In this detailed reference, we examine the history, development, and current state of antimicrobial polymers, as well as their processes, uses, and ecological effects.
Come along as we delve into the research behind antimicrobial plastics, examining their functional groups with insights from Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy, and discover how crucial they are to protecting public health and fostering sustainable lifestyles, all while exploring their water vapor permeability characteristics.
What is Antimicrobial Plastic?

Antimicrobial plastic is a cutting-edge polymer that inhibits the multiplication of microorganisms (germs) on its surface, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi.
To do this, unique coatings or additives are used during the production process. Silver nanoparticles are a popular antibacterial treatment due to their ability to inhibit microbial development.
These plastics may be used for a variety of purposes. They provide a sterile setting when utilized in the production of medical devices and equipment.
They contribute to a decrease in the likelihood of contamination in food packaging, aligning with stringent standards set by the European Food Safety Authority, thereby increasing the shelf life of the product.
They’re also used in food applications within the food preparation industry to make things like cutting boards and cutlery cleaner and safer to use.
Take the First Step:
Requst for an Inquire
Quality Meets Affordability. Inquire Now for High-Quality Products at Low Volumes.
Antimicrobial plastics, with their embedded active agents, have many uses, but their disposal raises environmental problems. To avoid polluting the environment, these materials must be disposed of properly.
Antimicrobial plastic is a game-changer for many industries because of its ability to prevent the spread of germs and bacteria. Its antibacterial activity and qualities are crucial for the prevention of infections and the preservation of the product.
However, ecologically safe production and disposal procedures may be the sole means of easing environmental issues.
Understanding the Science Behind Antimicrobial Plastics
Antimicrobial plastics’ amazing properties come from a well-constructed scientific process. These polymers’ innovative incorporation of antibacterial chemicals into their molecular structure makes them effective barriers to pathogenic germs.
The plastic components contain antimicrobial agents such as silver ions, zinc pyrithione, and isothiazolinones.

Incorporating these compounds into synthetic polymers makes them inherently resistant to bacteria, viruses, and other pathogens; this makes them useful in a wide variety of fields, from medicine to consumer products manufacturing.
Integration of Antimicrobial Agents
The key to the success of antimicrobial plastics is their capacity to incorporate antimicrobial chemicals into the polymer material without affecting its performance in any way.
The antibacterial capabilities are uniformly dispersed throughout the plastic thanks to this molecular integration, resulting in products that not only provide hygiene benefits but also potentially offer a longer shelf life.
To obtain the required degree of microbial resistance, it is necessary to pick a suitable antimicrobial agent and determine the optimal concentration. The antimicrobial ingredient is subsequently incorporated into the polymer in a well-blended manner.
After the ingredients have been combined, they are processed using methods like extrusion, injection molding, and compression molding to take the required form, whether it is a medical tool, a food container, or something else entirely.
This careful procedure guarantees that the antibacterial characteristics will hold up over time.
Take the First Step:
Requst for an Inquire
Quality Meets Affordability. Inquire Now for High-Quality Products at Low Volumes.
Common Antimicrobial Agents
Antimicrobial plastics are made using a wide variety of antimicrobial chemicals. The capacity of plastics to resist the growth of microbes is largely due to the presence of these substances. A few examples of antimicrobials that are often used are listed below.
- Silver Ions: It has powerful antimicrobial capabilities and is hence a popular antibacterial agent. They hinder the development of germs when introduced into polymers by interfering with their biological activities. As a result, silver-infused polymers are increasingly being utilized in healthcare facilities, where strict hygiene standards must be adhered to.
- Zinc Pyrithione: Another powerful antibacterial agent is zinc pyrithione. Zinc pyrithione-containing plastics are widely used in consumer goods like shower curtains and kitchenware to prevent the formation of mold and germs and provide a healthy environment.

