Is silicon the backbone of your industry? From semiconductors to construction materials, this element powers countless B2B applications.
In this article, we’ll explore its origins, composition, and manufacturing process. We will also shed light on the production uses and benefits of silicone.
What is Silicone Rubber?

Silicone Rubber is not the same as standard silicone and rubber separately. The former is a specially processed form that undergoes vulcanization to achieve enhanced
- Elasticity
- Heat and cold resistance
- Tear strength
- Weather resistance
- Biocompatibility
Raw silicon is a polymer that is flexible and has an unstructured form. However, silicon rubber is a resilient and rubber-like material that is cured using chemical elements and heat.
So in industrial applications where flexibility and resistance are needed, silicon rubber seems the perfect fit.
Compared to raw silicone, which is softer and more susceptible to deformation, silicone maintains its shape under stress. Moreover, it offers superior tear strength and remains stable across a wide temperature range.

Beyond flexibility and heat resistance, silicone rubber is also known for its biocompatibility, electrical insulation properties, and weather resistance. It does not degrade easily when exposed to moisture, ozone, or harsh chemicals.
This makes it ideal for sealing applications, and medical applications including respiratory masks, and high-performance gaskets.
The Origins of Silicone
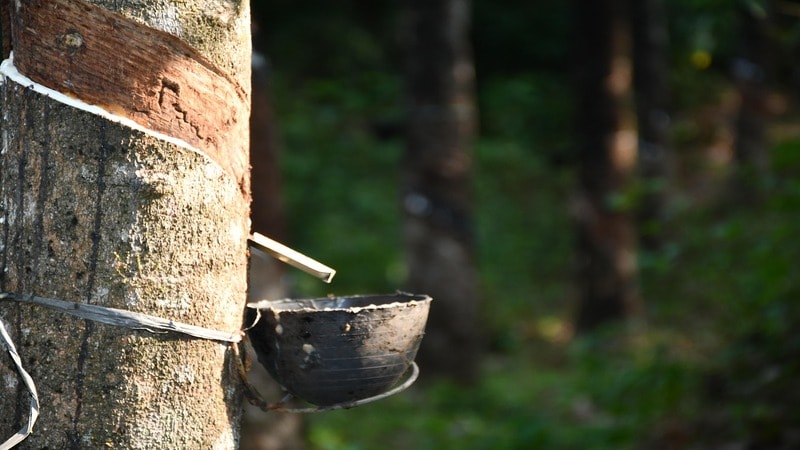
Silicone is primarily derived from silica. Silica (SiO₂) is one of the most abundant materials on Earth, making it a readily available resource for industrial processing. Its chemical stability and high purity make it an ideal raw material for producing silicone-based products.
Extraction and Processing of Silicone

The transformation of silica into silicone begins with its extraction from natural deposits. This is followed by purification to remove impurities.
The purified silica is then subjected to a high-temperature reduction process with carbon in an electric arc furnace. This produces metallurgical-grade silicon. This silicon is further refined through chemical reactions, such as the Müller-Rochow process.
Natural vs. Synthetic Silicone Sourcing
Silica can be obtained naturally from sand and quartz. It can also be synthesized from industrial byproducts. Natural silica is widely available and cost-effective, but its purity varies depending on the source.
On the other hand, synthetic silica is produced through controlled chemical processes and offers higher consistency and fewer impurities. This makes it suitable for high-tech applications such as electronics and pharmaceuticals.

How Is Silicone Rubber Made?
The process begins with the polymerization of siloxanes, which are chains of silicon-oxygen (Si-O) bonds. Here is what happens next. Moreover, methyl chloride and quartz sand are also involved in the process. Here is the process in detail.
Step 1: Polymerization of Siloxanes
The silicon-oxygen bond provides silicon atoms with unique flexibility and thermal stability. The polymerization process involves chemically modifying silanes to form long siloxane chains, which serve as the backbone of silicone elastomers.
Step 2: Adding Fillers and Additives for Specific Properties
To enhance performance, fillers and additives are incorporated into the polymer base. Common fillers, such as silica or carbon black, improve tensile strength, durability, and thermal resistance.

