Today, I’m planning to offer you a deep discovery of PTFE World, where you will understand what is PTFE, how it’s produced, its unique physical properties, what benefits you can get from them, and definitely an insight into its mindblowing application. Are you ready to unlock a definitive guide about Polytetrafluoroethylene? Let’s get started.
What is PTFE?

PTFE stands for Polytetrafluoroethylene, is a synthetic polymer that comprises only two elements: one is carbon and the second is fluorine. These two simple elements a versatile materials, derived from tetrafluoroethylene (TFE). By the way, PTFE was first discovered on 6th April 1938.
Let’s break down what it is and why it’s considered so important in various industries:
Synthetic Material
It is a synthetic fluoropolymer derived from TFE. Carbon and fluorine composition make this high-molecular-weight polymer.
- Hydrophobic: It means that PTFE can repeat water and water-containing substances. This property is due to the low electric polarizability of F atoms in the polymer.
- Low Friction: You must be quite familiar with the extremely slippery function of a nonstick pan. It’s because PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid.
- Environmental Concerns: PTFE is a part of PFAS/per- and poly-fluoroalkyl substances, which is a group of chemicals often known as forever chemicals as they remain persistent in the environment. These forever chemicals are toxic and there are many concerns about their production processes.
In the past, PTFE products included perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA)- which posed serious health concerns. Modern manufacturers have adopted advanced manufacturing practices, they started relying on alternative chemicals to mitigate this health concern related to PFOA.
Production Process of PTFE
The production of PTFE Polymer is done in two stages. In the first stage, PTFE Monomer is produced and the second stage involves the polymerization of TFE.
Stage 1-Tetrafluoroethylene(TFE) nomer Prep
- The synthesis of TFE begins with the reaction of Fluospar (CaF2)and sulphuric acid (H2SO4), this reaction produces hydrofluoric acid (2HF).
- Next reaction of hydrofluoric acid (2HF)with Chloroform (CHCI3) produces CHCIF2 (Monochlorodifluoromethane).
- For the preparation of monomer, CHCIF2 pylorated its boiling point -40.8 °C is used as a refrigerant.
- The compound produced during pyrolysis has some impurities such as highly toxic ring structures. So, once the TFE monomer is produced, it is purified. The gas is scrubbed to remove any hydrochloric acid HCL. Then it is distilled to separate the gas from impurities.
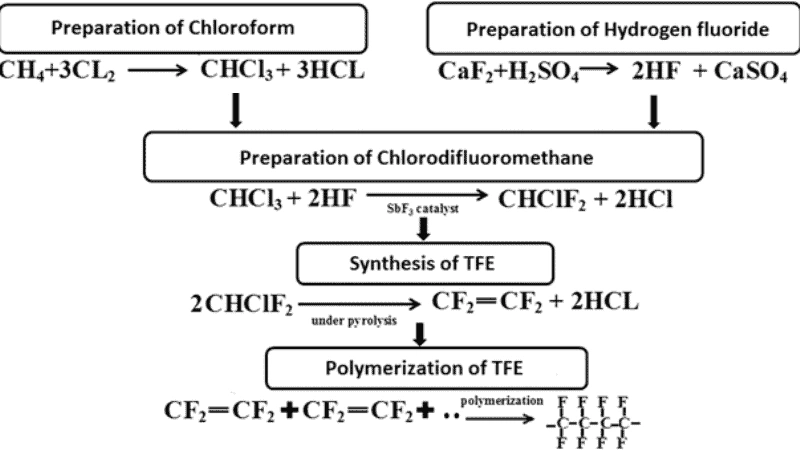
Stage 2- Polymerization of TFE
The first stage brings pure TFE monomer which is polymerized in a silver-plated reactor. A solution comprised of 1.5 parts borax, 100 parts of water, and 0.2 parts of ammonium persulphate is mixed with a pH of 9.2. The reactor is quarter-filled with this solution and then closed and evacuated after 30 parts of monomers are filled inside it. For almost an hour, this reactor will be agitated at 80°C. The last step is to cool down the reactor and get an 86% yield of polymer.
Here is the Chemical structure of PTFE:
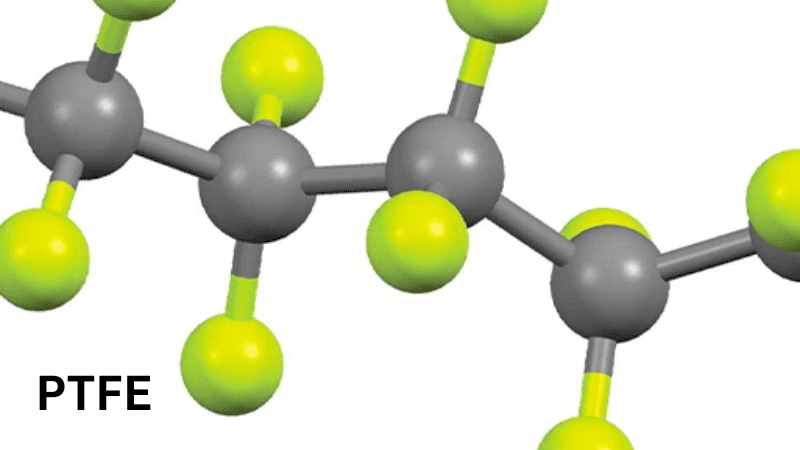
When you check the chain structure of PTFE, you find out that fluorine items create a uniform and continuous sheath all-around carbon bond. As a result of this fluorine sheath, PTFE provides electrical inertness, chemical resistance, and stability to the molecule.
Send Your Inquiry Now!
Quality Meets Affordability. Inquire Now for High-Quality Products at Low Volumes.
Forms and Grades of PTFE
Understanding these different forms and grades is crucial for selecting the right type of PTFE for a particular use. Here are some of the common forms and grades of PTFE:
Forms of PTFE
PTFE is available in three distinct forms, each with unique properties and applications. Now, let’s delve deeper and unlock the detailed characteristics of these forms, exploring how each one caters to specific needs and applications in various industries.
1. Granular PTFE