- Isothiazolinones: They are widely utilized antibacterial agents in a variety of fields. Isothiazolinone-infused plastics, recognized for their effectiveness against a wide variety of microorganisms, have versatile applications in various settings, including medical and food packaging, in alignment with the stringent standards set by the European Food Safety Authority.
When these antimicrobial compounds are carefully incorporated into plastics, they provide an effective barrier against infectious microorganisms. Antimicrobial plastic may be adapted to meet the needs of several sectors and applications since the agent used is determined by those factors.
Knowing the rationale behind antimicrobial plastic and the importance of antimicrobial agents helps us value the progress that ensures our health and environmental safety in the twenty-first century. These polymers are more than just a material; they represent the best of human creativity in the service of a better world.
Take the First Step:
Requst for an Inquire
Quality Meets Affordability. Inquire Now for High-Quality Products at Low Volumes.
Key Properties of Antimicrobial Plastics
Antimicrobial plastics are distinguished from their traditional equivalents by a unique collection of features. Because of these qualities, they are in great demand in a wide range of sectors where cleanliness and security are of the utmost importance.
- Microbial Resistance: This is the fundamental and most important feature of antimicrobial polymers. They serve as a barrier, stopping the spread of microbes, including bacteria, fungi, and viruses.
- Long-Lasting Protection: Antimicrobial plastic provides continuous protection throughout their lives, unlike topical antimicrobial coatings, which may wear out over time. This durability guarantees continued cleanliness.
- Non-Toxic: Many of the antibacterial compounds utilized in these plastics, including silver ions, are safe for human consumption. Because of this, they may be used in products that come into regular contact with humans, such as food packaging and medical equipment.
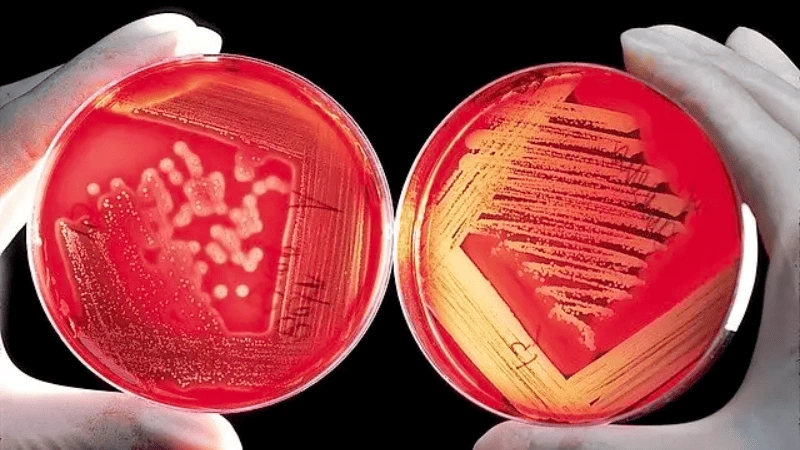
- Durability: Antimicrobial plastic is durable and resistant to wear and tear. This makes them suitable for applications where frequent cleaning or handling is necessary.
- Wide Application Range: They are versatile and find applications in various industries, including healthcare, food processing, consumer products, and more.
- Enhanced Hygiene: Antimicrobial plastics contribute to improved hygiene by reducing the risk of contamination and infection. In healthcare settings, for instance, they help in preventing the spread of pathogens.
- Odor Control: In some cases, antimicrobial plastics, infused with compounds like lactic acid, also offer odor control properties, making them ideal for products like sports equipment, footwear, and textiles.
- Customizability: Manufacturers can tailor the antimicrobial properties of plastics to meet specific needs, allowing for customization in different applications.
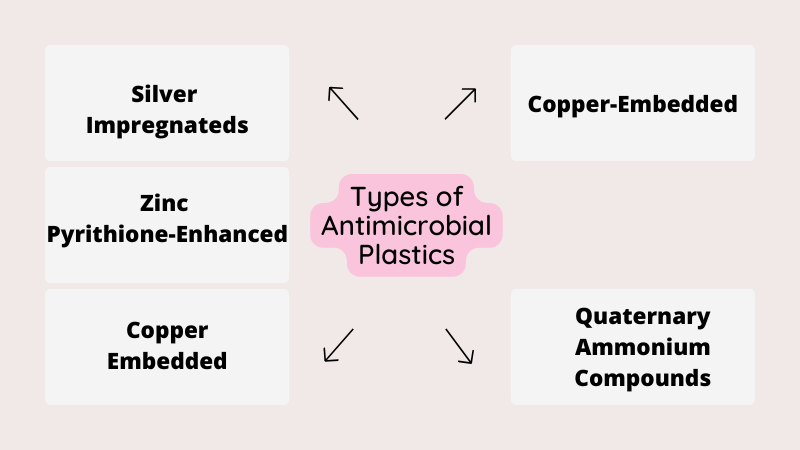
Types of Antimicrobial Plastics
Diverse varieties of antimicrobial plastics cater to different applications and industries. Each type possesses unique characteristics that make it suitable for specific purposes. Let’s explore some common types:
- Silver-Impregnated Plastics: Silver ions are well-known for their antimicrobial properties. Plastics infused with silver ions exhibit robust microbial resistance and are often used in healthcare settings for medical devices and equipment.
- Zinc Pyrithione-Enhanced Plastics: Zinc pyrithione is another effective antimicrobial agent. Plastics incorporating this compound are used in consumer products like shower curtains and kitchenware to prevent mold and bacterial growth.
- Copper-Embedded Plastics: Copper has natural antimicrobial properties, and when embedded in plastics, it creates surfaces with enhanced surface characteristics that actively inhibit microbial colonization. This type of antimicrobial plastic is used in hospital fixtures and public spaces.
- Triclosan-Infused Plastics: Triclosan is a common antimicrobial agent used in personal care products. Toothbrushes and cutting boards are only two examples of the many goods that benefit from the use of plastics containing triclosan.
- QACs: Incorporating antimicrobial agents such as polymeric quaternary ammonium compounds (QACs) into polymers makes them more resistant to a wide variety of microorganisms. Both the food packaging and medical fields, as well as food processing, make extensive use of them.
Take the First Step:
Requst for an Inquire
Quality Meets Affordability. Inquire Now for High-Quality Products at Low Volumes.
Application of Antimicrobial Plastics
Antimicrobial plastics have a wide range of applications. These polymers have several uses, ranging from medical settings to food packaging. Here, we’ll explore several practical applications of antimicrobial polymers to demonstrate their adaptability. Some important uses are listed here:
- Healthcare: The medical field greatly benefits from antimicrobial plastic materials. They aid in keeping healthcare facilities clean and infection-free by being employed in the production of medical tools, apparatus, and even antimicrobial apparel.
- Food Packaging: Food safety is paramount, and antimicrobial plastics play a crucial role in preserving it. They are used in food packaging materials to extend the shelf life of products by minimizing the risk of contamination.

