Want to know more about how plastic extrusion works and how it can be helpful for your business? This article will help you widen your lens to see how plastic extrusions aid every industry today. Let’s uncover the untold proficiency of plastic extrusions.
What is Plastic Extrusion?

Plastic extrusion is a large-scale plastic goods manufacturing process that continuously shapes thermoplastics like pellets, powder, and granules into uniform sections of long products like pipes and plastic sheeting after melting them and forcing them through a die under pressure. The extracted plastic stream follows a cooling process to maintain its final shape.
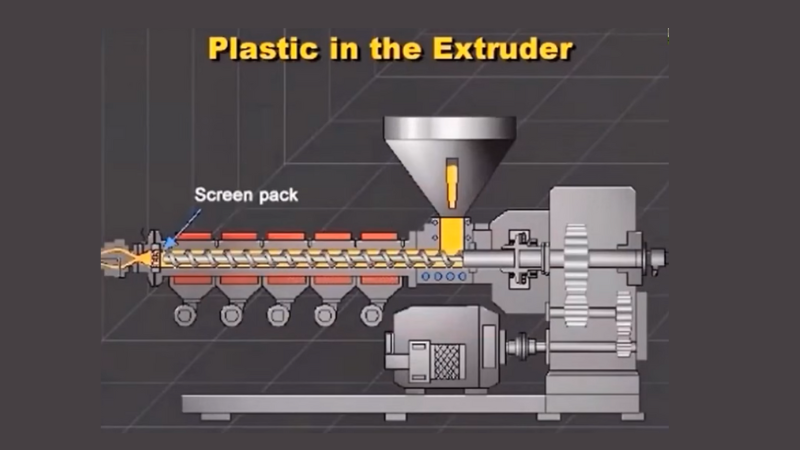
For the extrusion process, plastic granules or pellets travel through machines called plastic extrusion machines. This long, metal cylinder-type machine comprises several components, like:
- Hopper: Allows feeding plastic pellets or granules into the machine.
- Screw: A long rotating screw inside the extruder barrel pushes the raw material inside the melting barrel. BTW, these screw extruders also have subtypes like twin screw extruders.
- Barrel: The hot chamber melts the plastic beads or pellets at a suitable high temperature.
- Die: The die is the mold that shapes the molten plastic into its final form, coming from the barrel, pushed through the screw.
Thus, plastic extrusion is the process of producing long-form plastic extrusion products like pipes, sheets, and films without dividing them into parts.
Types of Plastic Extrusion
Although plastic extrusion is a high-volume plastic molding process, it has two main types depending on how the plastic flows through the extruding machine:
1. Continuous Extrusion of Raw Plastic Material
Continuous extrusion is the most commonly used type of plastic extrusion process, and it supports high volume and fast production. Fulfilling the true purpose of extrusion molding, in continuous extrusion, a constant feeding of raw plastic material results in a never-ending stream of plastic.
This steady supply of plastic nurdles melts into the melting barrel inside the machine. Then, molten plastic passes through the die to take the desired shape. The continuous extrusion method is ideal for making elongated products like pipes, thin films (like plastic wrap), and sheets (used for signs or packaging).
2. Intermittent Extrusion

Unlike continuous extrusion, Intermittent extrusion requires a limited release of melted plastic to make one specific shape and stop it. The process continues with a “start-and-stop” approach to creating a particular number of pieces. Mainly, intermittent extrusion helps with making hollow shapes or more complex products. Yet, the process further has 2 common subtypes, as follows:
- Blow Molding: This technique works like blowing a balloon. This inflates the flow of molten plastic with air to form hollow shapes. It helps create bottles, toys, fuel tanks, and kayaks.
- Ram Extrusion: The technique of ram extrusion involves pushing the molten plastic into the mold cavity using a piston-like ram. Once the plastic cools inside the mold, the ram retracts and ejects the finished product. Ram extrusion mainly helps create complex shapes like window frames or automotive parts.
So, the choice of extrusion methods depends on what you want to make. Continuous extrusion is ideal for long-form simple shapes like pipes and thing plastic wraps, and intermittent works best for creating hollow or intricate designs.
Send your inquiry for prompt quotations!
Types of Plastic Extrusion Process
Plastic extrusion work comes in flavors! Here are four common types:
1. Tubing Plastic Extrusion
Tubing extrusion, a type of plastic extrusion works by forming long molten plastic snakes. The plastic extruder pushes this plastic through a circular die, forming tubes of various sizes. This process creates products like pipes, straws, and even medical tubing.