Step 3: Curing Methods: Peroxide Curing vs. Platinum Curing
Curing is the process that transforms raw silicone into a durable rubber material. In the next stage, the curing of peroxide happens, which involves organic peroxides. This is cross-linked under after heat transfer.
Overview of Quality Control During Production
Industrial standards are extremely crucial when it comes to production. Manufacturers conduct tests for:
- Mechanical strength
- Thermal resistance
- Chemical stability to verify consistency
Moreover, factors like viscosity, curing efficiency, and impurity levels are monitored throughout production. On top of that, the production requires compliance with industry regulations, such as FDA, ISO, and ASTM standards.
What Are the Applications of Silicone Rubber?
There are many industrial applications for the product. Here is a guide to production uses of the rubber.

| Types of the silicone rubber | Application |
|---|---|
| Medical | It is used in prosthetics, implants, respiratory masks, and medical-grade adhesives due to its biocompatibility, flexibility, and resistance to bacteria. |
| Construction | It is essential for sealants, weatherproofing, and coatings. These features offer durability, water resistance, and stability in harsh conditions. |
| Automotive | Silicone substances are used in gaskets, tubing, and engine components because they can withstand temperatures, and show flexibility, and longevity under mechanical stress. |
| Consumer Products | It is found in kitchenware, electronics, and wearable devices due to its non-toxicity, heat resistance, and ability to maintain performance over time. |
Different Types of Silicone Rubber and Silicone Materials
There are many different types of silicone rubber, each suitable for a different purpose. Here are the top types:
| Type | Key Characteristics | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Food-Grade Silicone | Non-toxic, odorless, heat-resistant | Baking tools, kitchenware |
| Medical-Grade Silicone | Biocompatible, sterilization-resistant | Implants, tubing, adhesives |
| Industrial-Grade Silicone | Tough, weather-resistant | Seals, insulation, automotive parts |
| High-Temperature Silicone | Stable at up to 300°C | Aerospace, electronics |
What Makes Silicone Rubber an Ideal Material?
Silicone is considered an ideal material because of its durability, resistance to heat, and greater flexibility. Here are these features in detail.

1. Exceptional Heat and Cold Resistance for Extreme Environments
It remains functional in temperatures ranging from -60°C to 300°C. It does not crack, melt, or degrade under extreme heat or freezing conditions.
2. Long-lasting durability and Resistance to Wear and Aging
Unlike conventional rubber materials, the rubber does not break down easily over time. Moreover, it resists UV rays, ozone exposure, and mechanical wear.
3. Superior Chemical Resistance for Industrial and Medical Use
It is non-reactive with most chemicals, oils, and solvents. This makes it suitable for applications in healthcare, pharmaceuticals, and manufacturing.

4. High Flexibility and Customization for Various Applications
It is easily molded into complex shapes and structures. Moreover, it is widely used in medical devices, electronics, and consumer goods.
5. Excellent Electrical Insulation for Safe and Reliable Electronics
With outstanding dielectric properties, silicone rubber prevents electrical component leakage and withstands high voltages. It is a key material in insulating wires, circuit components, and high-performance electrical equipment.
Silicone Rubber vs. Other Materials
Silicone Rubber vs. other elastomers
| Property | Natural Rubber | Synthetic Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Derived from the latex of rubber trees | Manufactured from petroleum-based chemicals |
| Cost | Less expensive | Can be more expensive due to production processes |
| Durability | Less durable | More durable (used in seal applications) |
| Elasticity | Excellent flexibility and resilience | Varies by type |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable | Non-biodegradable |
When it comes to high-temperature environments, Silicone ones outperform traditional elastomers, such as nitrile or neoprene. While other elastomers degrade or lose elasticity above 150°C, silicone maintains its flexibility and integrity in temperatures up to 300°C.
Silicone Rubber vs. traditional rubber vs. plastic
| Property | Silicone Rubber | Natural Rubber | Plastic |
|---|---|---|---|
| Heat Resistance | -60째C to 300째C | -40째C to 100째C | <100째C |
| Flexibility | Excellent | High | Low |
| Chemical Stability | Excellent | Moderate | Poor |
| UV & Ozone Resistance | High | Low | Low |
| Durability | Long-lasting | Degrades faster | Prone to cracking |
What is Liquid Silicone Rubber?
LSR is a two-part, highly fluid silicone elastomer that can be easily injected into molds and rapidly cured into a solid rubber component. It is often used in applications requiring high flexibility, biocompatibility, and heat resistance.
Moreover, it is commonly found in
- medical devices
- automotive parts
- consumer electronics
Liquid Silicone Rubber Molded Components
- Two compounds are combined, one with a platinum catalyst and the other with a cross-linker and alcohol inhibitor.
- The mixture is injected into a mold cavity.
- Heat is applied to cure the mixture, resulting in a flexible silicone part.