This form of PTFE is produced in water with very very little or no extra substance that helps it to spread out during suspension polymerization. Suspension polymerization in an aqueous medium happens. This form looks like small grains, which are widely used in methods where it’s compressed or pushed through the mold to create some shapes such as ram extrusion, isostatic, and compression methods.
2. Water-based PTFE Dispersions
This form is also produced by an aqueous medium but more substances are added to spread the monomer out in the water. This liquid form of PTFE is used to produce some coatings or films because they spread easily over surfaces.
3. Fine Powder PTFE
The fine powder form of PTFE is produced through controlled emulsion polymerization. These white particles are usually used to create thin pieces through a method known as paste extrusion. These fine Ptfe powders can be processed and used as additives for other materials to make them more resistant to wear and tear.
Grades of PTFE

Moving on, let’s delve into the different grades of PTFE and explore their unique characteristics.
- Virgin PTFE: It is a PTFE without any kind of filler in it. This is a chemically inert material with diverse applications.
- Glass-Filled PTFE: As the name describes it a bit, this PTFE has 25 percent glass filler. This grade of PTFE has high compressive strength while it doesn’t deform under load. Besides, glass fiber PTFE performed well in oxidizing environments.
- Bronze-Filled PTFE: When PTFE gets bronze filler, then you can expect cold flow, and high dimensional stability from this grade of material. Bronze-filled PTFE compounds usually have low creep.
- Carbon-Filled PTFE: Carbon-filled PTFE is commonly used due to its high thermal conductivity with low permeability and thermal expansion. The Carbon fiber PTFE compounds the wear resistance and compressive strength of the material to a great extent.
- Stainless Steel PTFE: Whenever an application requires extremely stable, strong, and hard-wearing material under high loads and elevated temperatures, Stainless steel fibers are used as a filler for PTFE resins. The best thing about this material is that PTFE has an extremely low coefficient of friction of conventional PTFE.
We have explained only a few fillers, there are many others such as graphite-filled PTFE.
What is the Impact of Fillers on PTFE Characteristics
When fillers and additives are added to PTFE they make some positive changes to this material for example:
- They improve the mechanical properties of PTFE especially its wear rate and creep.
- They make changes in their electrical properties.
- They can increase the porosity of PTFE compounds.
- They can change the exceptional properties of polytetrafluoroethylene at low and high temperatures.
- As far as chemical properties are concerned, they are completely based on the type of filler.
Send Your Inquiry Now!
Quality Meets Affordability. Inquire Now for High-Quality Products at Low Volumes.
Applications of PTFE
PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) is renowned for its unique combination of properties, making it highly versatile and useful in a wide range of applications. Here are some key applications of PTFE:
- In the automotive industry, this material is used to create linings for fuel houses, power steering, O-rings, valve stem seals, shaft seals, and gaskets.
- In the chemical industry, PTFE coating is employed for pumps, impellers, tanks, reaction vessels, containers, autoclaves, and heat exchangers. Coating of PTFE into tubes is a common use.
- In the electrical and electronics industry PTFE plays a big role because this material is used for the production of semiconductor parts, flexible printed circuit boards, and electrical insulation. When you look into thermal and electrical conductivity you find out the thermal conductivity of PTFE is low while it has zero electrical conductivity. PTFE film and coating are highly insulated.
- In the medication industry, PTFE has diverse applications such as it is employed to produce ligament replacement, heart patches, and cardiovascular grafts.
- PTFE engineering applications include non-stick surfaces and coating for pipes, bearings, seats, etc. PTFE-made plugs are always in high demand.
- In the kitchen industry, non-stick properties make it an ideal material for the production of highly valuable nonstick cookware.
The applications of PTFE are vast and varied, owing to its remarkable properties such as high-temperature resistance, non-reactivity, low coefficient of friction, and electrical insulation capabilities.
PTFE vs. Teflon: Clarifying the Difference