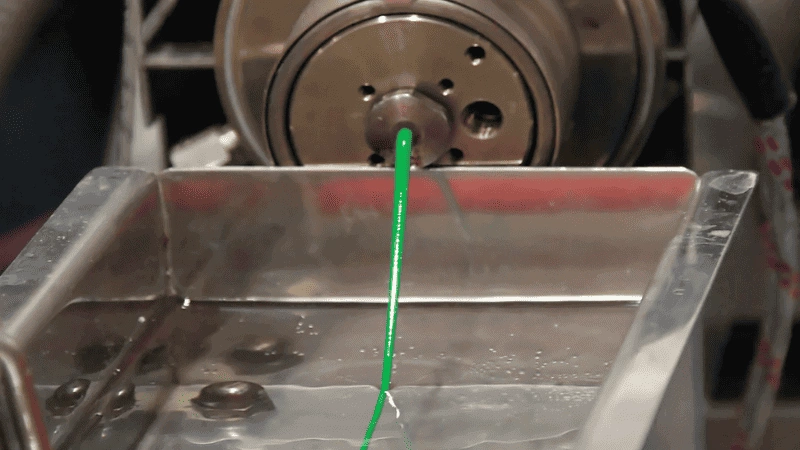
2. Blow Film Extrusion
Blow or blown film extrusion is like blowing up a plastic bubble. Melted plastic flows through a ring-shaped mold. Air is then blown into the center, inflating the plastic into a wide, thin tube. This tube is flattened and cooled, creating sheets of plastic film used for packaging, bags, and wraps.
3. Sheet Film Extrusion
This method makes flat plastic sheets, but without blowing. The plastic extruders squeeze melted plastic through a wide, flat die. Cooling rollers solidify the plastic into sheets used for signs, packaging, and even greenhouses.
4. Over-Jacketing Plastic Extrusion
This process acts like putting on a plastic coat. A wire or cable is fed through the center of a die. Melted plastic then surrounds the wire, creating a protective outer layer. This insulation is essential for electrical wires and cables.
Plastic Extrusion Process: How it Happens?
The plastic extrusion process might seem simple, with the uniform melting of plastic pellets pushed through a die, forming long shapes, and finally cooling them to get solid shapes.
But the truth is, the entire process is detailed and delicate at the same time. Here is how these basic steps help get your designed products.
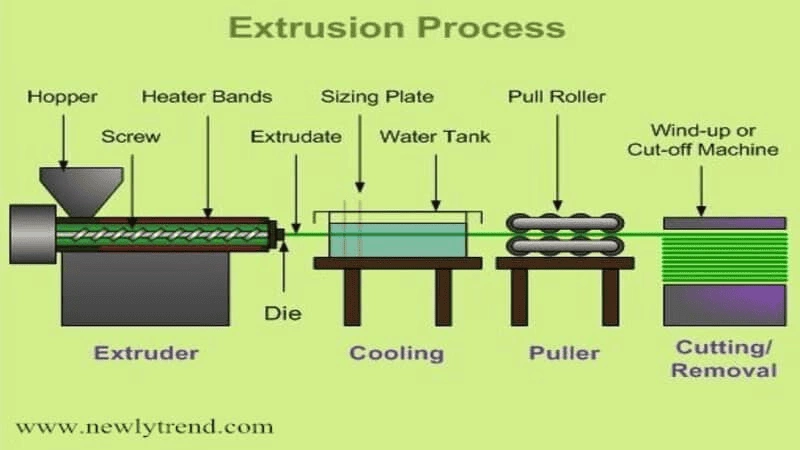
Step 1: Plastic Material Feeding
The plastic extrusion process begins with feeding a giant funnel at the top of the plastic extruder. This is known as a hopper. However, this hopper is not that simple. To avoid congestion of plastic pellets, this hopper has different specialized tools for moving stubborn plastic pellets without getting them stuck together. These tools are:
- Vibratory Feeders: These shaking platforms keep vibrating to move the plastic beads forward into the hopper steadily.
- Screw Feeders: These feeders have miniature rotating screws resembling Archimedes’ screws. This spiral-shaped tool rotates and continuously pushes the pellets toward the hopper from a separate container.
Simply put, these different feeding systems ensure a consistent supply of plastic pellets to the plastic extruder, which is crucial for the smooth extrusion process, which results in high-quality plastic products.
Step 2: Melting and Mixing
The melting and mixing process follows the feeding stage. It’s the heart of the entire extruding process. At this stage, solid plastic pellets melt inside the heated barrel in defined temperature ranges.
As soon as the pellets enter the barrel, a large heated barrel melts the plastic and mixes them with the help of the rotating screw’s friction. This engineered heating barrel isn’t that simple.
It has different heating zones, which help with the constant but gradual melting of the plastic. As a result, the entire molten plastic batch has a uniform consistency without any burns or lumps. At the same time, imitating the action of a dough mixing hook, the screw/twin rotating screws aid in making this plastic dough.
The screw’s action is crucial as it helps to mix the additives throughout the batch. These additives can be color pigments or strength-giving chemicals.
