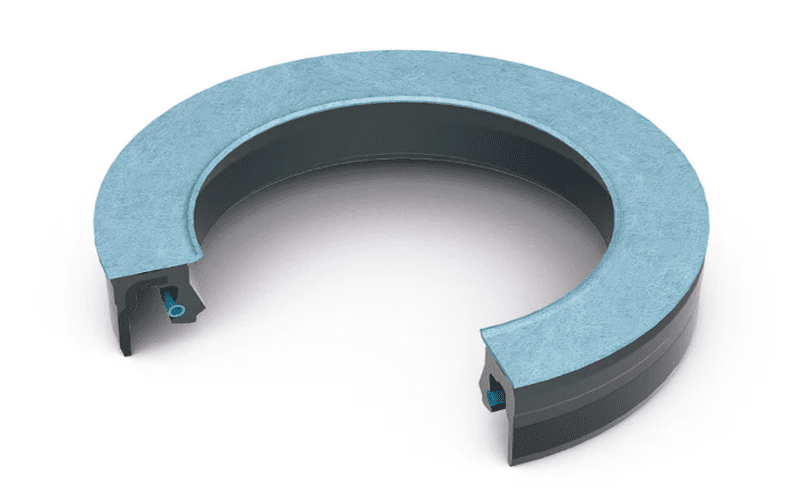
When the shaft rotates, it acts as a barrier to hold the lubricant. Pollutants are also prevented from entering the system.
4. U Cup and V Ring

As the name suggests, U-cups are U-shaped seals for hydraulic and pneumatic applications. They provide a leak-proof seal to hold fluid in high-pressure systems, and their flexible design helps avoid wear and misalignment.

The V-ring is a rotating seal attached to the shaft. These seals can rotate in two directions depending on the movement of the shaft. Designed for high-speed applications due to flexible design adaptability. They provide effective pollution protection.
5. Professional Seals
There are many other special seals on the market, including mechanical seals, hydraulic seals, and magnetic seals.
Mechanical seals are used in high-pressure applications such as pumps, mixers, etc. The mechanical seal is mainly used as a barrier between the rotating part and the stationary part of the pump. There are two sealing points in the mechanical seal; One is connected to the shaft and moves with it, and the other is stationary.
Hydraulic seals are used in hydraulic pumps to hold fluid in the system. These seals are made of polyurethane, Teflon, or rubber materials. Magnetic seals are less common but are very important in precision instruments, vacuum machines, etc. They use magnetic force to produce a sealing effect using ferromagnetic materials.
What are the functions of the oil seal?
These seals primarily prevent fluid leakage at high pressures but have other functions as well. Let us explore the function of these seals in detail:
Seal to prevent contaminants
Fast-moving parts, such as shafts and pistons, are sensitive to dust, foreign objects, and debris. Seals protect these critical components by limiting the flow of contaminants in the system. It uses rubber elements to form a barrier to block the entry of impurities. Any form of contaminant can cause wear, increase friction in the system, and lead to excessive wear.
Lubricate and maintain
During high-pressure operation, lubricants may leach out of the system. The seal is used to maintain the pressure required to hold the lubricant. They also fill in the space where the lubricant can leak.
Heat and pressure resistance
The seals are manufactured according to ISO and DIN standards. The type of oil seal varies depending on the application.The correct seal and material are selected based on the fluid to be sealed and the expected temperature and pressure levels. It ensures that the seal can withstand high temperatures, pressures, and chemical exposure.
Prevent leakage
Leaks are catastrophic for moving parts in machinery. Any difference in the optimal fluid level results in high friction, which affects performance. The seal can close the gap between the stationary housing and the moving shaft to prevent leakage.
How to Choose the Right Oil Seal?
When looking for the perfect seal, pay attention to the type, oil seal size, and material. Where will you install the oil seal? It answers which type best suits your needs. Next, determine the desired size and select the appropriate seal. You must measure the shaft diameter, slot diameter, and slot width.