- Consumer Products: Everyday items benefit from antimicrobial plastics. Cutting boards, kitchen utensils, bathroom fixtures, and other household products incorporate these materials to enhance hygiene and reduce the potential for germ growth.
- Automotive Industry: In cars and other vehicles, antimicrobial plastics are used in interior components to create cleaner, more hygienic environments for passengers.
- Electronic Devices: The surfaces of electronic devices like smartphones, tablets, and laptops can harbor germs. Antimicrobial plastics are used in device casings to minimize microbial growth, making these devices safer to handle.
Comparison with Regular Plastic
Antimicrobial plastics and regular plastics share a common origin in the world of polymers. However, their diverging paths in terms of functionality and purpose make them distinctly different materials.
Microbial Resistance
- Antimicrobial Plastics: These plastics, infused with plant essential oils, actively prevent the growth of microorganisms.
- Regular Plastics: Regular plastics do not naturally prevent the growth of microorganisms.
Hygiene Maintenance
- Antimicrobial Plastics: They are perfect for places where strict hygiene is crucial, boasting excellent antimicrobial efficacy, and generally require less cleaning.
- Regular Plastics: Regular plastics may need extra cleaning and maintenance to maintain hygiene standards.
Application Versatility
- Antimicrobial Plastics: Suitable for healthcare settings, food packaging, and maintaining a natural environment, these products are ideal for places where preventing infections is vital.
- Regular Plastics: Regular plastics are used in various industries but don’t offer inherent protection against microbes or provide an antibacterial effect.
Take the First Step:
Requst for an Inquire
Quality Meets Affordability. Inquire Now for High-Quality Products at Low Volumes.
Long-Term Efficacy
- Antimicrobial Plastics: These plastics remain effective in preventing microbial growth throughout their lifespan, addressing the major concern of microbial activity in various industries.
- Regular Plastics: The effectiveness of regular plastics, known for their low cost, can decrease over time, especially on surfaces that are frequently touched, due to factors such as wear and tear and a decrease in tensile strength.
Biofilm Prevention