You can compare this end-stage, homogeneously molten plastic with a cake dough in the mixer–perfect for attaining the shape of the mold/die.
Step 3: Ejecting Molten Plastic through Mighty Die
A mighty metallic die with a customized opening welcomes the flow of molten plastic. The screw in the barrel impels the molten plastic through the die opening. The die, acting like a funnel, guides the plastic into the desired shape.
As the plastic flow continues, the elongated products keep forming. However, these dies have different shapes and sizes depending on the use and end product. For instance, the pipe die has a simple circular opening.
The plastic film die has a wide opening, and the die has a wide, flat opening. The dies used to create complex shapes, like window frames, require dies that have intricate channels and shapes.
Step 4: Cooling Down
Finally, the cooling stage accompanies the molding process. These cooling systems exist around the dies. They remove the heat from the extruded plastic and harden it. The cooling stage helps the plastic extrusion process in two ways:
- First, these cooling systems are essential for solidifying the plastic
- Second, they ensure the product’s dimensional accuracy, leading to the perfect size.
However, to attain the accurate size of the end product, the cooling process needs to be super quick. It’s because slow cooling may cause the product to shrink in size–nobody wants an undersized product (that’s inaccurate and fails to fulfill its purpose).
The manufacturers employ different cooling approaches to aid in the quick cooling of the extruded plastic:

- Water Baths: This cloning technique works best with hollow products like pipes, tubes, and profiles. A water bath removes heat from the freshly extruded plastics and solidifies them to help them maintain their shape.
- Air Cooling: Relatively inexpensive and bio-friendly, air cooling aids remove heat from thin plastic films and sheets and solidify them. Usually, air cooling systems rely on fans only.
- Vacuum Cooling: This is a more complex but uniform and precise process of drawing heat out of complex shapes — It’s also environmentally friendly. For this process, a vacuum is applied around the die to suck out heat and moisture trapped inside the plastic. Because of this, you get the most accurate shape and size for your extruded plastic products.
Shaping and cooling work hand-in-hand to give the plastic product its form and solidify it quickly and accurately. So, the next time you see a plastic pipe or window frame, remember the magic of shaping and cooling that brought it to life!
Send your inquiry for prompt quotations!
Advantages of Plastic Extrusion
Plastic extrusion is popular indeed. But why? The list of its benefits is exhaustive, but some of the most common benefits are listed below:
1. Fast Production
Extrusion machines are workhorses of the factory world. They have a greater capacity to manufacture plastic products uninterruptedly. Their fast capability makes them ideal for high-volume production.
2. Shape Shifters
Whatever can be molded can be shaped through extrusion, whether toys or window frames, benefits from extrusion.
All you need is to get the relevant die, molten plastic with dough or melted-cheese-like plastic, and cool it when it comes out of the die–You’re done!
The versatility of the dies and smooth extruding process makes extrusion the best option for serving a wide range of applications.
3. Cost-Effective Champion

Extrusion is an economically friendly option for large-scale production. The beauty lies in its continuity with minimal waste. Once the plastic is melted, the easy molding process through custom dies keeps the process budget-friendly and efficient. This translates to lower costs per item.
4. Team Player
Extrusion doesn’t have to work alone–it’s a team player. It also integrates with other processes like cutting, welding, printing, and finishing for final product assembly. For instance, it helps you produce colorful pipes with engraved logos or toys with a smooth, shiny finish—these are all thanks to extrusion working alongside other techniques.
5. Material Master
Unlike other plastic molding methods, such as injection molding or blow molding, the extrusion method can handle a variety of thermoplastics. These plastic types vary from everyday materials like PVC to more specialized types like ABS (acrylonitrile butadiene styrene), PET (polyethylene terephthalate), and PC(polycarbonate).
In short, plastic extrusion offers a winning combination of speed, flexibility, affordability, and adaptability. It’s no wonder it’s a go-to process for so many plastic products we use every day!
Applications of Plastic Extrusion
Plastic extrusion is involved in everyday life! This fantastic process creates a wide range of products for daily use, from building your homes to packaging your food and entertaining your kids. You can find plastic extrusion involvement in different aspects of our lives:

1. Packaging
Have you seen plastic warps in your kitchen? Where do these thin plastic wrappings with such a precise thickness come from? Extrusion machines create your must-have food plastic wrap.
Likewise, the bottles you drink also come from extrusion, so you should thank intermittent extrusion. Hence, plastic extrusion keeps your beverages and other liquids safe and convenient from plastic bags to yogurt tubes and bottles.
2. Consumer Goods
Look around yourself…plastic extrusion is there.
The water hoses you use for watering your garden, electrical cables that power your devices, and even your children’s toys get born from extrusion.
By the same token, you have flexible plastic tubing for medical devices and air hoses in your workplaces. Extrusion’s versatile application has bestowed tons of consumer goods in today’s world.