The choice of oil seal material depends on its specific application. You should check the maximum pressure and temperature level expected for the seal. For example, PTFE is suitable for low-pressure applications.
We will look further at the application aspects of the material in the next section.
Oil Seal Materials and Specifications
Depending on the use, all parts of the seal have specific material requirements.
The housing is mounted on the shaft and undergoes certain resistance under high pressure. Therefore, it uses carbon steel for reinforcement and resistance.
After the outer case, the seal lip is the most critical part of the seal. The material selection depends on the fluid type and shaft speed. Seals commonly use rubber materials like nitrile rubber, fluorine rubber, and polytetrafluoroethylene.
The spring helps to ensure continuous contact with the moving parts. Preventing leaks in the machine is essential. Carbon steel springs are usually used because they do not deform quickly.
| Oil Seal Part Type | Common Materials |
|---|---|
| Outer Case | Stainless steel |
| Carbon Steel | |
| Aluminium | |
| Sealing Lip | Nitrile Butadiene Rubber material |
| Fluorine rubber | |
| Polytetrafluoroethylene | |
| Spring | Carbon steel |
| Copper alloy |
Oil seal installation and maintenance considerations
Are you looking for help installing an oil seal? Follow our step-by-step guide and install the seals like a pro. Don’t forget to check maintenance tips to ensure the durability and longevity of the seals.
Installation steps
Here’s a DIY installation guide. Follow each step to ensure proper installation and avoid any errors.
Prepare for installation
You must ensure that the seals, shafts, and holes are clean. In addition, surfaces and seals should be checked for damage or wear to prevent leaks. Apply lubricating grease to the shaft to facilitate the installation of O-rings and to avoid bouncing.
Proper alignment
The seal needs to be mounted vertically on the shaft and hole. If misplaced, the seal can experience high pressure, leading to leakage or failure.
Tools and materials required
Now that you know the initial steps, here are some essential tools for installing seals:
- Lubricating oil to make the seal slip.
- Gloves to grip firmly to prevent damage.
- Bearing Mounting Kit or Seal Drive for Mounting
Install oil seal
When installing seals, ensure proper alignment. Drive the seal into the hole using the bearing mounting tool.Choose the right tool to set the seal perfectly so that it does not have any skew or damage. If the seal does not fit, avoid hammering or forcing it. Realign the process appropriately.
Common mistakes to avoid
- Cleaning the installation area is necessary because any debris in the seal can cause a leak.
- Checking the alignment helps ensure the fit.
- Improper tool use or forced insertion can damage the seal.
Maintenance precautions:
Proper maintenance keeps seals intact for longer and ensures efficient operation.
- Arrange an inspection in time to check for damage, especially the seal lip.
- If the seal shows signs of damage such as cracking, hardening, or liquid oozing, you should replace it.
- Lubrication is necessary for the smooth operation of the seal. Use compatible lubricants for best results.
- Dust, debris, and other impurities can build up around the seal. Cleaning them prevents contamination and reduces wear and tear.
Seal Diagrams and Visual Instructions
Here is a seal diagram to explore the various parts of the seal:
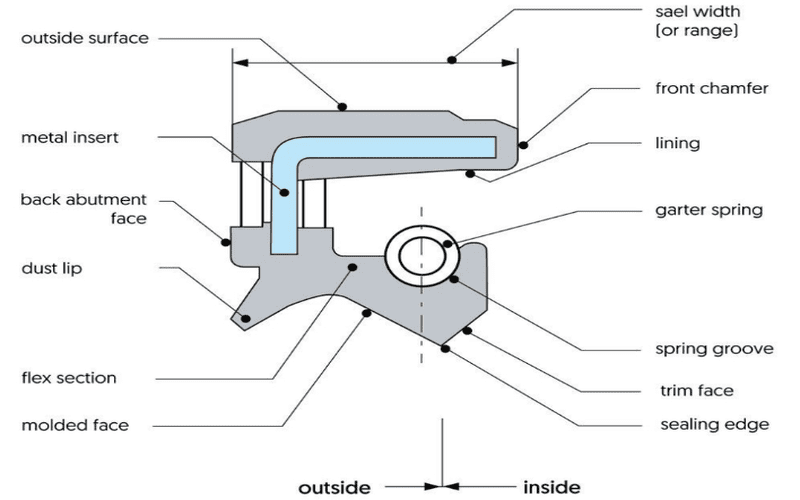
Description
The seal diagram shows a double-lip oil seal. Its external surface area is reinforced by rubber and has metal inserts. The rear contact surface and the opposite side provide a sealing effect. The dust lip blocks external contaminants. If the seal expands under high pressure, the elastic part increases flexibility and space.
The sealing edge is in direct contact with the surface of the shaft and seals the gap, while the metal trim face holds it in place. In addition, the garter spring stays within the spring groove.
You can check the seal width by measuring the outside. Metal face surface and inner face diameter, as shown in seal drawing. In addition, the shaft diameter also needs to be used to determine the oil seal size.
When reading the seal diagram, people often do not check the groove design, resulting in inappropriate fits. They also overlook seal sizes, believing that all seals are the same.
Common Applications of Oil Seals
Different types of oil seals are used in various industries; they are part of almost all mechanical systems involving fluids. Here are some of their common applications:
Automotive industry:
Oil seals are widely used in the automotive industry. For example, your car has multiple oil seals to prevent leaks and protect moving parts from contamination. Critical components of any vehicle type (buses, trucks, etc.), such as engine crankshafts, camshafts, and hubs, also have these seals.
Industrial use:
The high-power hydraulic pumps and compressors used in the manufacturing process have oil seals to hold the fluid. They also protect moving parts from impurities. There are different sizes of hydraulic pumps and compressors specially designed for large machinery.
Household Electric Appliances:
Household appliances such as washing machines and dishwashers have mechanical seals. These seals help prevent water leakage and protect the motor. The seals used in household appliances are simple and made of rubber.
Oil seal troubleshooting
Whenever you find a problem with the oil seal, you can diagnose it yourself. The most common problems are due to repeated errors – first and foremost, leaks. The leak is caused by wear and tear. You must check the seal for signs of breakage and cracks, especially on the sealing lip.
Another common problem that leads to leaks is improper installation. If the seal is improperly installed, leaks are sure to occur. Check the seals to identify any gaps or tilted installations. Ideally, you should replace the seals and install a new one correctly.
Frequently Asked Questions
What’s an oil seal for?
These seals have two main functions: to prevent leaks and to prevent dirt, dust, and debris.
How to identify the right oil seal?
Accurate measurements and the required application can help identify the correct seal. Measure the shaft size and housing diameter, then select the appropriate seal width. Check the use cases to determine the type and oil seal material specifications.
Can the oil seal be reused?
No, these seals must never be reused. They can cause sudden oil leaks and cause equipment failure.
Conclusion
Hopefully, your journey has been insightful, from exploring the right oil seal function to choosing the right seal. Now you can get the perfect seal according to your needs. Finally, a professional installation guide will play an important role in getting you started.
Next, you can learn more about oil seals. It’s recommended that you read 6 Reasons for Choosing FFKM O-Rings & Seals to better understand seals.
Prevent oil spills: Get the highest quality oil seal
Hongju has more than 20 years of experience in manufacturing high-quality oil seals. It serves a wide range of industries with tailor-made products to meet their needs. Do you also want a performance-specific oil seal? Come to us now!