- Antimicrobial Plastics: They prevent the formation of biofilms, which can be a concern in damp or high-traffic areas, as confirmed by infrared spectroscopy studies that demonstrate their extended product lifespan.
- Regular Plastics: Biofilms may form over time, especially in areas with moisture or a lot of activity.
Resistance to Microbial Growth
- Antimicrobial Plastics: They have a high resistance to bacterial, fungal, and viral growth, attributed to their exceptional antibacterial activities and unique physical properties.
- Regular Plastics: It can be susceptible to microbial colonization unless additional protective measures, such as enhancing thermal stability and optimizing molecular weight, are taken.
Safety
- Antimicrobial Plastics: The antimicrobial agents used in these plastics are carefully chosen to be safe for human contact.
- Regular Plastics: They are generally safe, but may require additional steps to control microbial growth, unlike biodegradable polymers, which offer unique physical characteristics in inhibiting microbial colonization.
Take the First Step:
Requst for an Inquire
Quality Meets Affordability. Inquire Now for High-Quality Products at Low Volumes.
Benefits of Using Antimicrobial Plastics in Healthcare Settings
Healthcare facilities are environments where stringent hygiene standards are non-negotiable. In this context, the utilization of antimicrobial plastics has proven to be a game-changer, offering a multitude of benefits that contribute to patient safety, infection control, and overall well-being.
Below, we delve into the compelling advantages of incorporating antimicrobial plastics in healthcare settings:
Infection Control
- Reduced Microbial Growth: These plastics inhibit the growth of bacteria, viruses, and fungi, thereby reducing the risk of healthcare-associated infections.
- Surface Sterilization: Continuously active antimicrobial surfaces can lower the bacterial load without the need for continuous cleaning.

Patient Safety
- Reduced Cross-Contamination: Helps in minimizing the risk of cross-contamination between patients, especially in high-touch areas like bed rails, call buttons, and IV stands.
- Enhanced Wound Care: Antimicrobial plastics in wound dressings can promote faster healing and lower the risk of infection.
Durability and Longevity
- Material Integrity: Antimicrobial additives can enhance the lifespan of plastics by preventing the degradation caused by microbial activity.
- Low Maintenance: Reduced microbial activity can extend the intervals between required cleanings, thereby reducing maintenance costs.
Operational Efficiency
- Reduced Cleaning Time: The antimicrobial properties can reduce the frequency and intensity of cleaning required, thereby saving time and resources.
- Cost Savings: By reducing the rate of healthcare-associated infections, antimicrobial plastics can indirectly result in significant cost savings in terms of treatment and legal.

Sustainability Concerns of Antimicrobial Plastics
Antimicrobial plastics, while valuable in terms of infection control and product preservation, do raise certain sustainability concerns that warrant careful consideration.
Their impact on sustainability and recycling efforts can be both aligning and conflicting, depending on various factors.
Alignment with Sustainability
Reduced Waste:
- Antimicrobial plastics can contribute to sustainability by extending the lifespan of products and reducing the need for frequent replacements. For example, medical devices made from these materials may last longer, resulting in fewer discarded items.
Lower Chemical Usage:
- By inhibiting microbial growth, antimicrobial plastics can reduce the need for harsh chemical disinfectants. This can lead to a decrease in the consumption of chemicals that may have adverse environmental impacts.
Conflicts with Sustainability

- Recycling Challenges: Antimicrobial additives can complicate the recycling process. Separating and reusing these plastics can be challenging due to the presence of antimicrobial agents, potentially leading to a higher rate of disposal rather than recycling.
- Environmental Impact: The antimicrobial agents themselves, such as silver nanoparticles, may have environmental impacts when they enter ecosystems. These agents can leach out of plastics over time and potentially accumulate in the environment, posing risks to aquatic life and ecosystems.
- Resource Intensity: The production of antimicrobial plastics often requires additional resources to incorporate the antimicrobial agents. This can result in a higher environmental footprint compared to conventional plastics.
- End-of-Life Disposal: The disposal of antimicrobial plastics, especially in healthcare settings, requires careful consideration. Incineration, a common disposal method, can release harmful byproducts into the atmosphere.
Take the First Step:
Requst for an Inquire
Quality Meets Affordability. Inquire Now for High-Quality Products at Low Volumes.
Conclusion
In this comprehensive guide, we’ve explored the multifaceted world of antimicrobial plastics. From their scientific underpinnings to their practical applications and sustainability considerations, antimicrobial plastics are undeniably a vital innovation in the world of materials.
Polymers play an increasingly important role in ensuring the cleanliness and safety of modern enterprises.
Explore the World of Antimicrobial Plastics with Hongju
At Hongju, we’re not just about plastics; we’re about innovation, sustainability, and a safer tomorrow. Join us in shaping a world where hygiene meets sustainability, and where antimicrobial plastics play a pivotal role in safeguarding public health. Your journey into the world of antimicrobial plastics starts here.
Contact us now and get a free consultation to take the next step with Hongju today!