3. Automotive Industry

The automotive industry, despite being a heavy industry, calls for plastic-extruded articles. Your car’s interior parts, like dashboards and door panels, come from dies fixed to extrusion machines. These durable, lightweight, and effortlessly customized plastic parts are helpful for different car models.
4. Medical Applications
The medical field also relies extensively on plastic extrusion for necessary tools. For instance, flexible intravenous drip tubes (IV) and catheters are made through plastic extrusion.
So, the next time you use uniformly made plastic, you may need to thank plastic extrusion. Ultimately, it’s helping you with its versatility and efficiency, shaping your world in countless ways.
Send your inquiry for prompt quotations!
Plastic Extrusion vs. Injection Molding
By now, you may be wondering how plastic extrusion differs from its other popular counterpart, injection molding, and why you should choose it. After all, both serve the plastics industry, but they excel at different tasks. Here’s a quick breakdown to help you choose the winner:
Extrusion as King of Long Shapes
Need a long, never-ending stream of inflated or inflated plastic? Extrusion can help you. It continuously squishes melted plastic through a mold, forming things like pipes, films, and building materials. It’s fast and efficient for high-volume production.
Injection Molding – Master of 3D Shapes
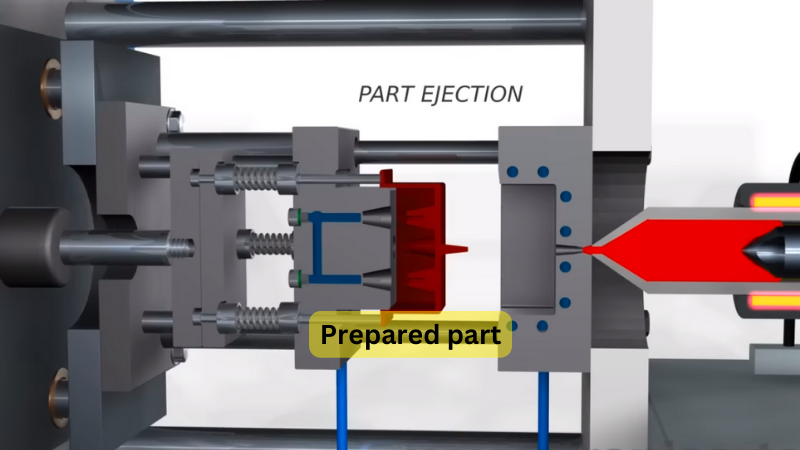
Want a complex 3D shape like pocket combs, automotive parts, wire spools, or water cans with handles? Injection molding will help you. It will get you your desired plastic shoes by pouring hot plastic into a mold to create a specific 3D shape. Thus, it’s perfect for manufacturing complex parts like toys, toolboxes, or even medical equipment.
Here is the breakdown of the key differences between plastic extrusion and injection molding to help you make a more informed decision.
| Feature | Plastic Extrusion | Injection Molding |
|---|---|---|
| Process | A continuous flow of plastic melted and pushed through a die. | Molten plastic is injected under high pressure into a closed mold cavity. |
| Suitable for Shapes | Long, continuous profiles with uniform cross-sections (pipes, films, sheets) | Complex 3D shapes with intricate details (gears, housings, toys) |
| Production Volume | Ideal for high-volume production of identical parts. | Efficient for high-volume production once the mold is made. |
| Mold Cost | Lower upfront cost for dies, simpler design. | The higher upfront cost for complex molds with intricate details. |
| Material Usage | More efficient material usage with minimal waste. | Some material waste can occur from sprue and runners. |
| Production Speed | Faster production due to continuous process. | Slower production due to mold opening/closing cycle. |
| Design Flexibility | Limited to shapes with consistent cross-sections. | Highly versatile for complex and detailed designs. |
| Applications | Pipes, films, sheets, building materials, wires, hoses. | Electronics housings, car parts, furniture components, toys, medical devices. |
So, which should you choose?
- Opt for extrusion if you need long, continuous shapes.
- Choose injection molding if you’re looking to create a complex, 3D part.
- But which could work for high-volume production? Both can be fast, but extrusion might edge out for simpler shapes.
Ultimately, the best choice depends on the specific product you’re making.
Send your inquiry for prompt quotations!
Conclusion
So, this was all about plastic extrusion and how this process works. If we summarize, we can say that plastic extrusion, with its versatility and high-volume process for shaping thermoplastics, including silicone, can get you anything from building materials to medical tools. We hope that now you have all the answers to what plastic extrusion is and how it works.
Hongju – Your Most Trusted Plastic Manufacturing Partner
Do you want to transform plastic into parts that fit your project needs? Partner with Hongju. Our expert team with 20 years of experience in manufacturing plastic parts will help you get your custom plastic and silicone rubber products that uplevel your manufacturing game to save you cost and invite the business growth you long for. Get your quote today by contacting us.