The terms PTFE and Teflon are often used interchangeably, but it’s essential to understand their distinctions and similarities. Here’s a breakdown to clarify the difference:
PTFE as a Material
PTFE or Polytetrafluoroethylene is a synthetic fluoropolymer of tetrafluoroethylene. Fluoropolymer is a class of plastics with a range of applications.
Teflon as a Brand
The brand name of PTFE is Teflon, which is made by Chemours (formerly a part of DuPont). The material was discovered by accident in 1938 by Dr. Plunkett at DuPont. At that time, it was developed by the DuPont Co. And later it was managed by a spin-off of DuPont Co-Chemrous.
Chemrous registered a trademark of the name Teflon in 1945 and started selling products treated with this material in 1946. It is a synthetic polymer comprised of carbon and fluorine. The name of this synthetic polymer is polytetrafluoroethylene or PTFE.
PTFE vs Teflon
- Material vs. Brand: PTFE is the chemical compound, while Teflon is a brand name for products made with PTFE.
- Not All PTFE is Teflon: There are other brands and products made with PTFE that are not under the Teflon brand.
- Quality Perception: Some might perceive Teflon as higher quality due to brand recognition, but essentially, the base material properties of PTFE remain consistent across brands.
- Application-Based Decision: Whether to choose a Teflon-branded product or another PTFE-based product can depend on specific application requirements and budget considerations.
Send Your Inquiry Now!
Quality Meets Affordability. Inquire Now for High-Quality Products at Low Volumes.
Advantages and Benefits of Using Teflon
Teflon, a well-known brand of PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene), offers a range of advantages and benefits, making it a popular choice in various industries. Here are some of the key advantages and benefits of using Teflon:
1. Non-Stick Nature
Can you imagine your egg breakfast without a nonstick pan? Of course, you won’t because without these pas eggs won’t slide right off the pan. Teflon is a common material used to create non-stick pans but it’s not the only application. Wherever sticky materials are a no-go, it is a must-have material for that specific application.
2. High Heat Resistance

PTFE exhibits strong heat resistance, they can easily handle temperatures up to about 260°C (500°F). In the cookware industry, this material made a mark due to this property. But these properties are usually impacted by preform pressure and cooling rate.
3. Chemical Resistance
One of the best PTFE mechanical properties is high chemical resistance, it doesn’t get along with other chemicals. This property makes it an ideal material for pipework and containers for reactive and corrosive chemicals.
4. Low Friction
Application, where you want things to move smoothly, requires PTFE, it is super slippery. Since it has low friction, it is good for applications like gears, slides, and bearings.
The diverse properties of PTFE undoubtedly qualify it as an excellent material for numerous industry applications. What do you think?
Why PTFE and Teflon are Preffered in Most Applications

As I told you before this material has diverse applications, but it’s time to know why exactly this material is preferred over others. Let’s unlock some good reasons behind this preference:
- Exceptional Non-Stick Properties: Both PTFE and Teflon-coated surfaces prevent materials from adhering, making them ideal for cookware, bakeware, and industrial molds.
- High Temperature Resistance: They can withstand extreme temperatures without degrading, which is crucial in applications like aerospace, automotive, and industrial machinery.
- Chemical Inertness: PTFE and Teflon are resistant to most chemicals, making them suitable for use in chemical processing equipment, laboratory containers, and protective coatings.
- Low Coefficient of Friction: Their slippery surface reduces friction, beneficial in applications such as bearings, gears, and slide plates.
- Excellent Electrical Insulation: With their high dielectric strength, they are used in the insulation of wiring and electrical components, especially in high-temperature situations.
- Moisture Resistance: They repel water and are not prone to corrosion, making them ideal for outdoor and marine applications.
- Durability and Longevity: PTFE and Teflon are known for their durability, often extending the life of products they are used in.
- Biocompatibility: The non-reactive nature of PTFE makes it safe for medical and food contact applications.
Send Your Inquiry Now!
Quality Meets Affordability. Inquire Now for High-Quality Products at Low Volumes.
Conclusion
Finally, you have enjoyed a 360-degree view of Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE). This comprehensive guide provided insight into this high-performance polymer that has its unique production process and outstanding properties. PTFE has changed many sectors from cookware to aerospace.
In addition, now you can make a difference between PTFE and Teflon easily as you know that both have the same chemistry. This guide is not just a discovery of PTFE but it’s a quick journey through the landscape of human innovation and I’m sure you have enjoyed it. Haven’t you?
Embrace the Future with Hongju’s PTFE O-rings and Gaskets
If you want to achieve excellence in any project, picking the right material makes a big difference. At Hongju Silicone, we specialize in the production of high-quality PTFE O-rings and gaskets made by expanded PTFE. Our products are designed to meet and exceed client’s specifications and expectations.
When you need a partnership that emphasizes quality, efficiency, and customer satisfaction, feel free to contact our experts who can push the boundaries of what’s possible and drive innovation forward in your industry.