Silicone Rubber in Extreme Temperatures
Unlike conventional elastomers, which degrade at high temperatures, the silicone ones remain stable under intense heat.
The “melting point” of the rubber is generally not a relevant factor, as it does not melt like thermoplastic materials. Instead, it begins to degrade or lose structural integrity at temperatures above its maximum heat resistance.
Additionally, its auto-ignition temperature, which is typically above 450°C, ensures that it will not spontaneously combust under normal conditions. However, prolonged exposure to excessive heat may lead to surface degradation.

The Environmental Impact and Sustainability of Silicone Production
High temperatures are required for the extraction and processing of silicone materials. This makes the process very energy-intensive, particularly when it comes to converting silica into metallurgical-grade silicon.
This process, combined with the need for chemical treatments to produce silanes, contributes to a notable environmental footprint.
Despite the energy costs associated with product production, silicone materials are highly durable and resistant to extreme temperatures, UV rays, and weathering. You do not need to replace silicone during production.
This longevity helps reduce the overall environmental impact over the product lifecycle. Moreover, silicone is recyclable, and efforts are being made to improve silicone recycling methods, allowing the material to be reused in different applications.

How to Choose the Right Silicone Rubber?
When selecting silicone rubber, it’s crucial to consider the temperature range it will be exposed to. This is because silicone is known for its ability to withstand both extreme heat and cold.
It can be customized to meet the precise needs of different industries. B2B buyers can select from a variety of grades, colors, and hardness levels. They can also incorporate additives such as flame retardants or conductive properties.
Many important certifications, such as FDA, ISO, or UL, will ensure that silicone rubber meets industry standards for safety, quality, and performance.
These certifications are especially important for applications in the medical, food, and pharmaceutical industries, where regulatory compliance is critical.
Conclusion
Silicones’ exceptionally diverse properties make them a versatile material used across many industries in a wide range of applications. While it is derived from a natural product (silica), its production and material pose a significant environmental impact.
However, advancements in silicone recycling and sustainable manufacturing practices are helping to minimize this footprint.
Are You Ready to Transform Your Business with High Quality Silicone Components?
Hongju is committed to delivering top-notch products designed to meet your specific business needs. With years of experience and a dedication to quality, we specialize in providing silicone solutions that stand out for their performance and durability.
Request a free consultation or download our product catalog to see the wide range of options we offer. Let Hongju help you achieve business success with customized silicone solutions tailored to your requirements.
FAQs: What Are the Most Common Questions About Silicone Rubber?
Q1. Is silicone rubber eco-friendly?
A. Yes, silicone rubber is considered more eco-friendly than many other materials due to its durability and recyclability.
Q2. What’s the difference between silicone rubber and other elastomers?
A. Silicone rubber differs from other elastomers like natural or synthetic rubber in its superior heat resistance, flexibility, and chemical stability.
Q3. How does the curing method affect product performance?
A. Platinum-cured silicone is more suitable for medical and food-grade applications due to its purity and non-toxicity. However, peroxide-cured silicone offers higher strength and is used in industrial applications.
Q4. What industries benefit the most from silicone rubber?
A. Silicone rubber is widely used in industries like healthcare, automotive, aerospace, food, and electronics.
Q5. How customizable is silicone rubber for specific needs?
A. Silicone rubber is highly customizable to meet specific industry requirements. It can be tailored in terms of hardness, color, and additives, such as flame retardants.